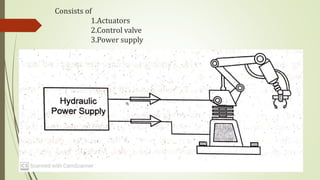
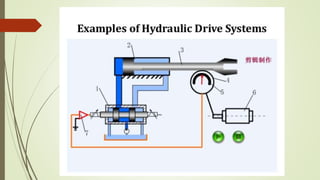
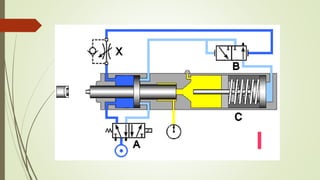
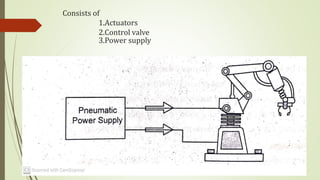
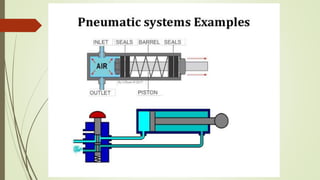
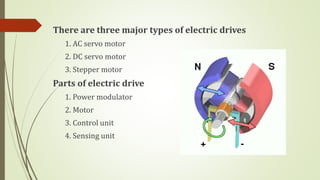
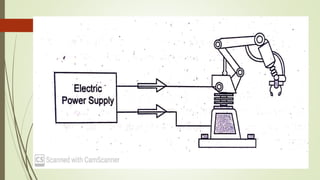
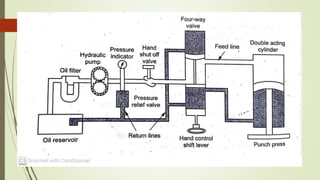
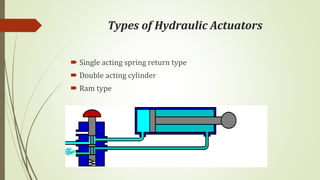
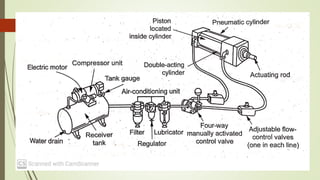
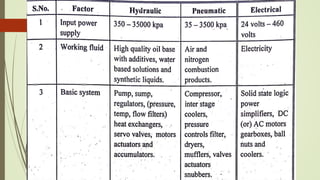
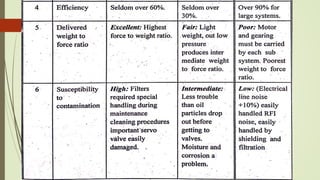
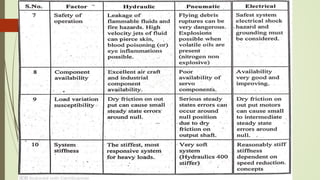
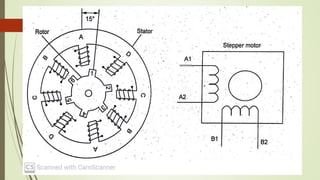
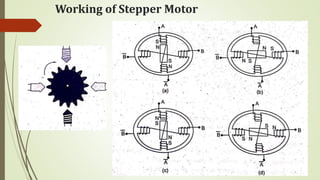
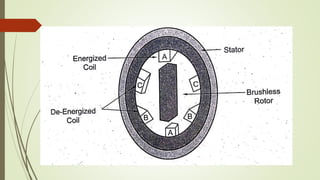
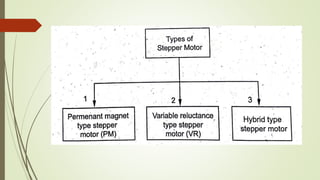
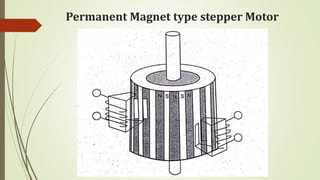
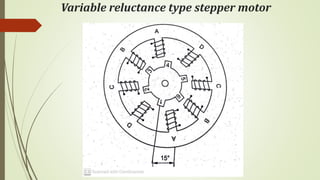
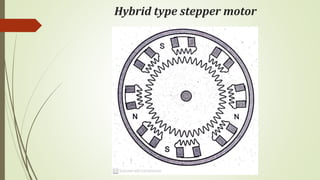
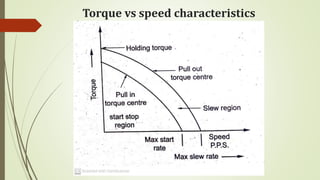
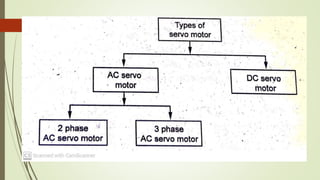
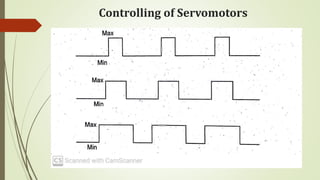
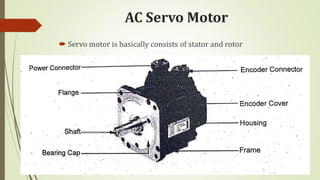
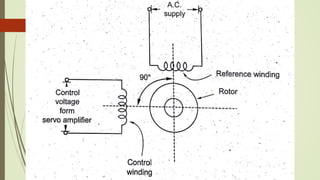
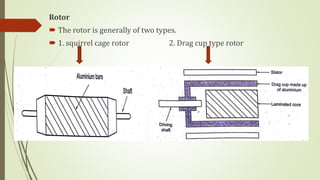
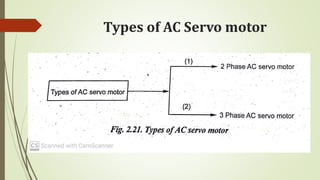
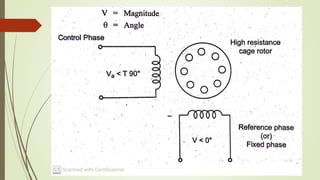
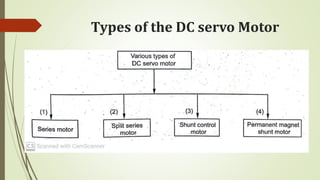
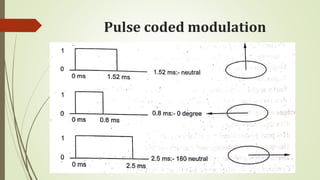
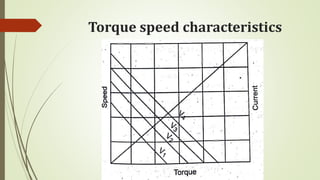
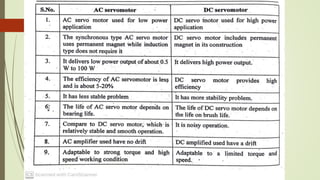
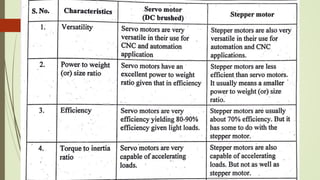
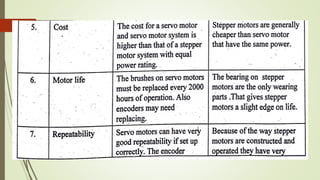
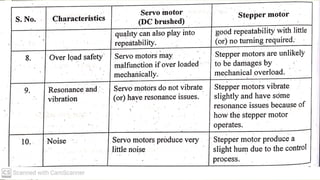
This document discusses various robot drive systems and end effectors. It describes several types of drive systems including hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric drives. Hydraulic drives are suitable for heavy loads but require more maintenance. Pneumatic drives are cheaper but generate more noise and vibration. Electric drives offer cleaner operation but require larger motors. Within electric drives, the document discusses stepper motors, servo motors, and their operating principles. It also covers various types of actuators and their applications in robotics. Grippers are discussed as a type of robot end effector.