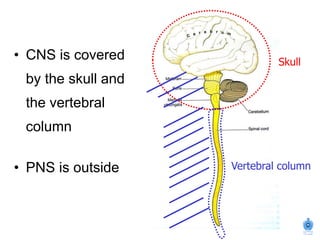
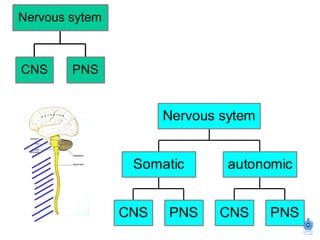
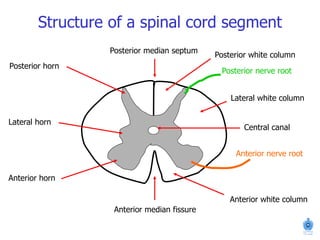
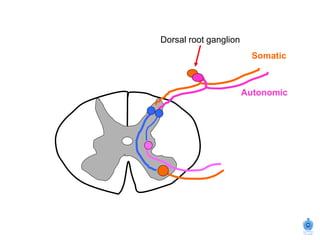
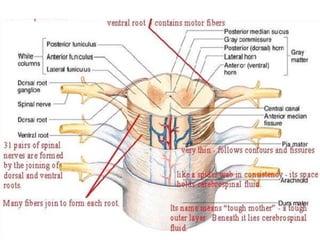
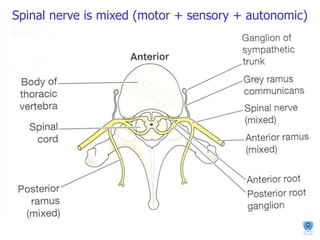
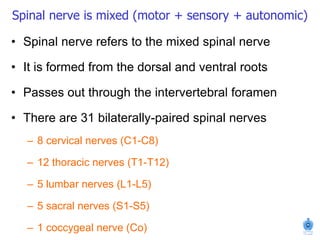
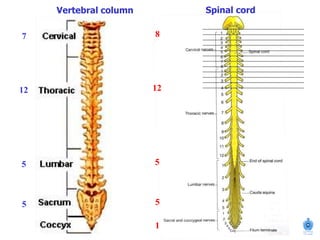
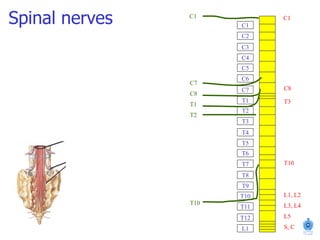
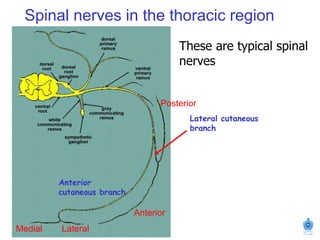
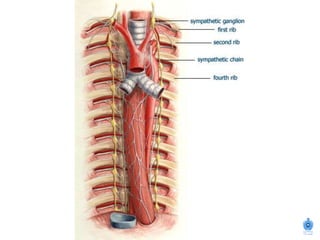
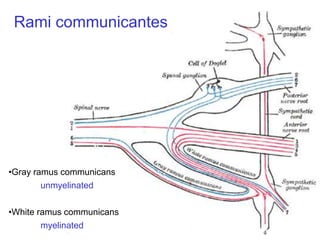
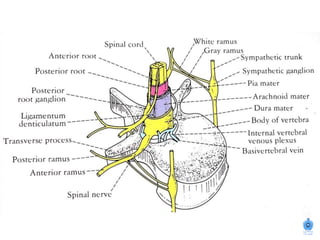
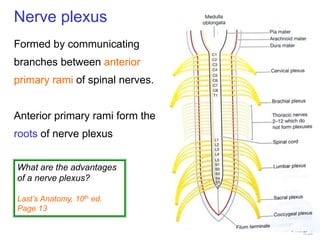
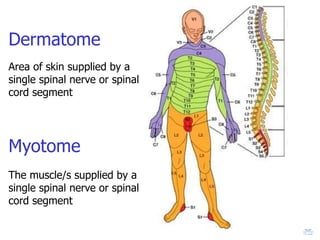
The document summarizes the structure and organization of typical spinal nerves. It discusses how spinal nerves are formed from the dorsal and ventral roots, containing both sensory and motor fibers. Each spinal nerve exits the vertebral column through an intervertebral foramen, forming 31 pairs of spinal nerves that innervate different regions of the body. The anterior and posterior primary branches of spinal nerves further branch to supply specific regions like the skin and muscles of the back and body wall.