Embed presentation
Downloaded 310 times





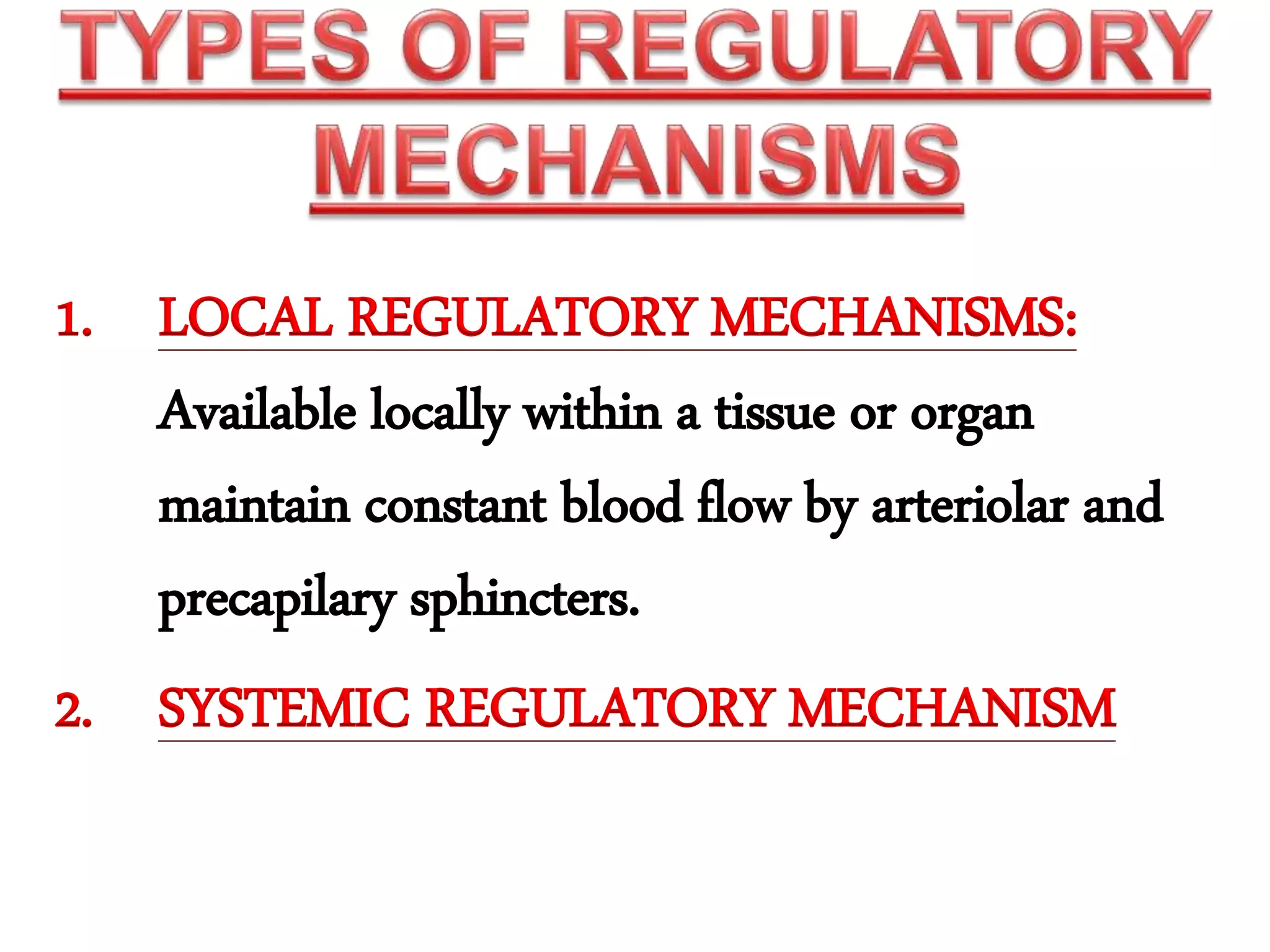


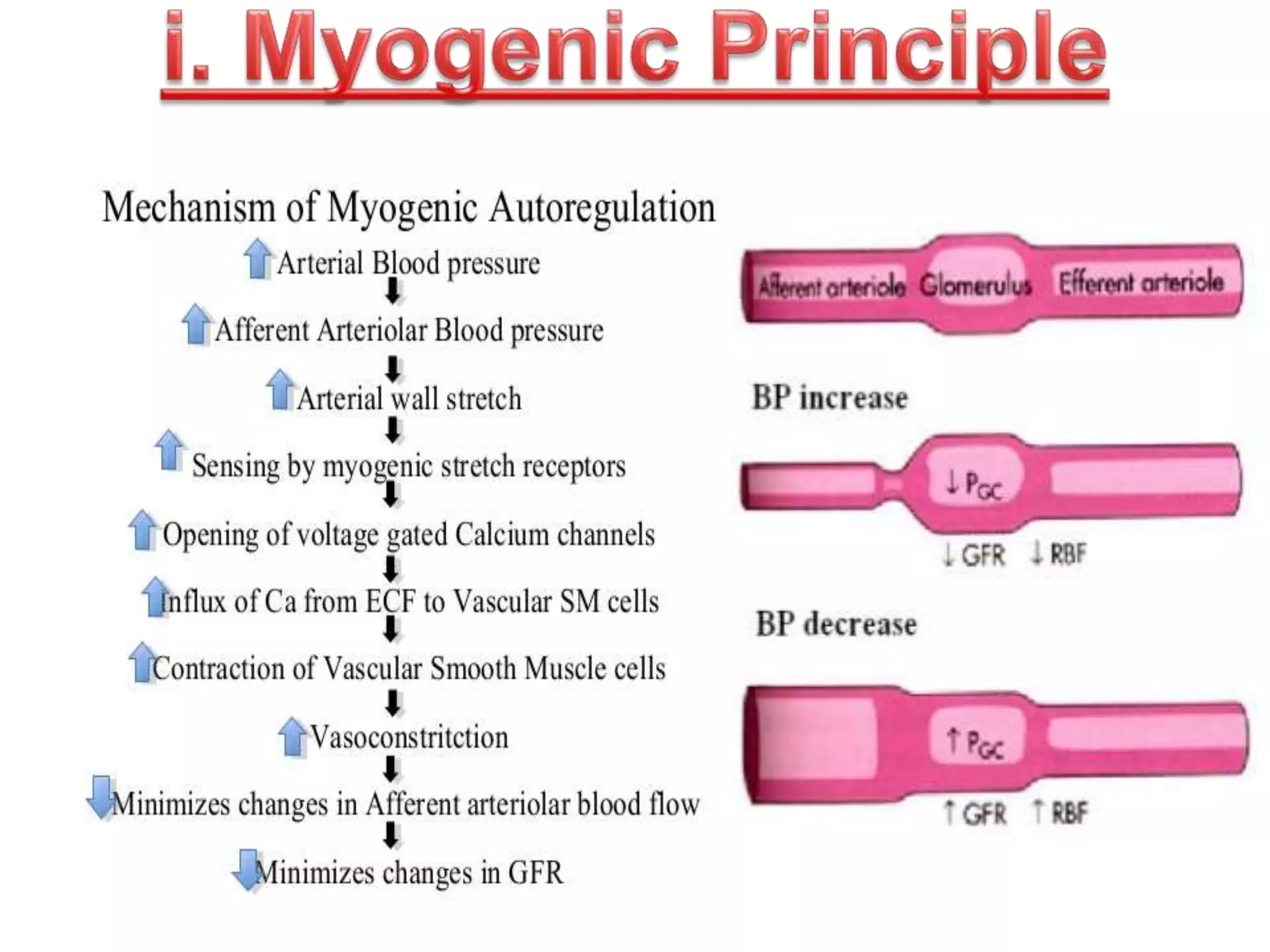

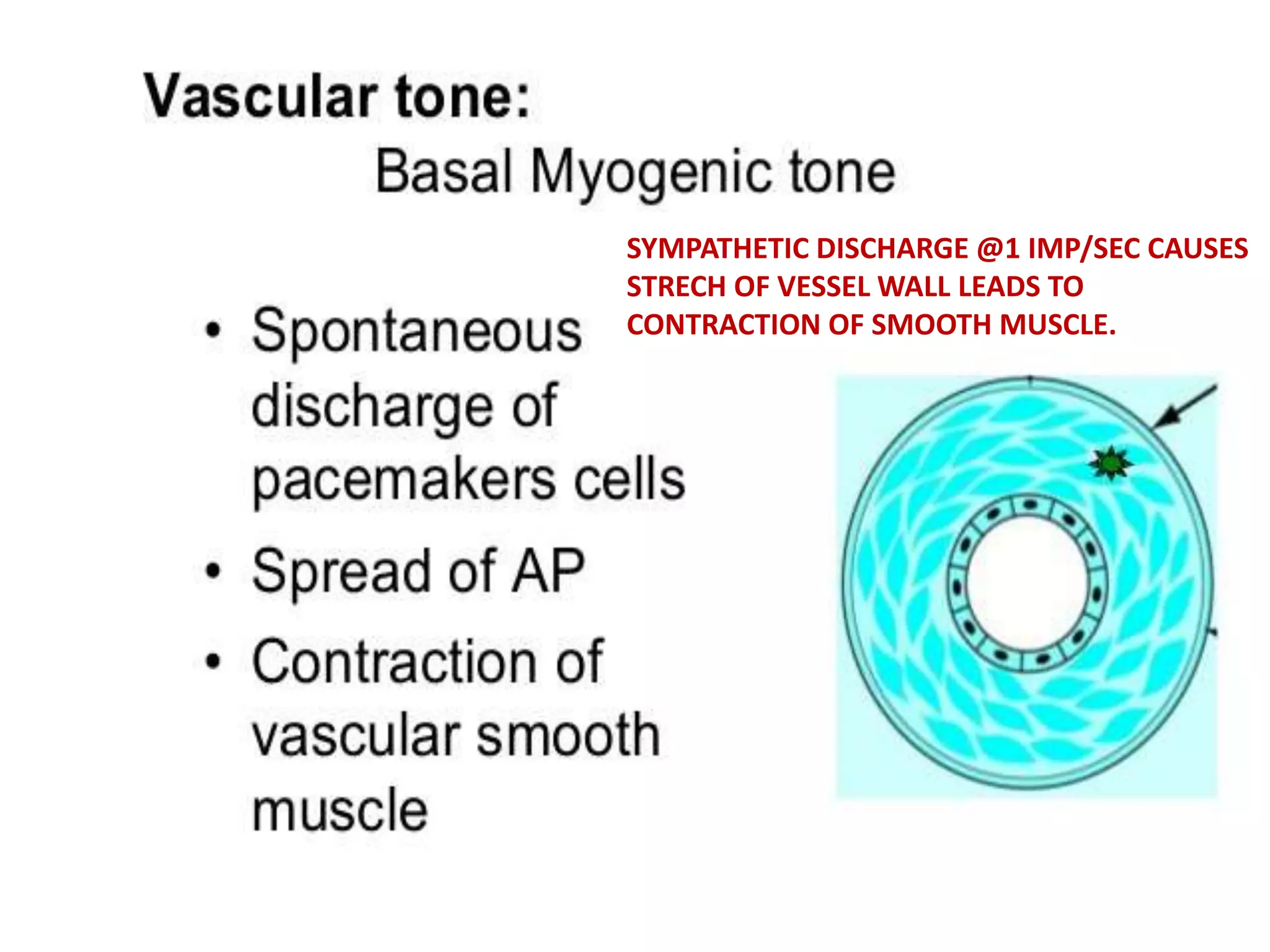

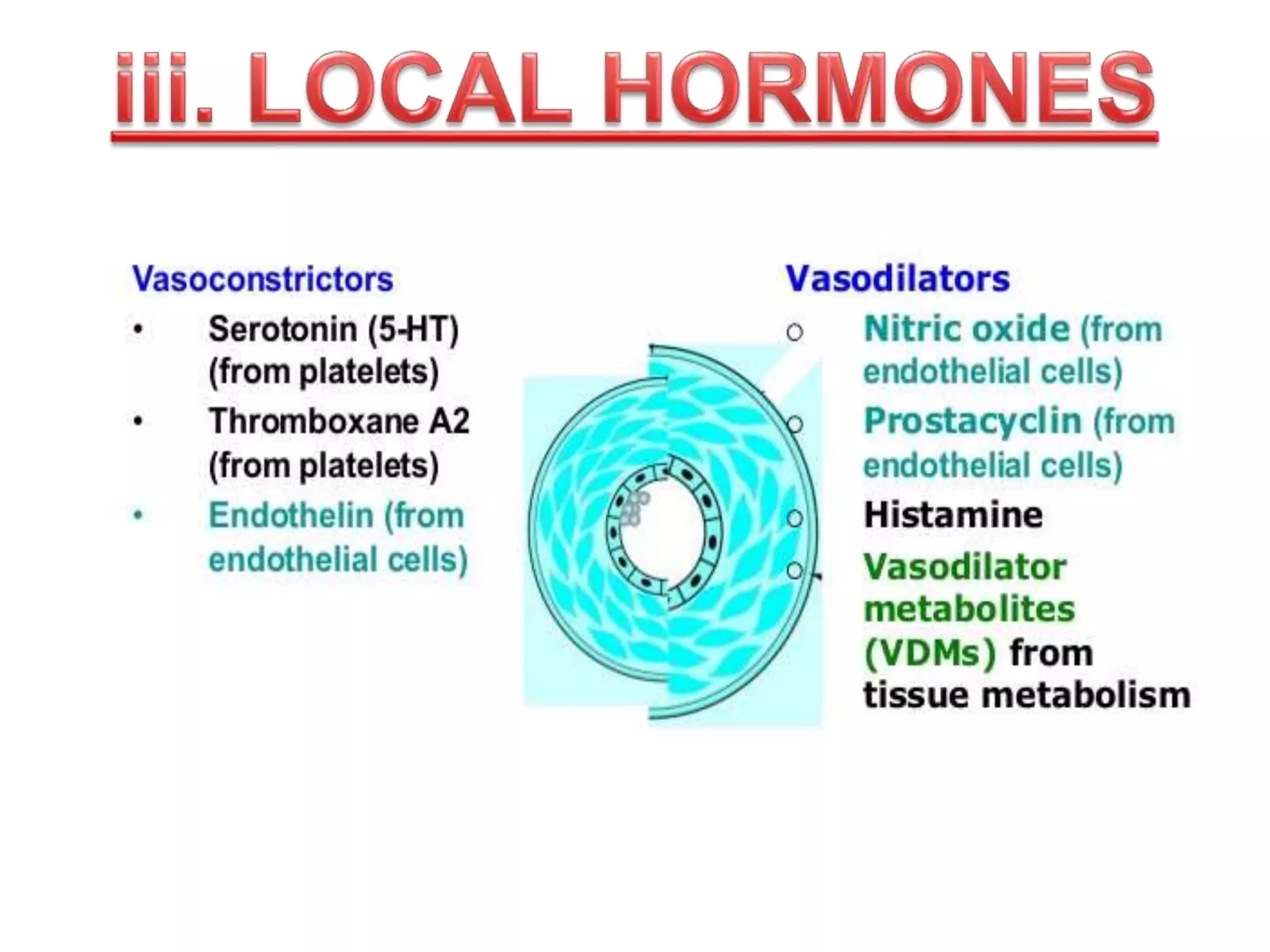
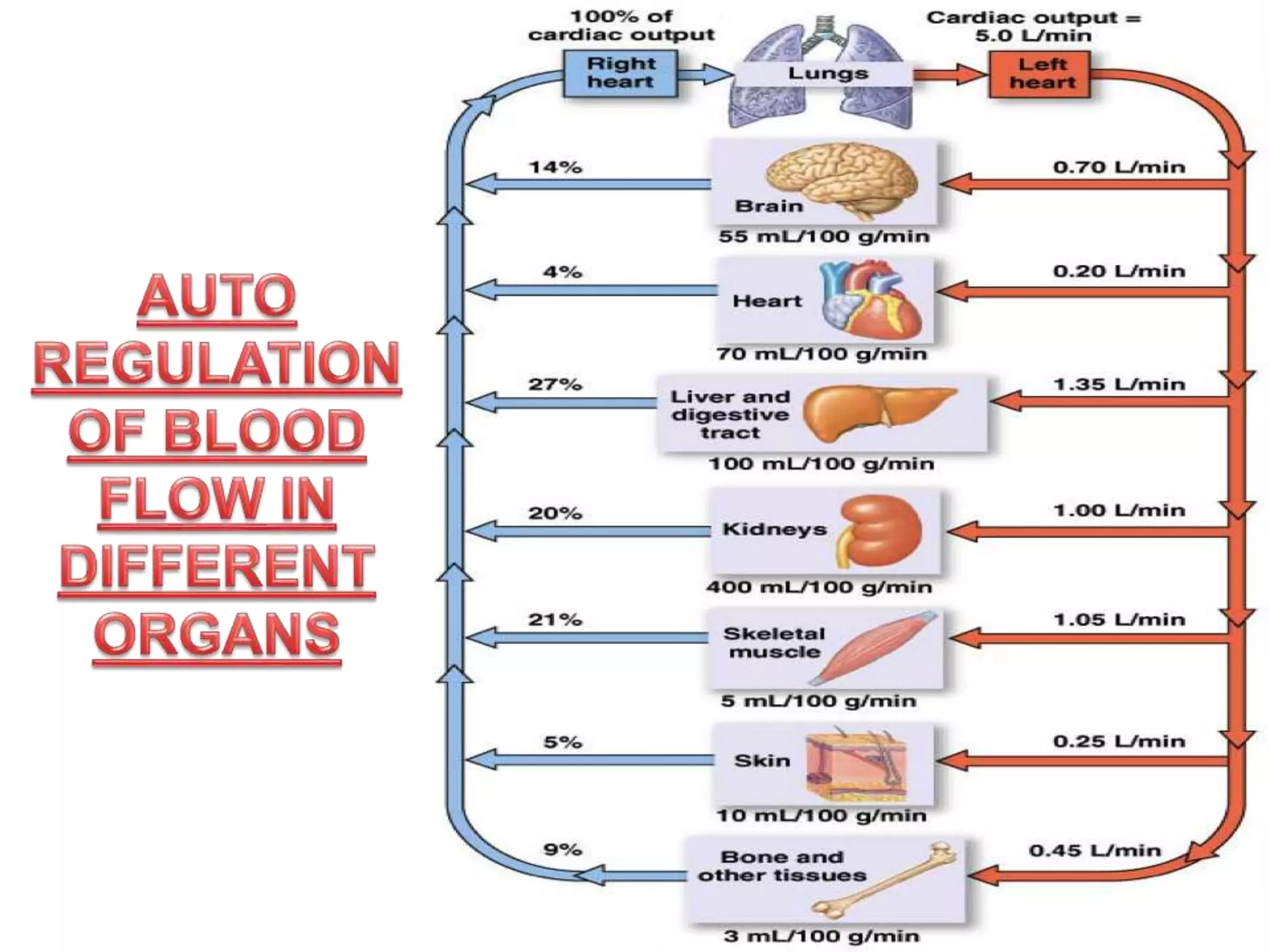




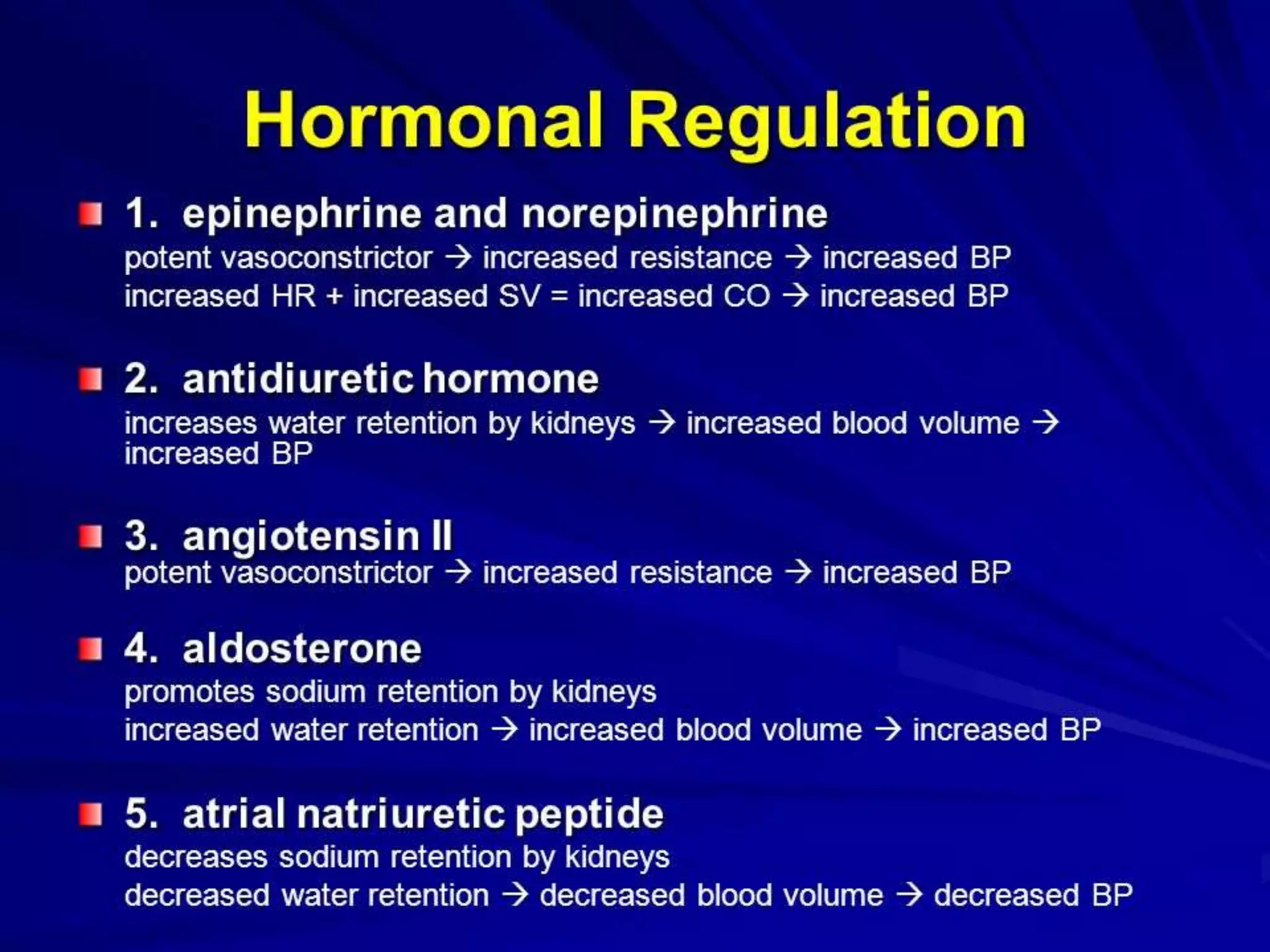


The document discusses blood flow regulation mechanisms, detailing local regulations that maintain constant flow in tissues via arteriolar adjustments and systemic regulations that allow organ-specific blood supply control. It explains acute regulations including myogenic responses, metabolites, and hormones, along with long-term adaptations like angiogenesis for restoring flow in response to ischemia. Additionally, it mentions hormonal, chemical, and neural regulators in systemic mechanisms.



















