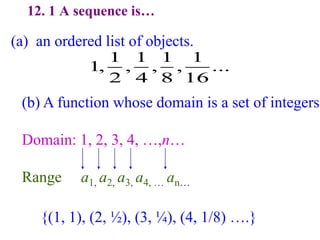
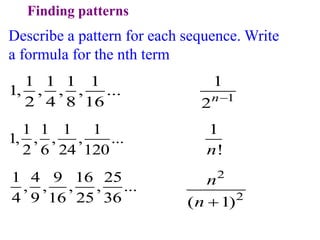
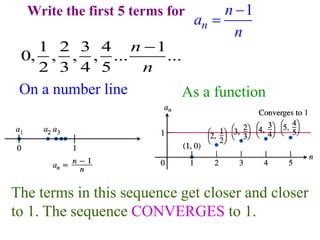
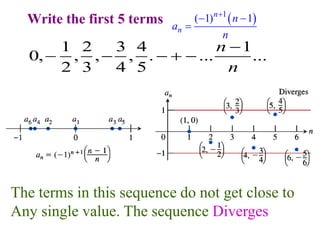
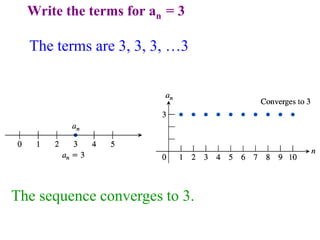
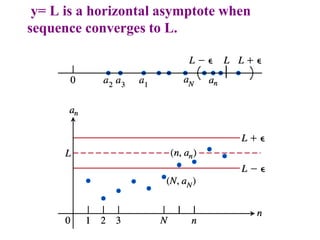
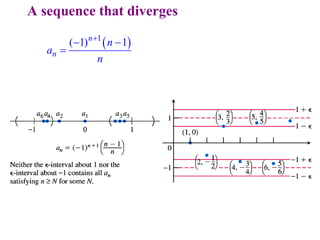
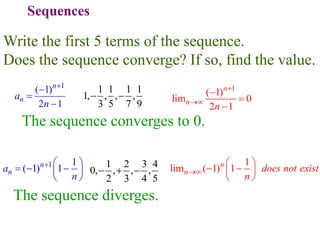
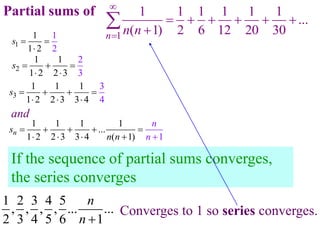
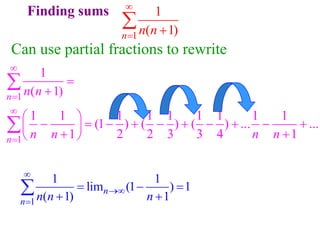
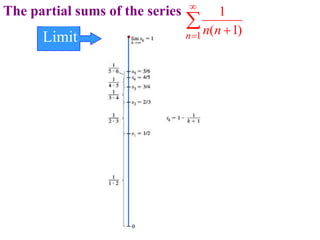
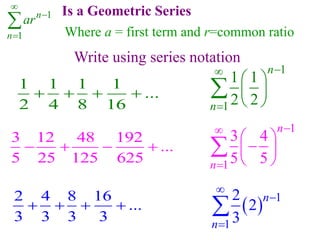
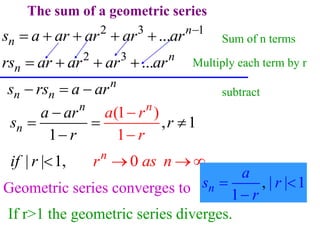
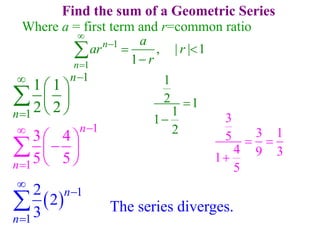
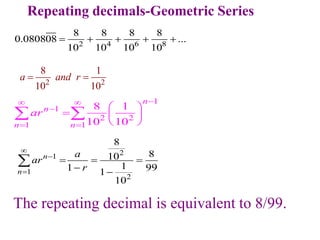
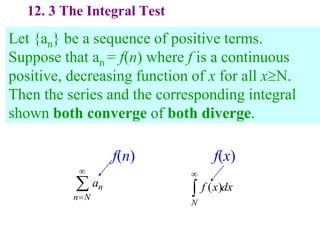
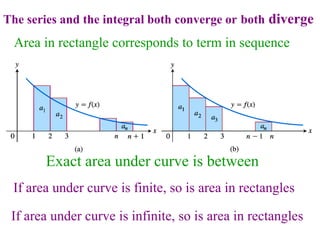
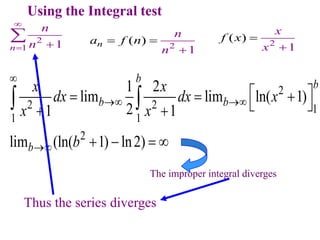
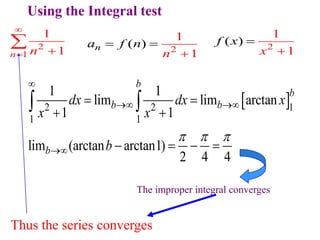
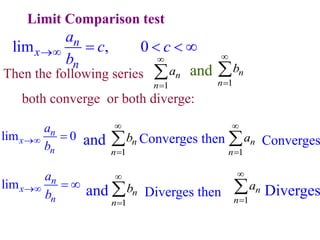
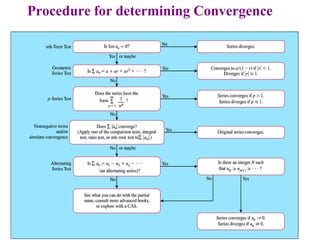
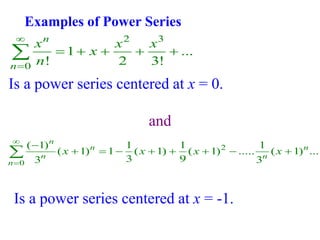
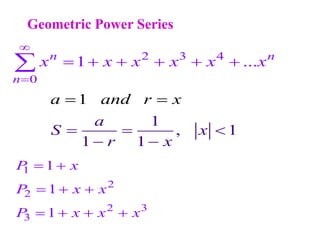
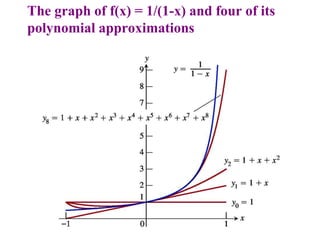
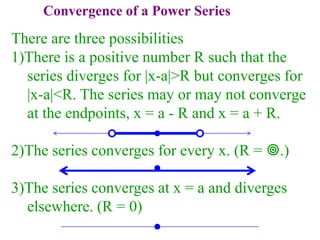
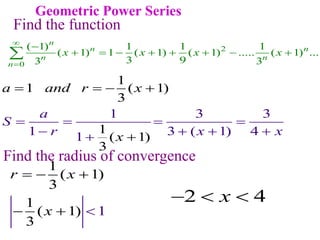
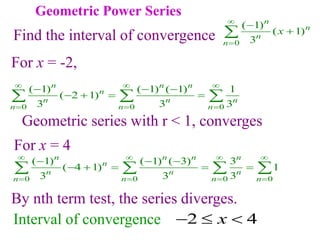
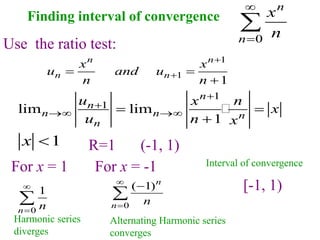
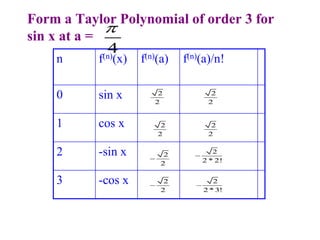
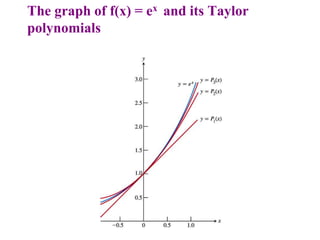
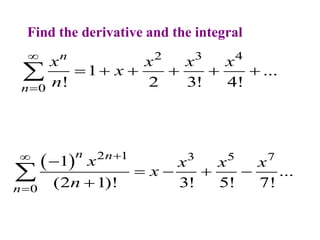
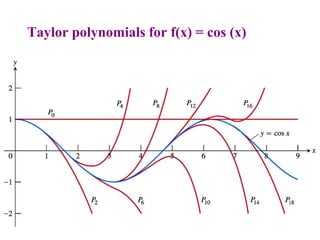
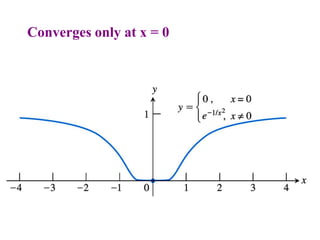
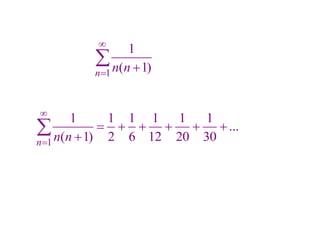This document discusses convergence of sequences and series. It defines a sequence as an ordered list of objects and describes how to write the first few terms. A sequence converges if its terms get closer to a single value, while a divergent sequence does not. Infinite series represent the sum of the terms in a sequence. A series converges if the partial sums converge to a finite limit. Geometric series have a common ratio between terms and their sums can be determined based on this ratio. The integral test can be used to determine if a series converges by comparing it to a corresponding integral.