1. Plants have internal mechanisms for tolerating variations in external environments like water deficit, cold, and heat stress.
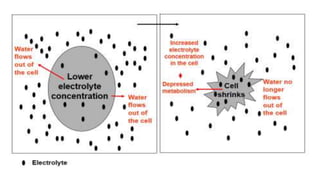
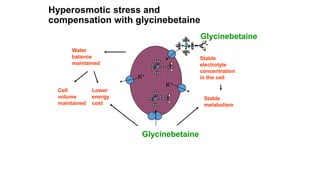
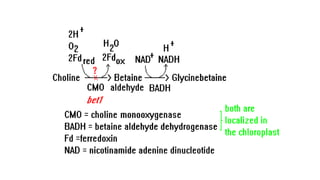
2. Engineering stress tolerance focuses on producing osmoprotectants like glycine betaine and sorbitol to reduce osmotic stress from water deficit. Glycine betaine is produced through pathways using enzymes like choline monooxygenase.
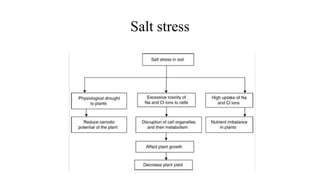
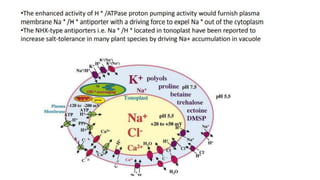
3. Salt tolerance has been engineered by transforming plants with genes for vacuolar antiport proteins like NHX1 to transport sodium ions out of cells.