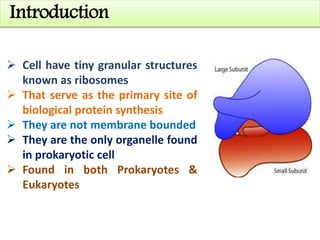
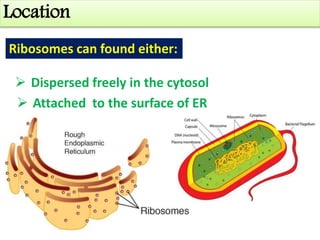
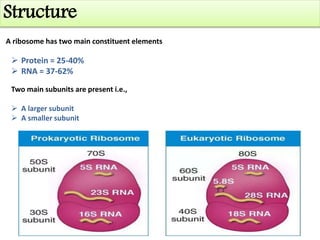
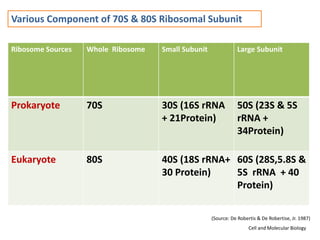
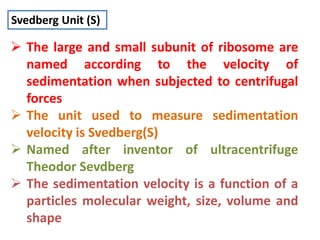
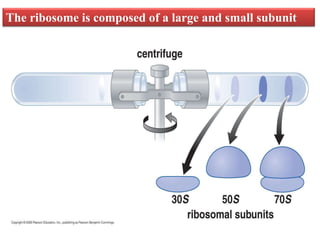
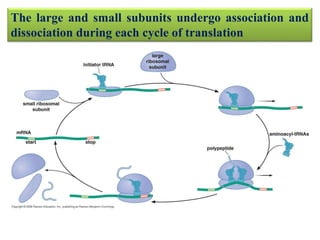
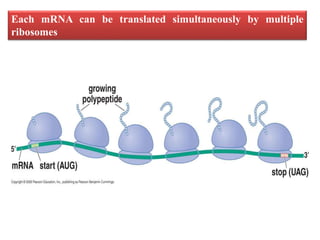
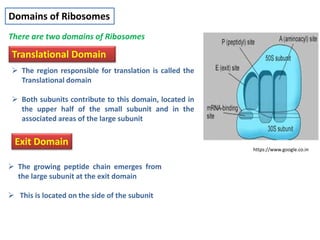
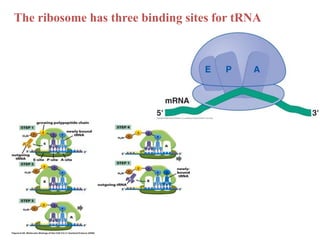
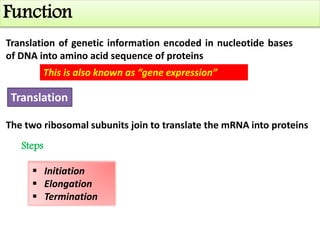
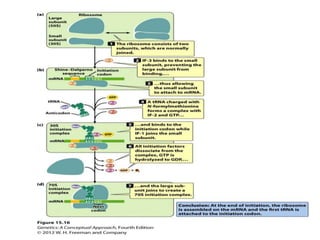
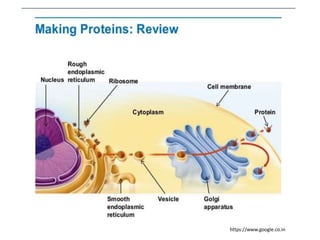
Ribosomes are tiny organelles found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that serve as the site of biological protein synthesis. They were first observed in the 1930s-1950s using microscopy and electron microscopy. Ribosomes have two subunits - a large subunit and a small subunit - and are composed of RNA and proteins. They can be free in the cytoplasm or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes translate mRNA into proteins through the three steps of initiation, elongation, and termination.