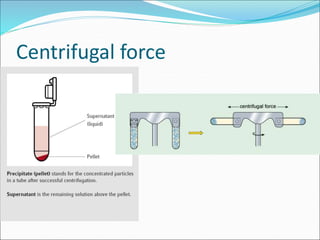
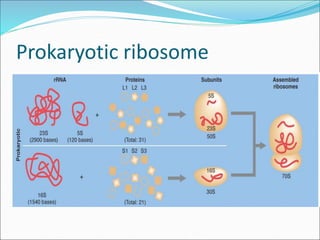
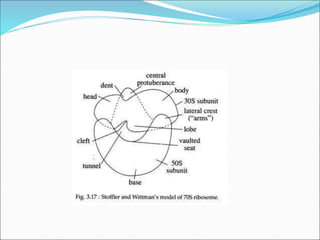
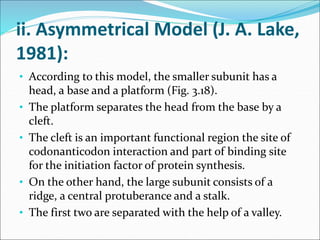
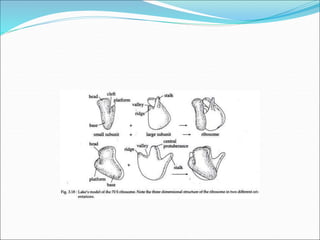
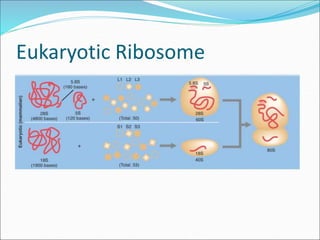
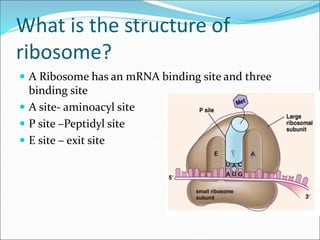
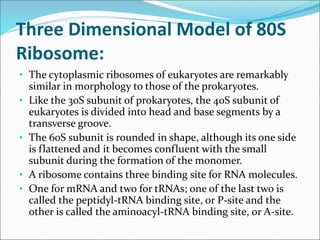
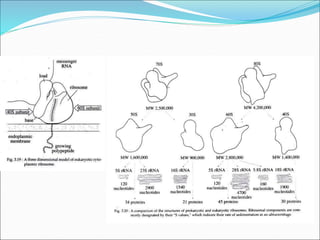
Ribosomes are essential molecular machines within living cells that facilitate protein synthesis by linking amino acids as specified by mRNA. They consist of small and large subunits, composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins, and exist in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic forms, differing in size and composition. The document also outlines models of ribosomal structure, highlighting the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes.