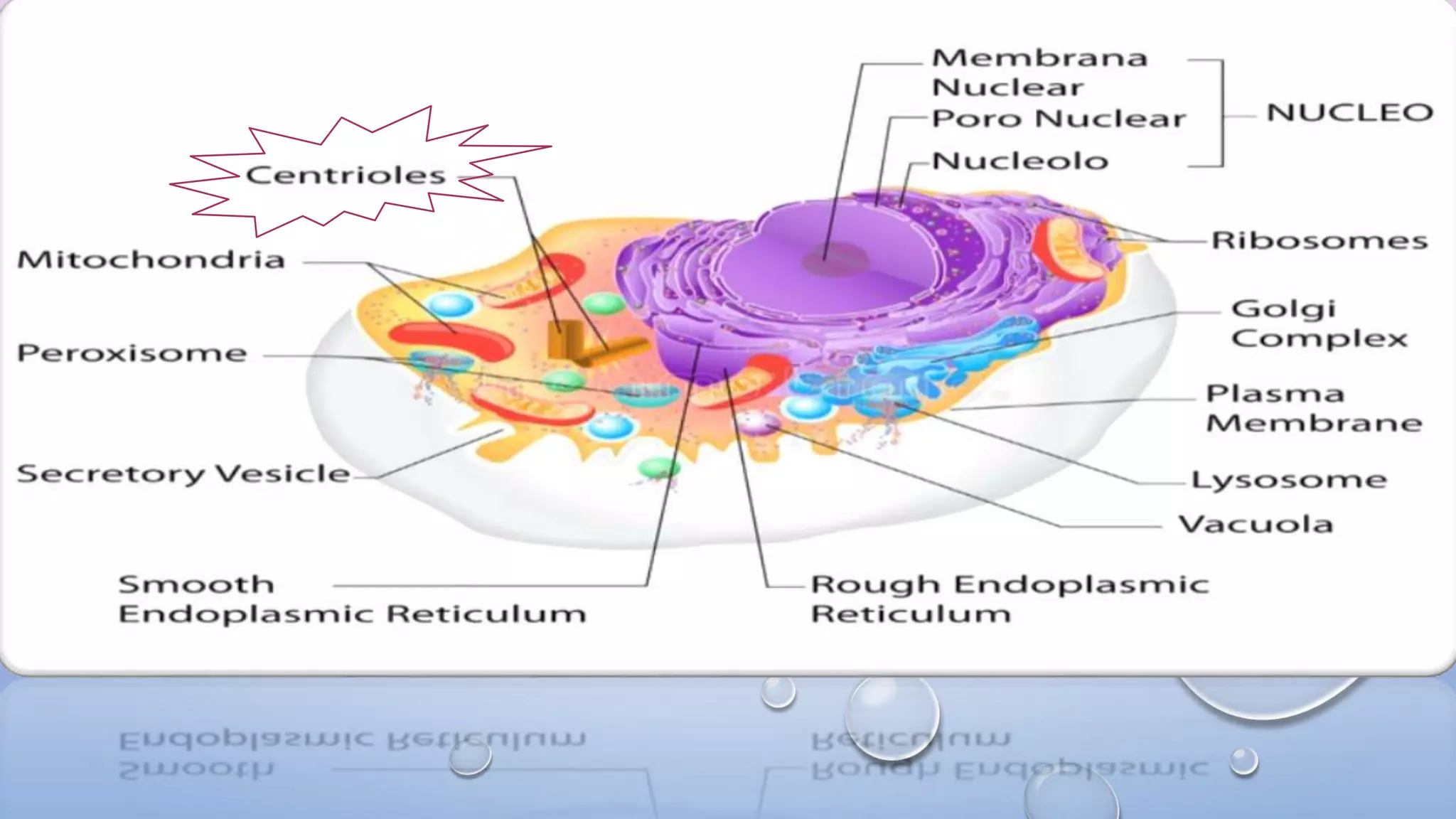
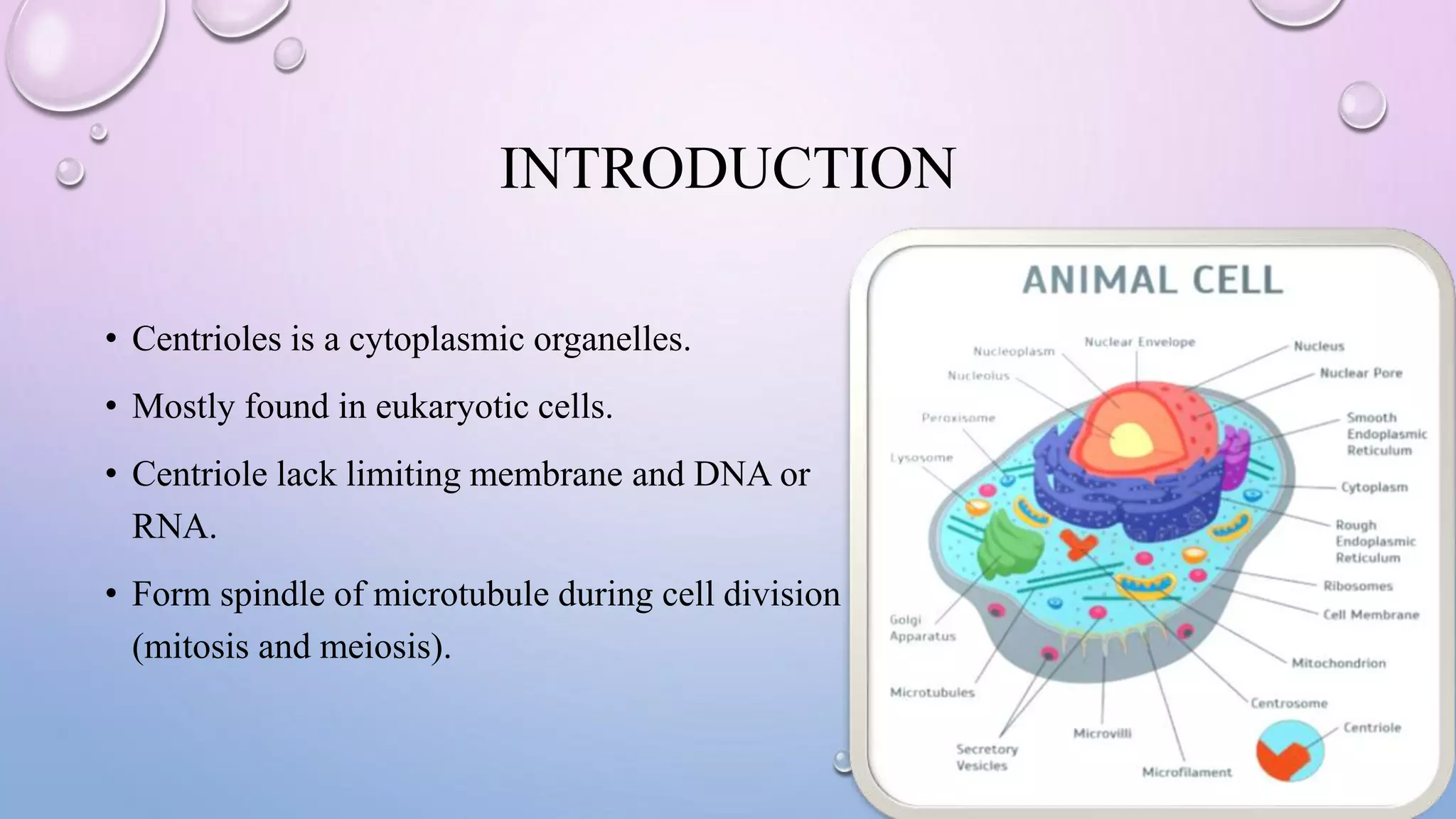
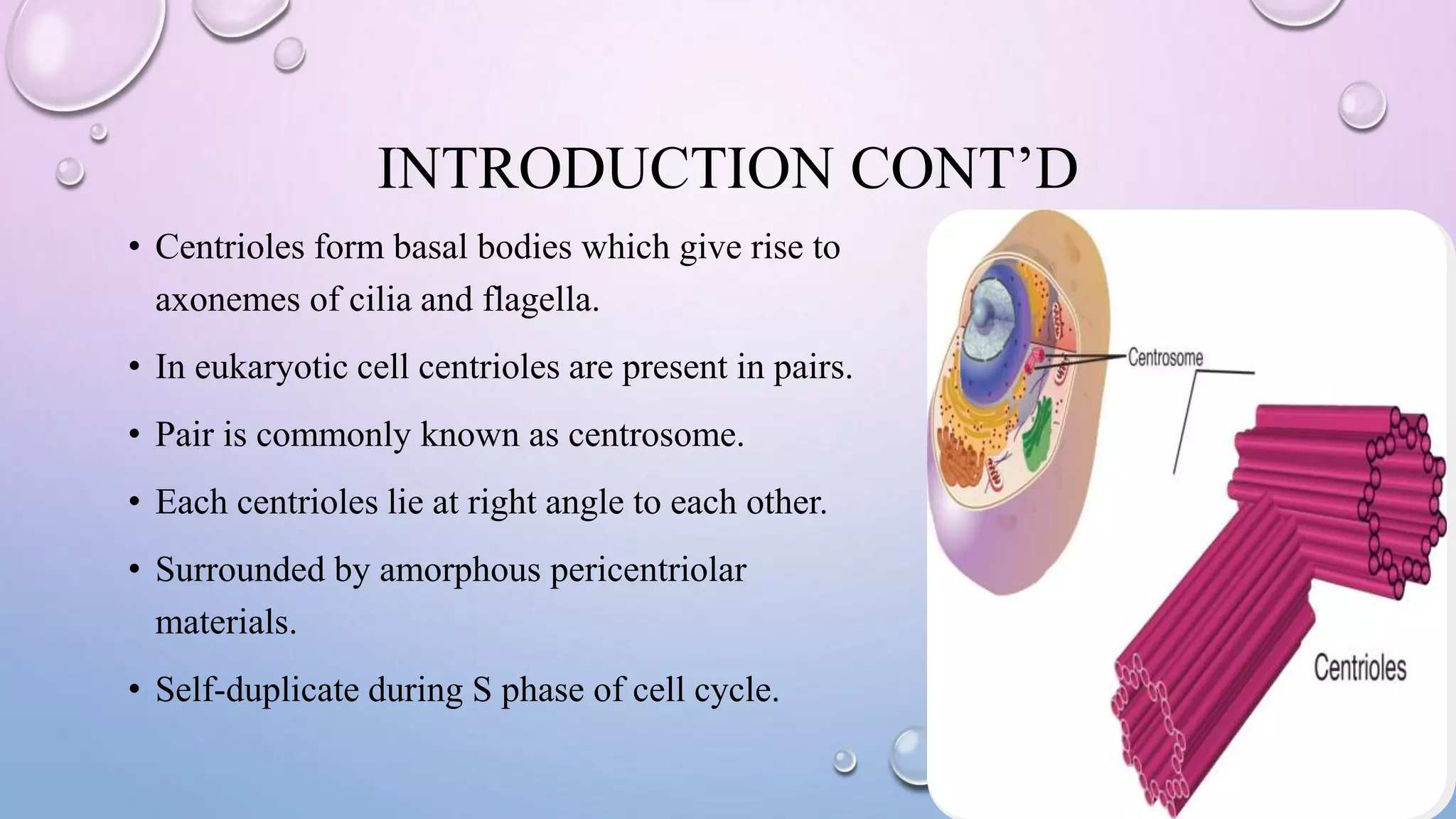
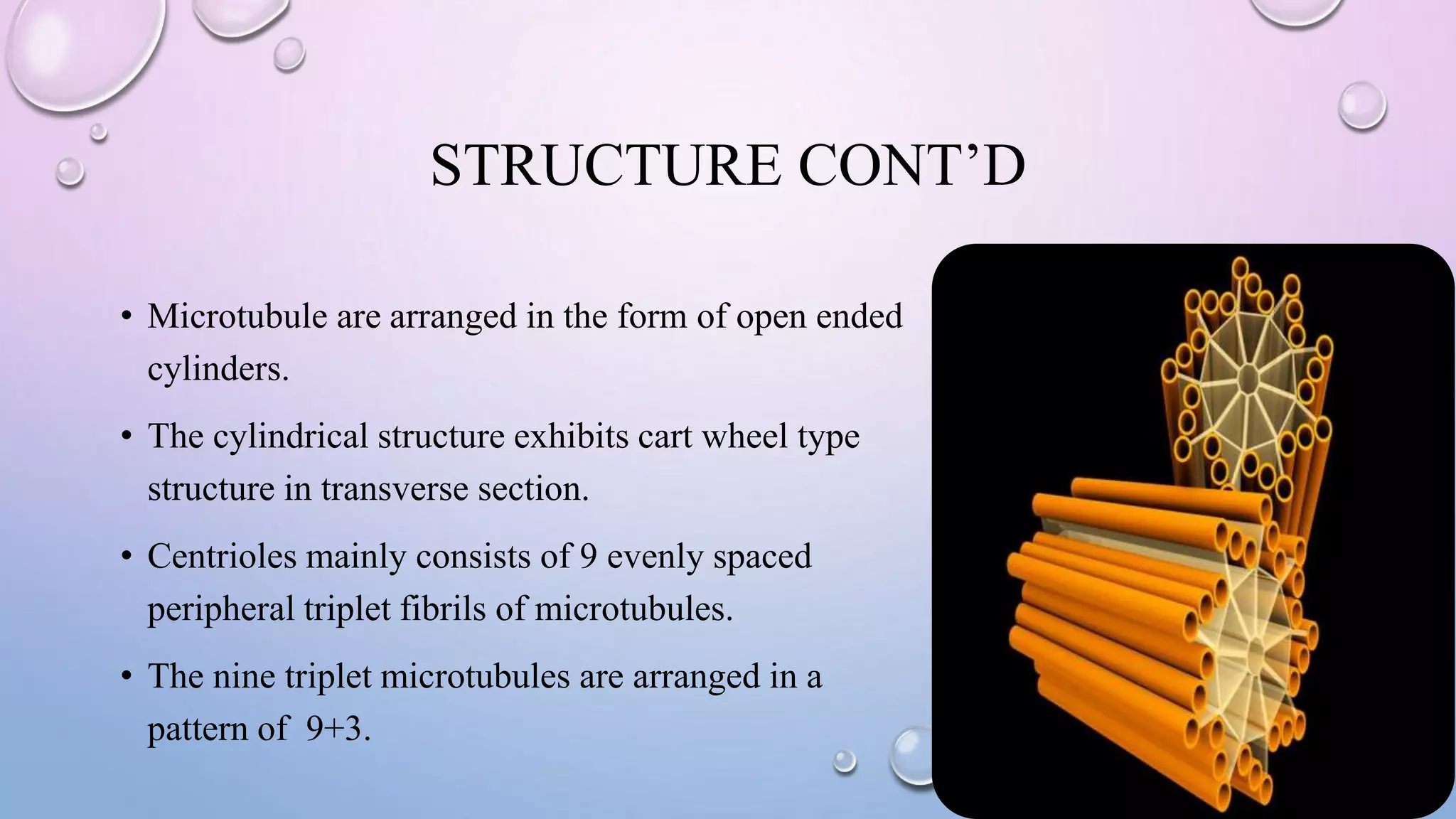
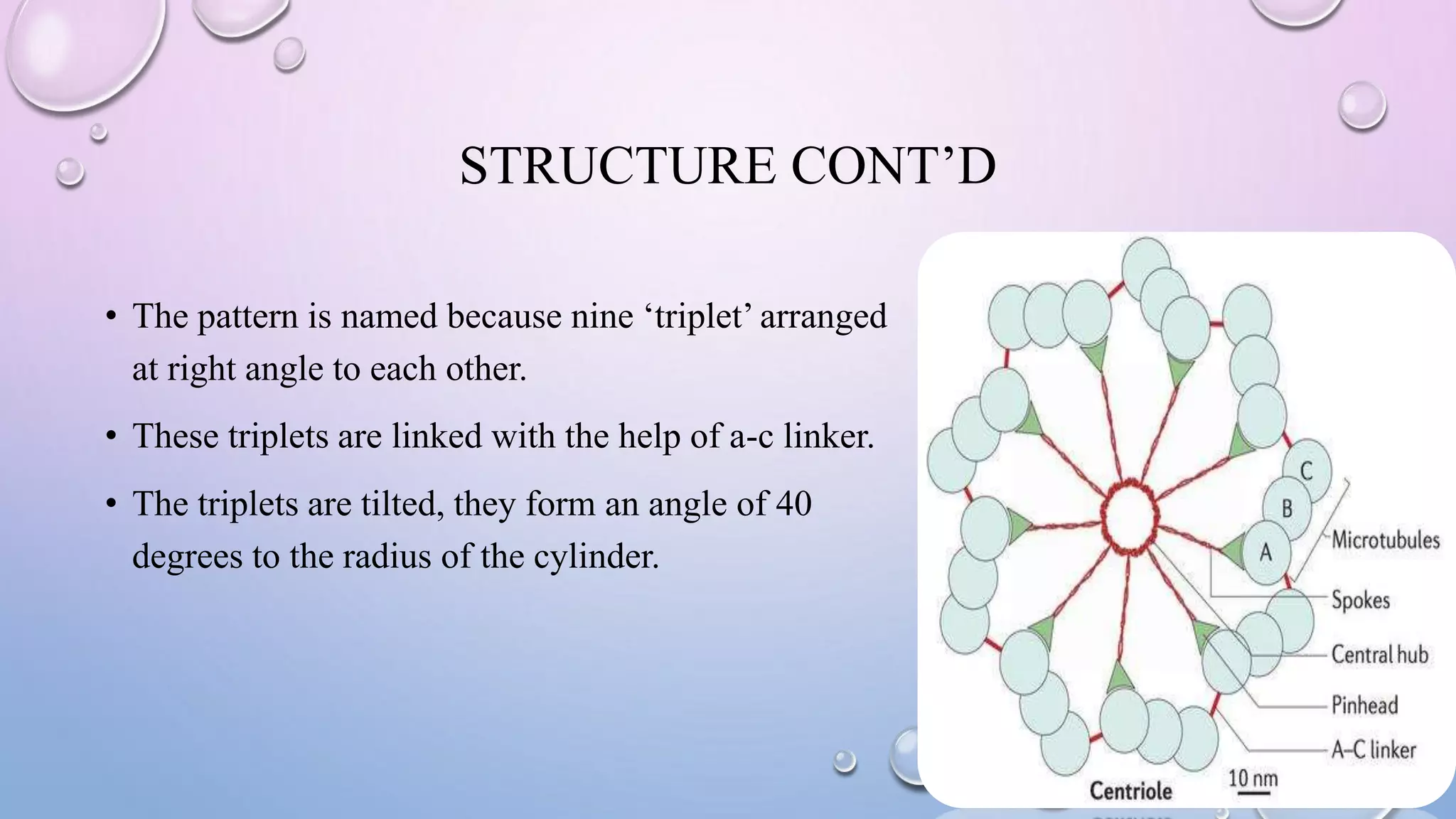
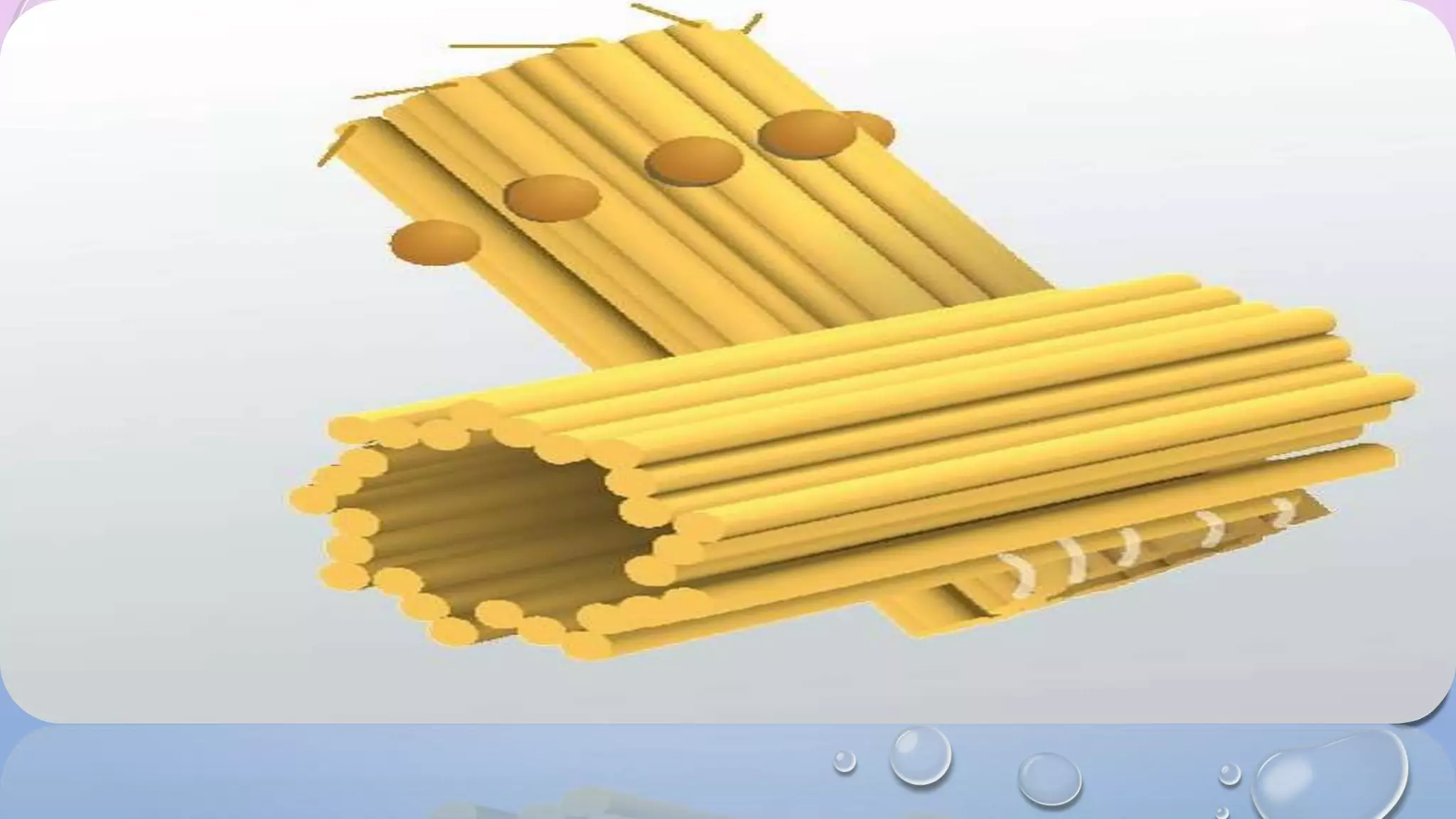
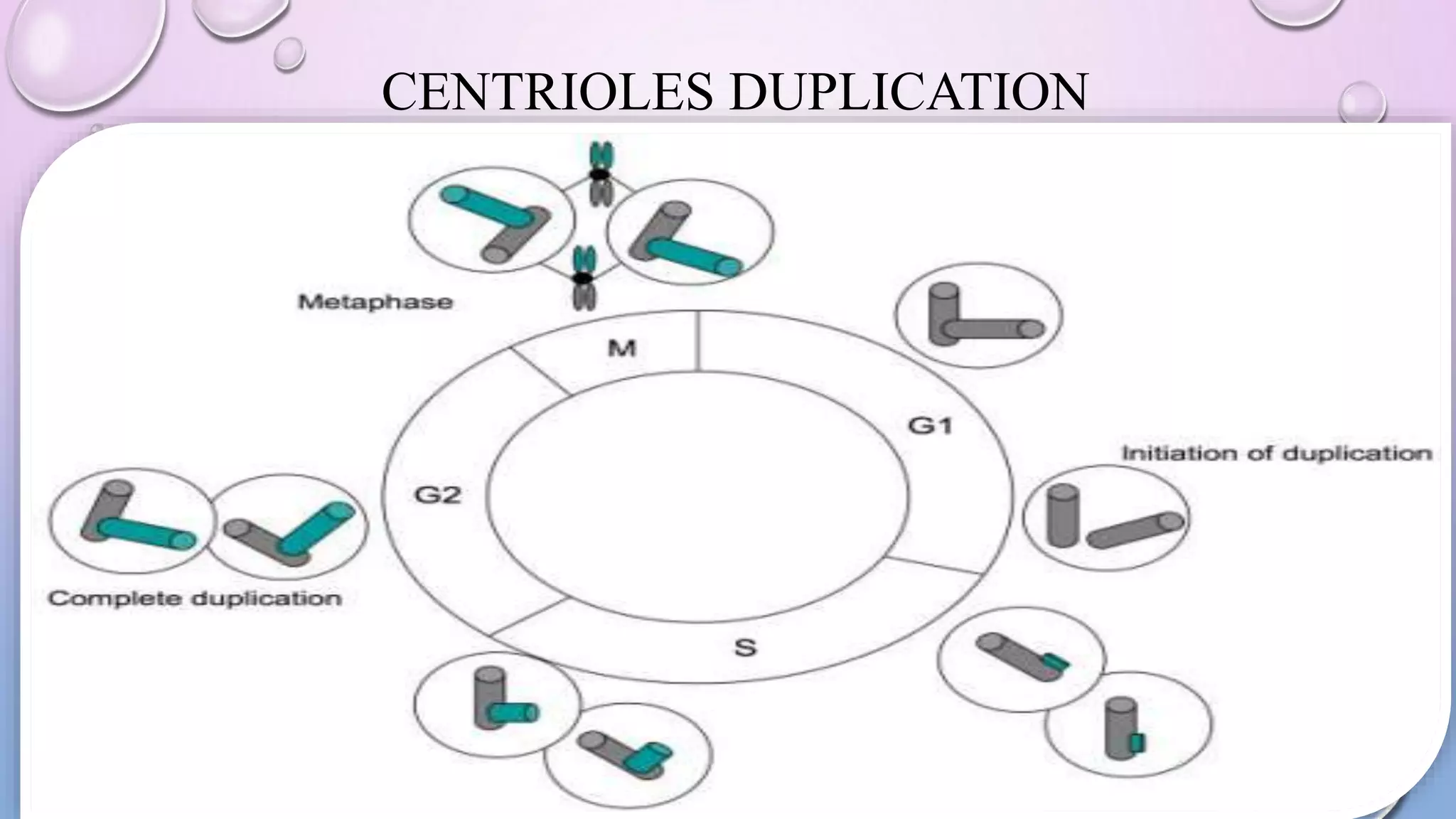
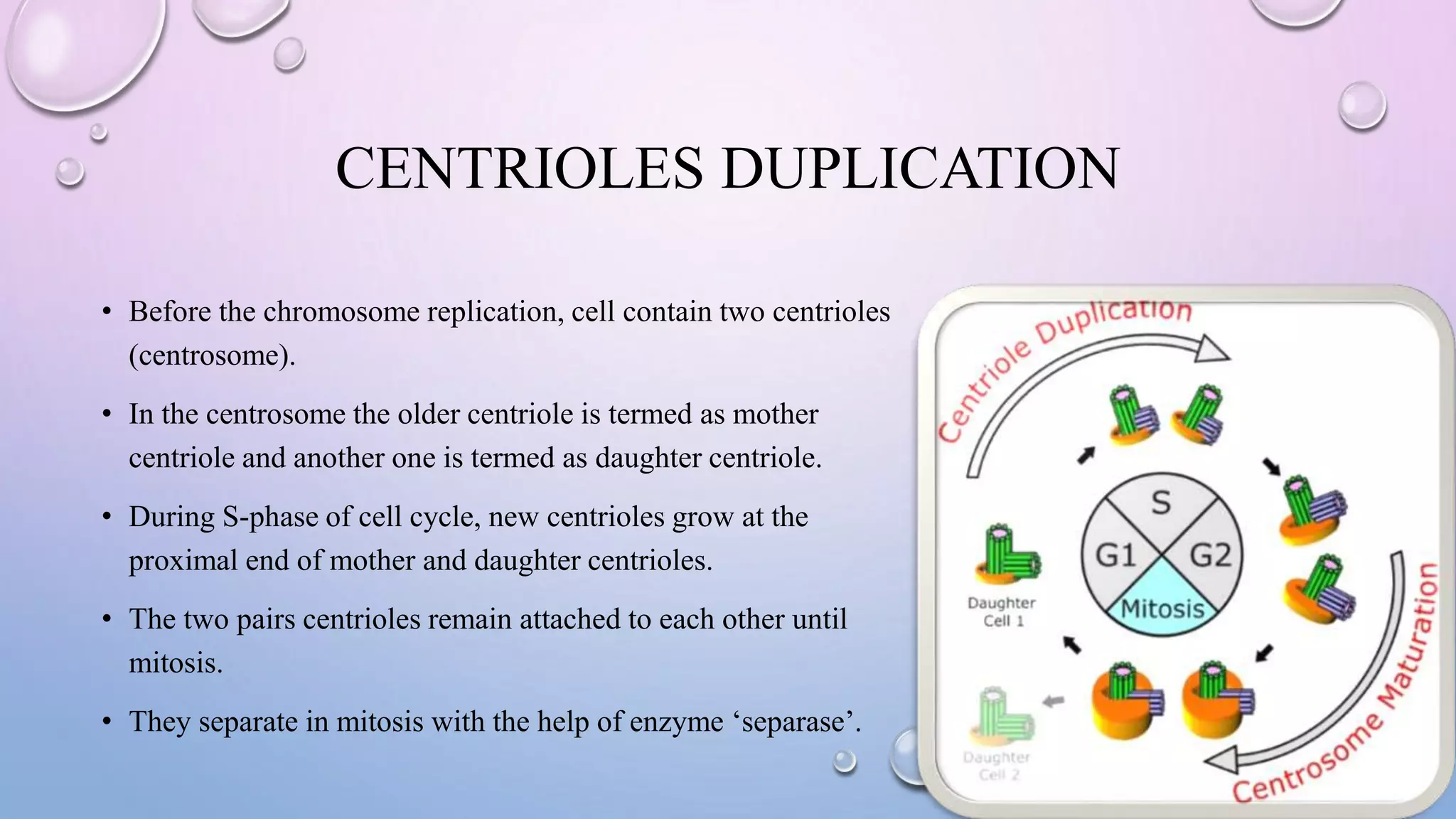
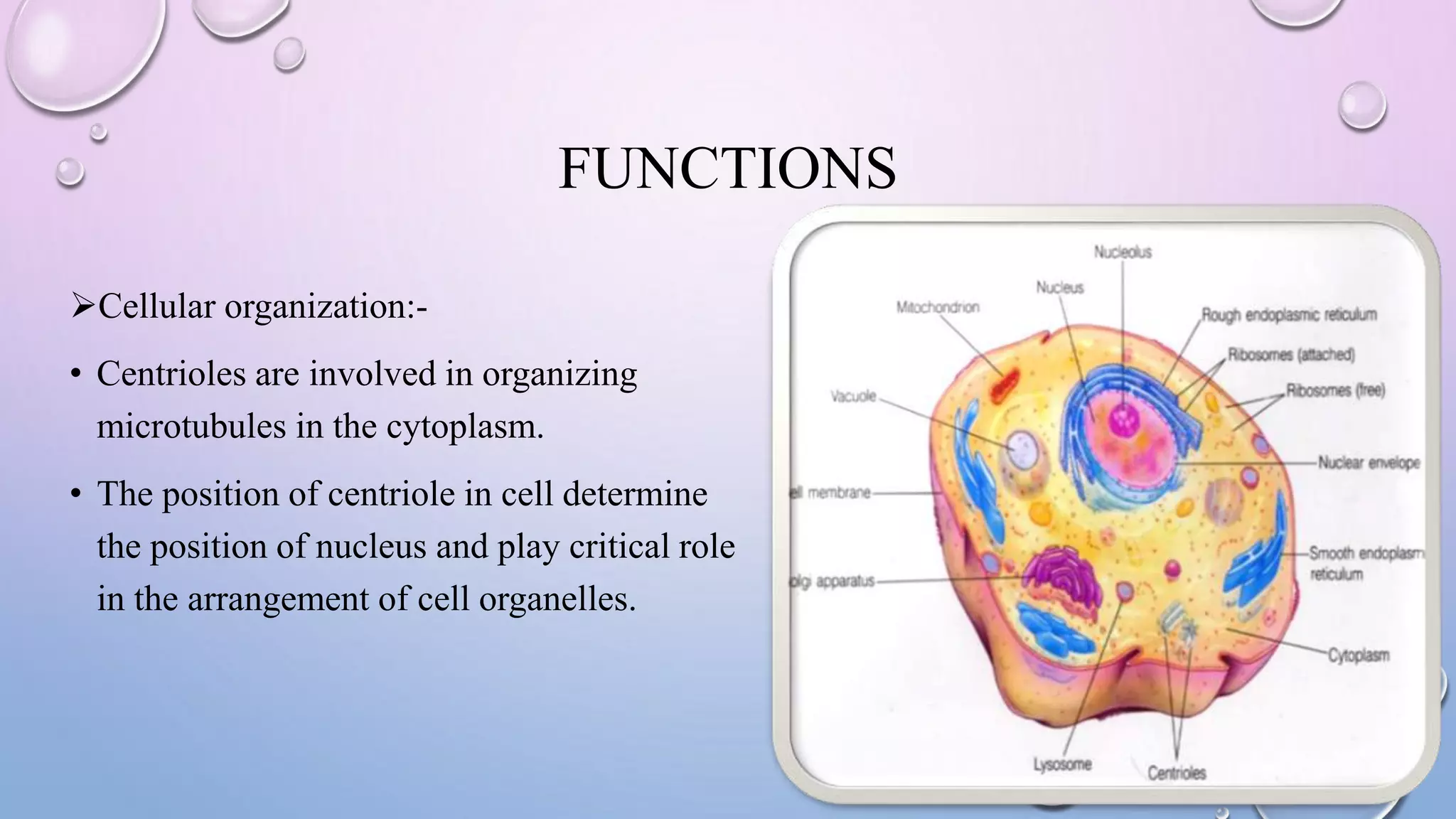
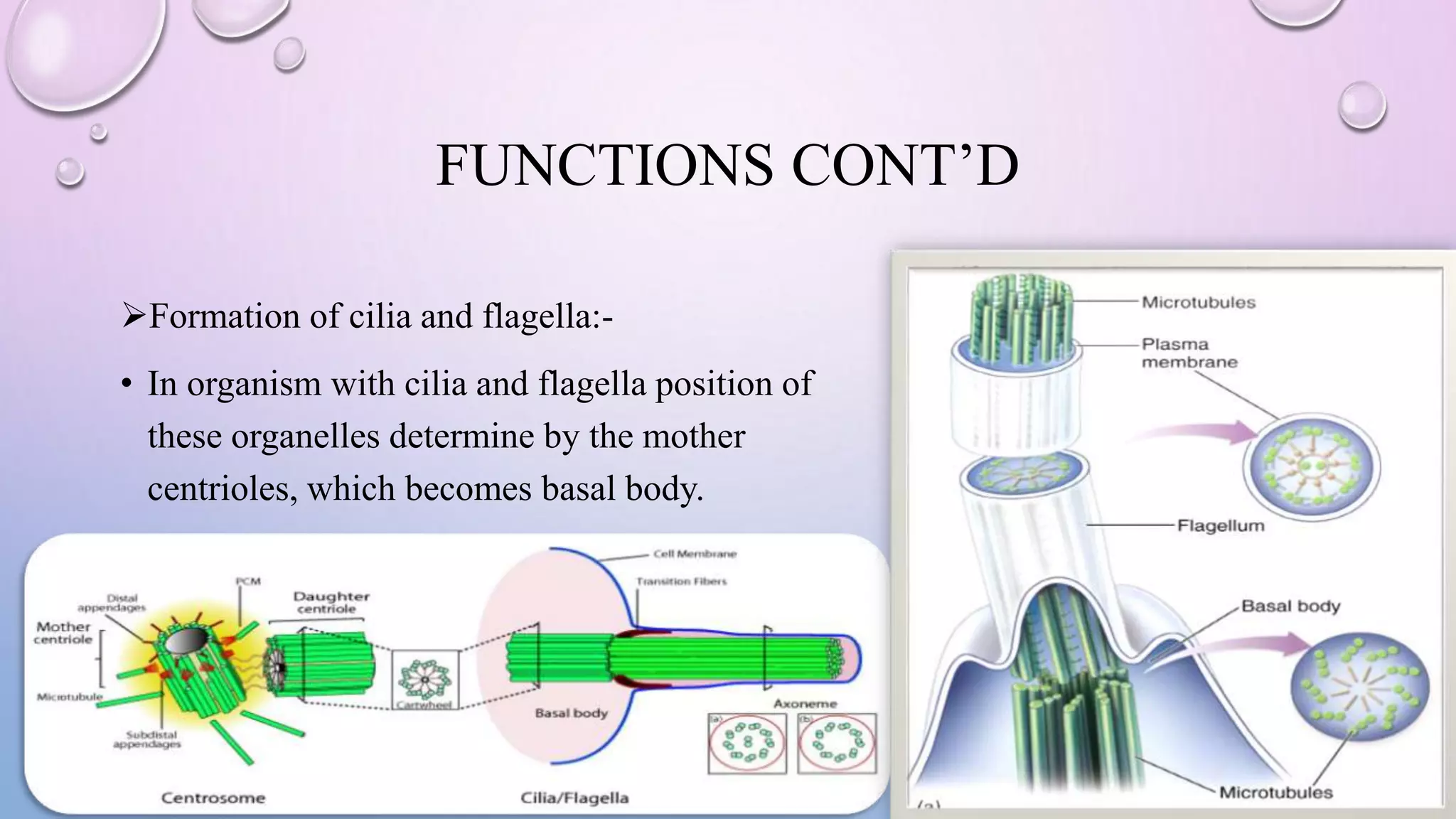
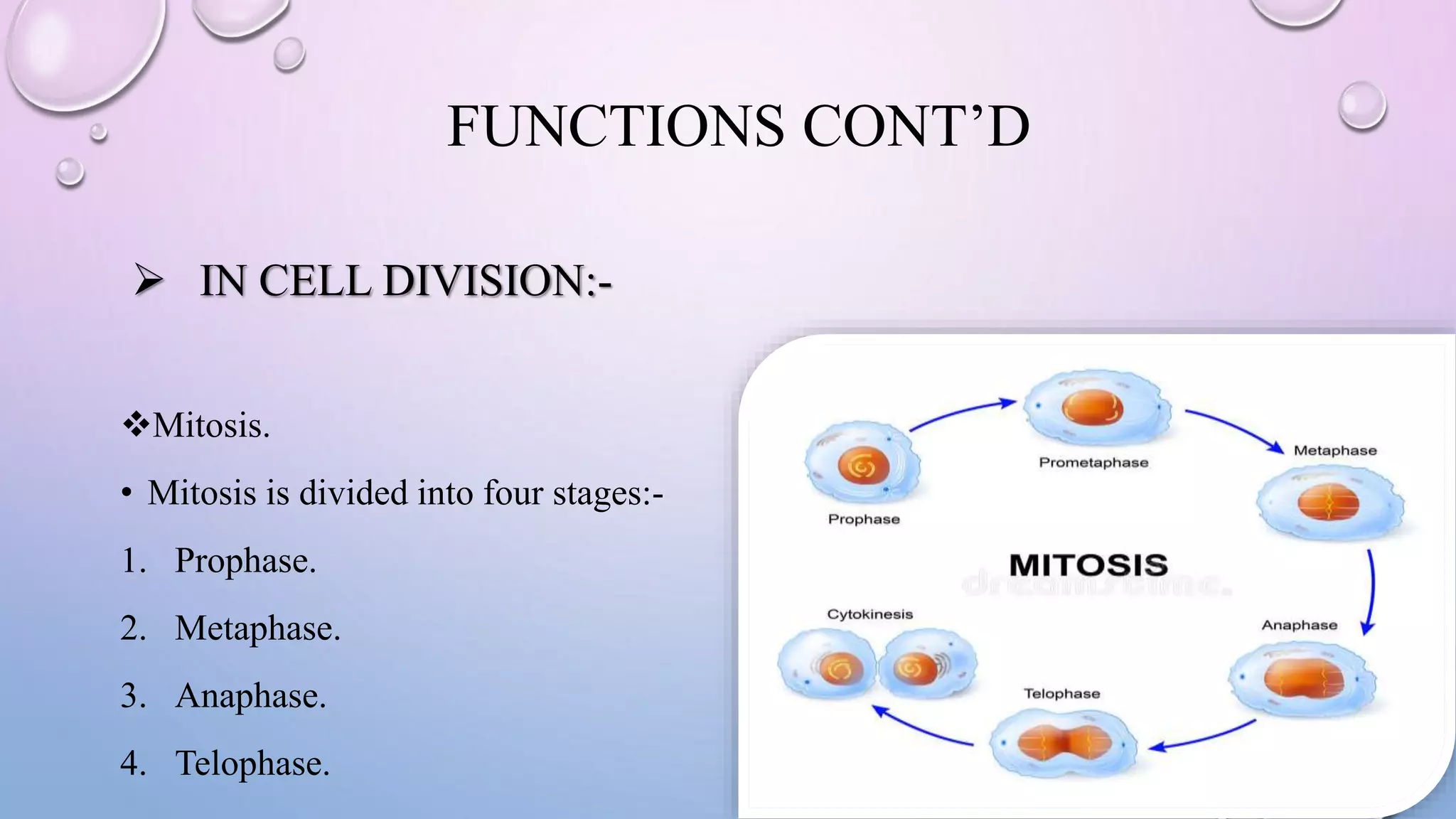
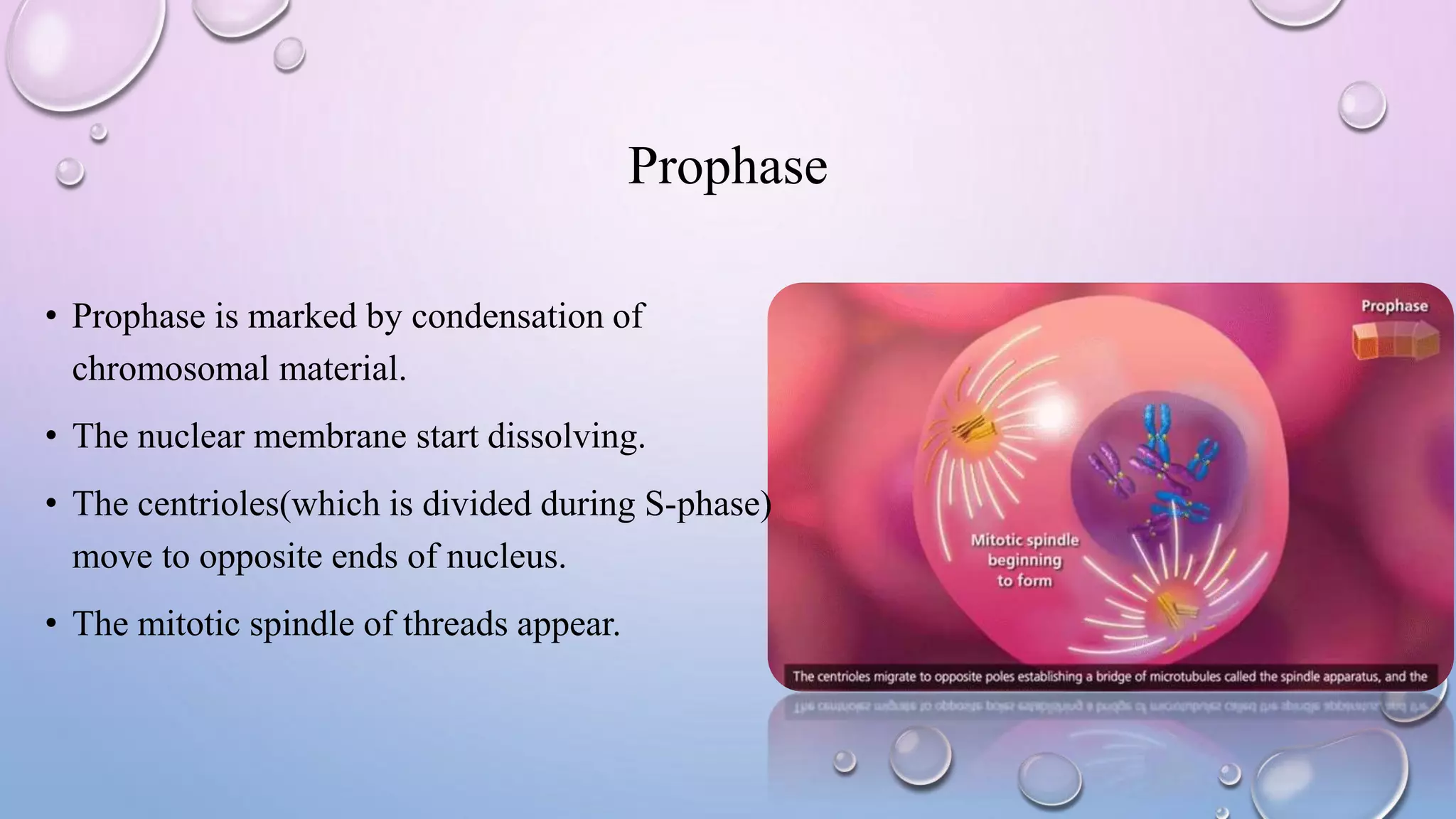
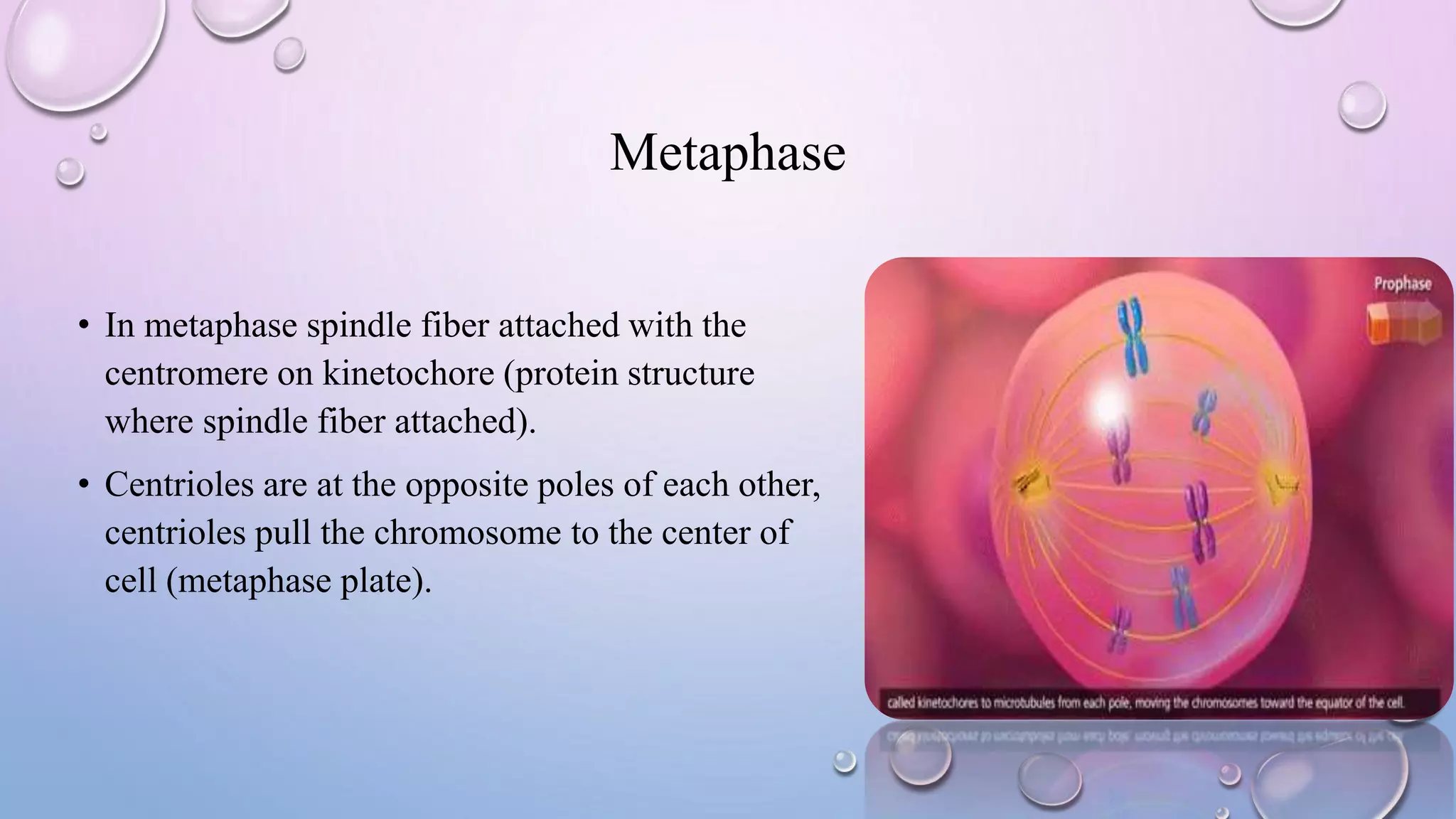
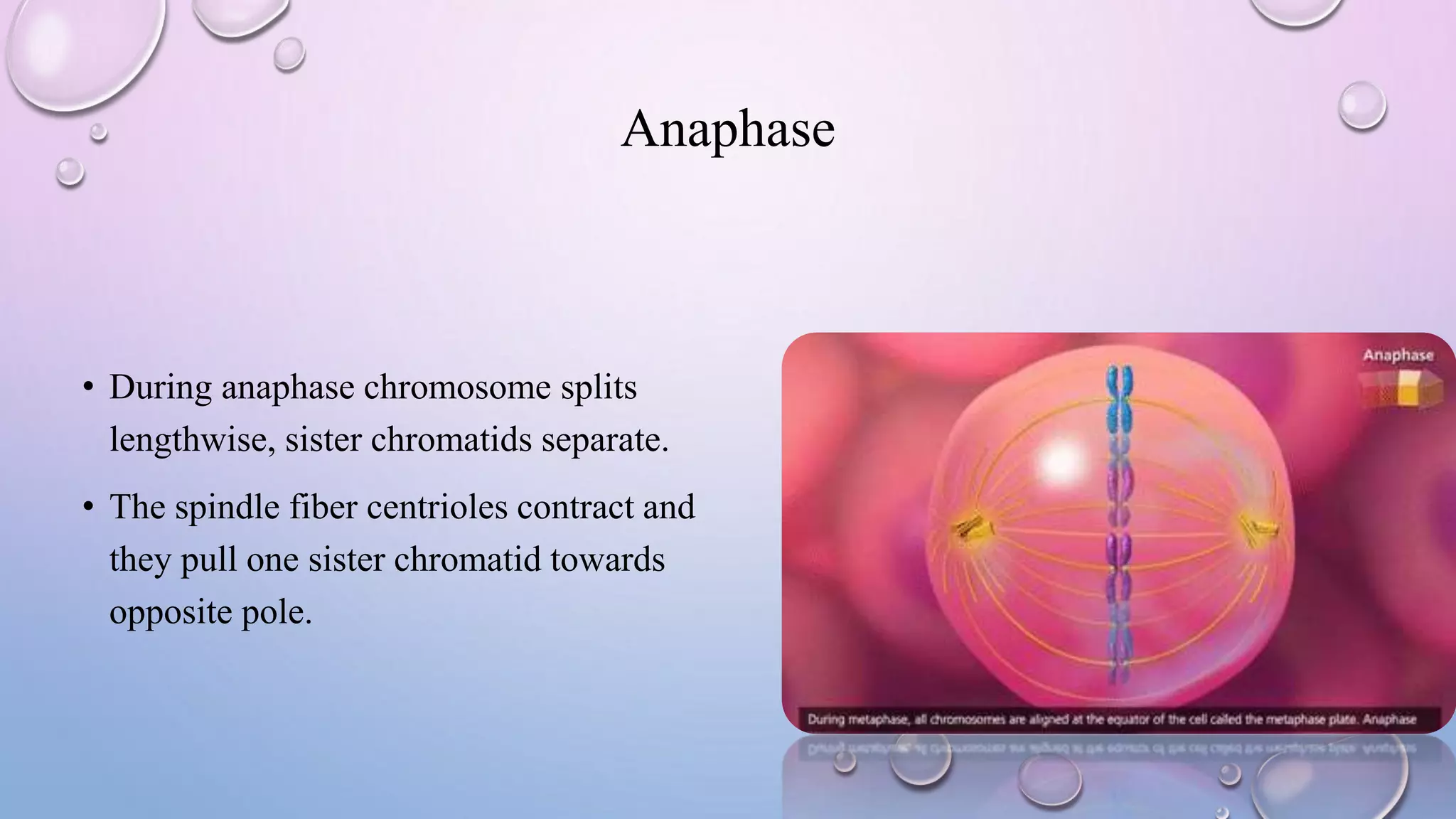
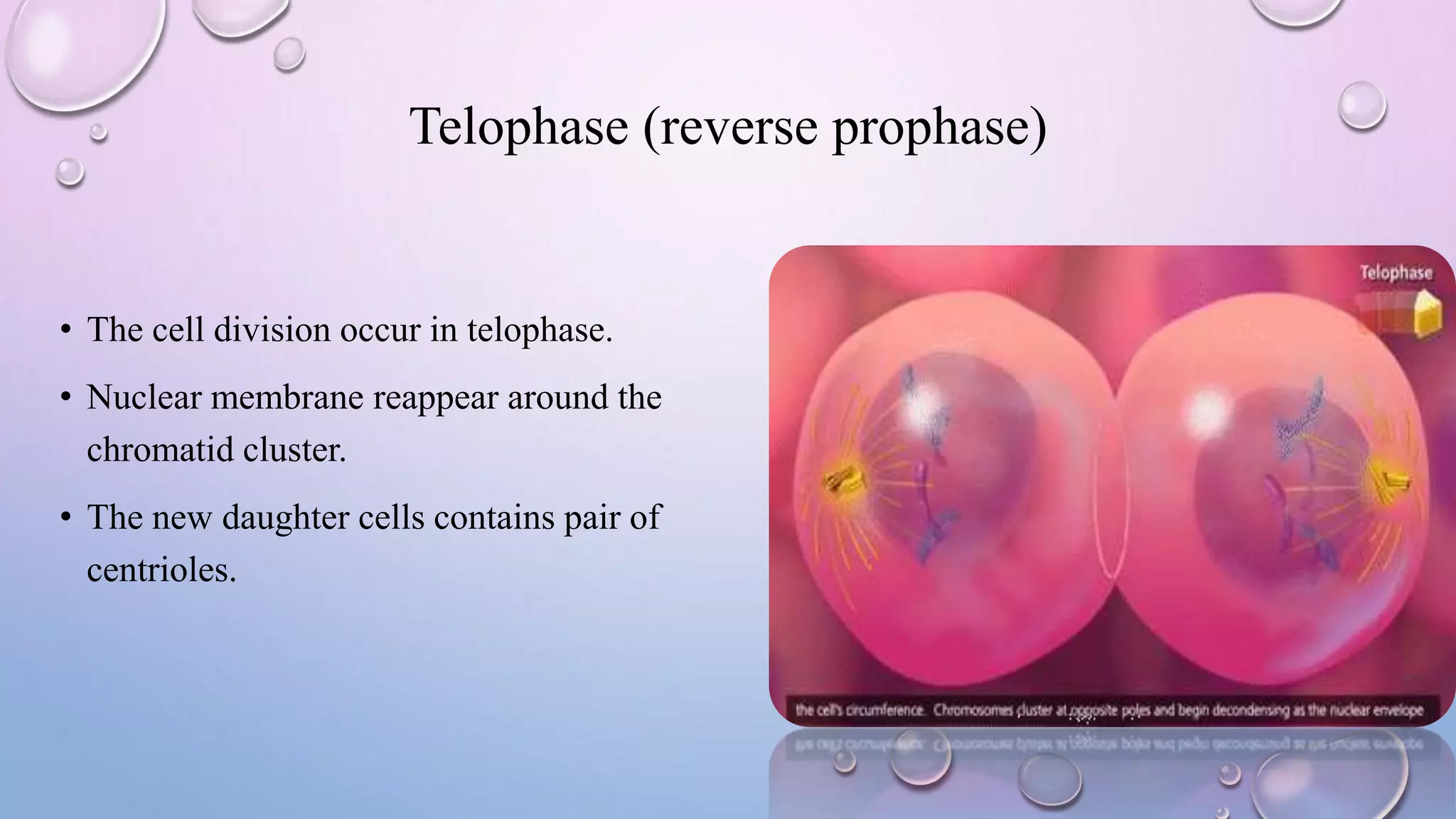
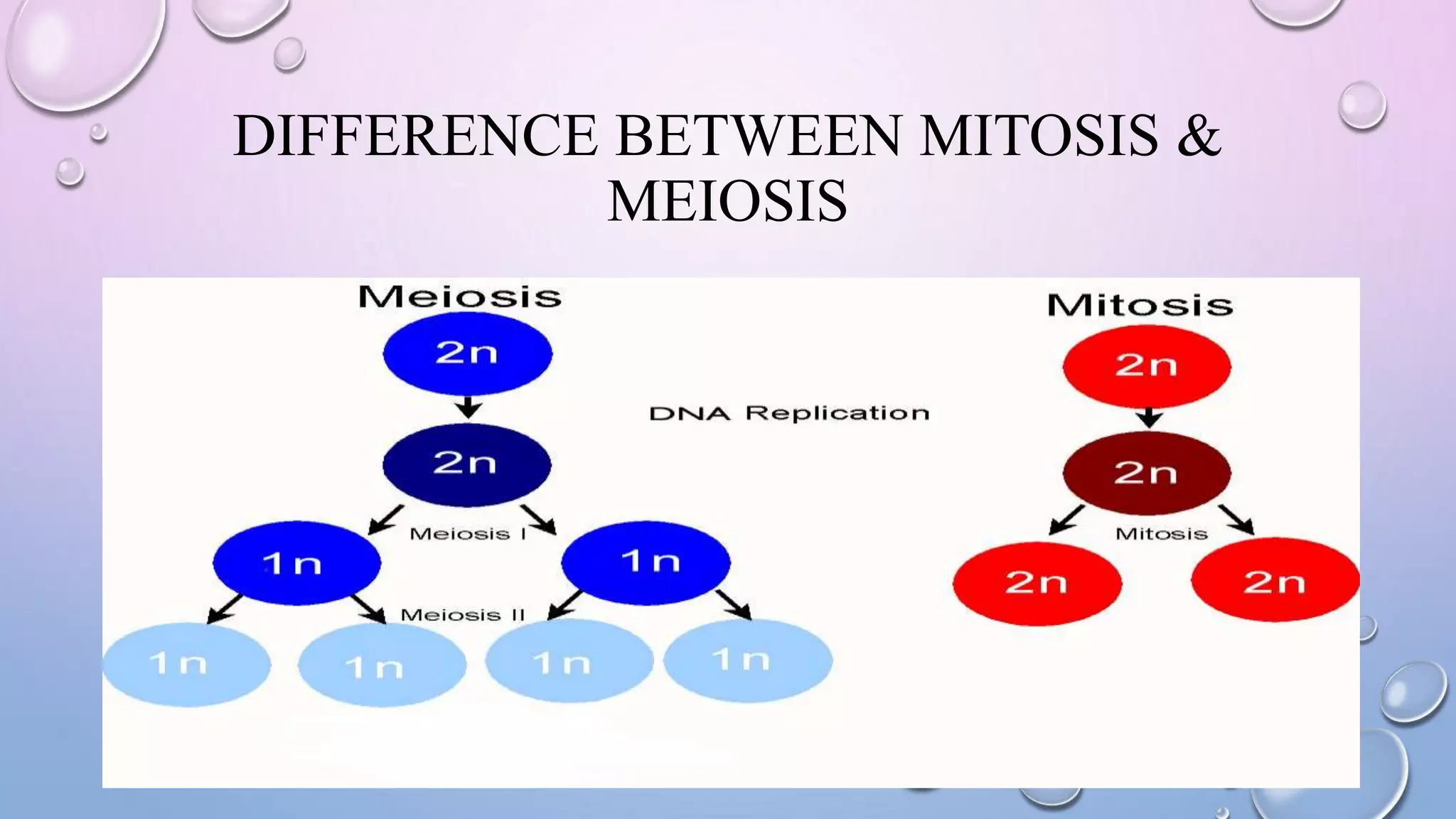
Centrioles are cytoplasmic organelles found in eukaryotic cells that lack a limiting membrane or DNA. They are composed mainly of tubulin protein and arranged in a 9+3 pattern of microtubules. Centrioles help organize microtubules and form basal bodies for cilia/flagella. During cell division, the centrioles move to opposite poles and form the mitotic spindle, helping pull sister chromatids apart into daughter cells. Centrioles duplicate during S phase and are involved in both mitosis and meiosis.