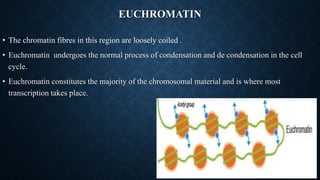
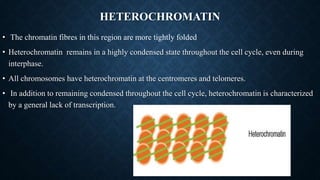
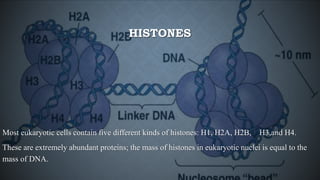
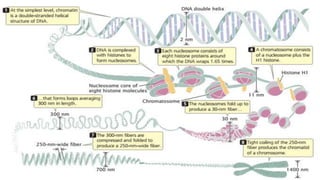
Chromatin is composed of DNA wrapped around histone proteins, which allows it to be tightly packed in the cell nucleus. There are two main types of chromatin: euchromatin, which is loosely coiled and allows for transcription; and heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and generally not transcribed. DNA combines with histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which involve 146bp of DNA wrapped around an octamer of core histone proteins. Nucleosomes further fold into a 30nm fiber, which then loops and coils to allow the long DNA molecules to fit inside the cell nucleus.