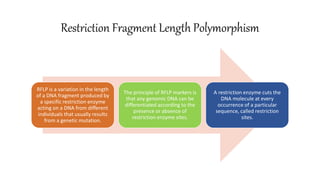
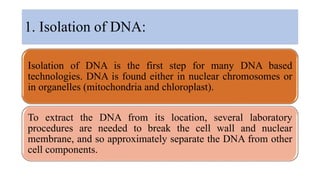
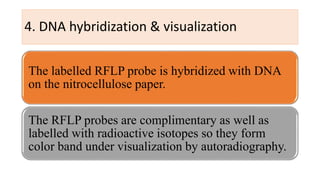
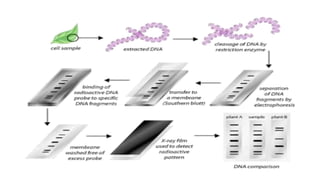
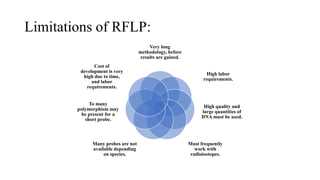
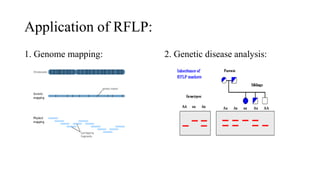
This document discusses several molecular techniques used in microbiology, including restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS). RFLP detects genetic variations by cutting DNA with restriction enzymes and comparing fragment lengths. PFGE improves on standard gel electrophoresis by applying an alternating electric field to better separate very large DNA molecules. CAPS combines PCR and RFLP to detect single base changes without radioactive probes. These techniques are useful for genome mapping, disease analysis, and forensic or epidemiological investigations.