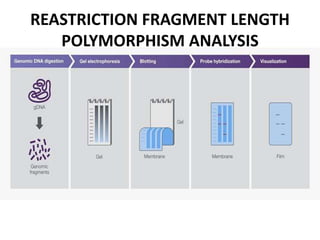
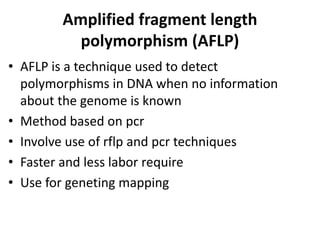
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis detects variations in DNA fragment length to distinguish individuals. It involves incubating DNA with restriction endonucleases that cut DNA at specific recognition sites. Differences in the resulting fragment patterns between individuals arise from variations in restriction enzyme recognition sites. RFLP analysis can be used for genetic fingerprinting, paternity testing, and studying diversity. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) are PCR-based methods that detect polymorphisms without prior DNA sequence knowledge and are faster than RFLP analysis.