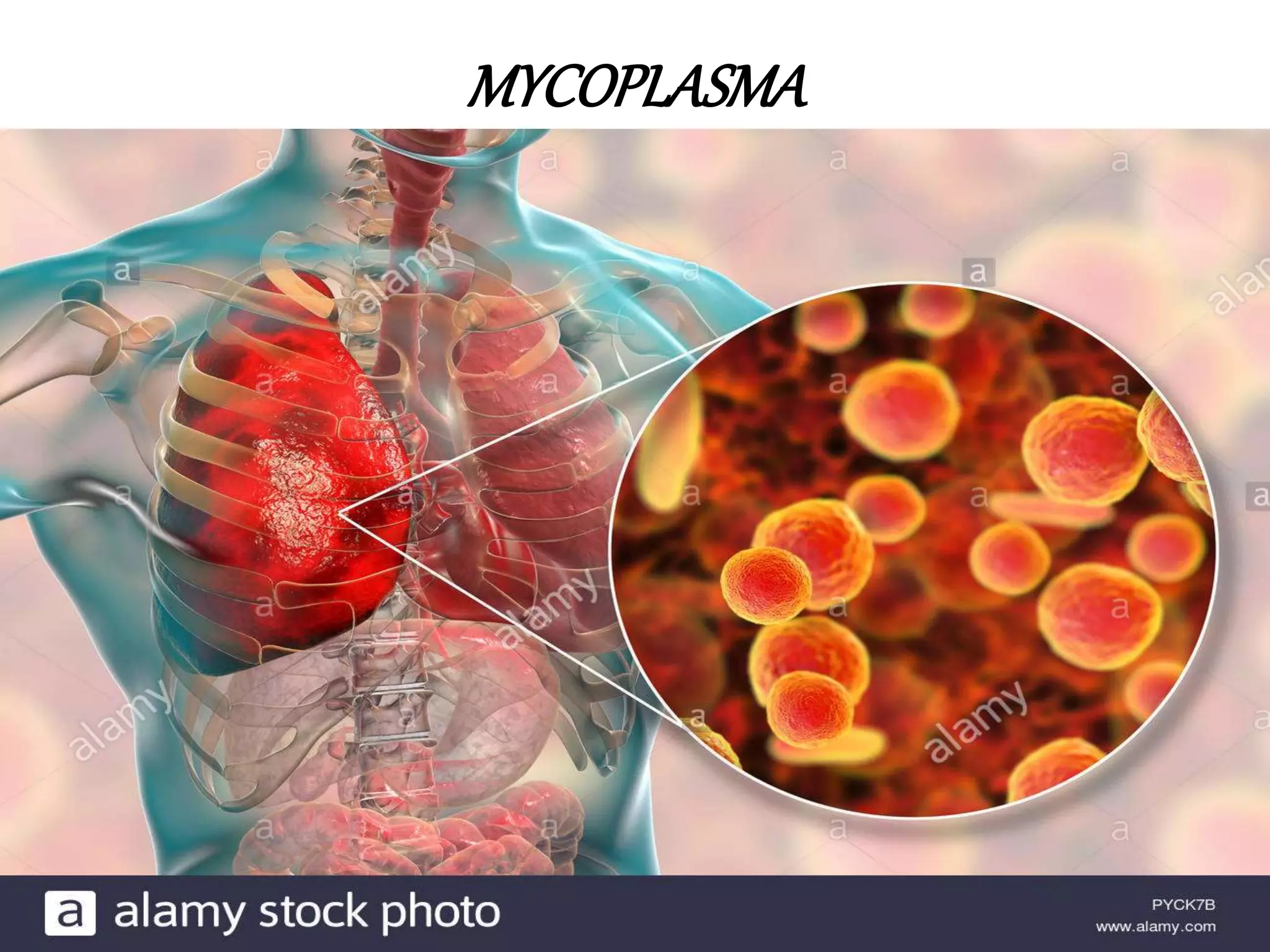
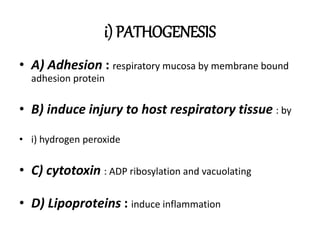
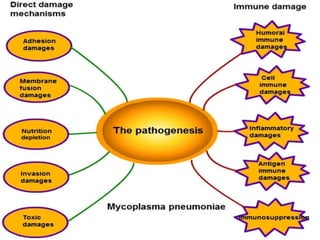
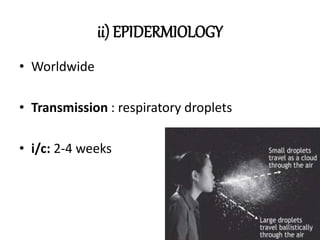
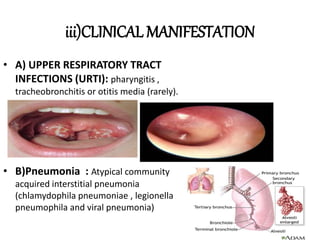
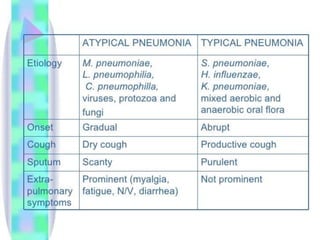
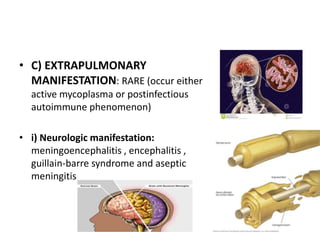
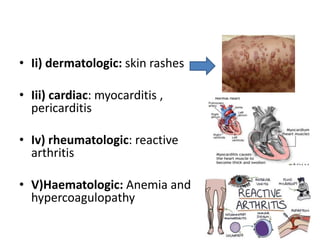
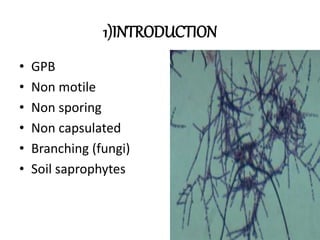
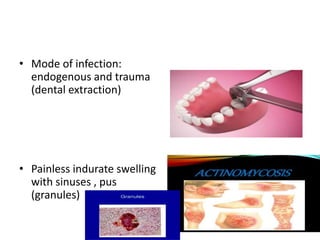
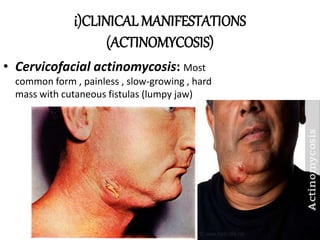
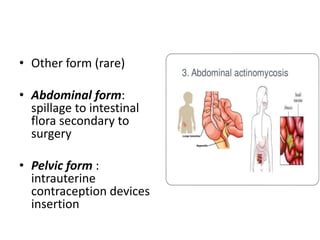
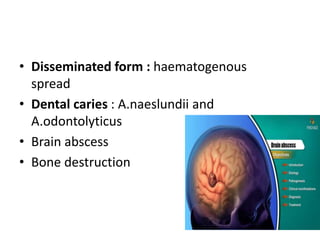
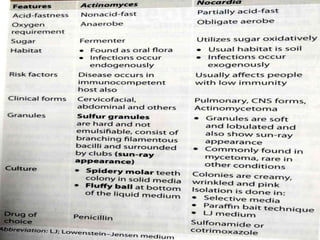
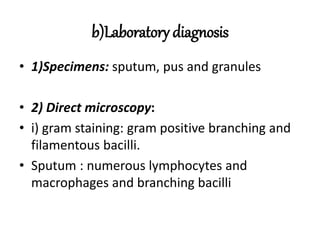
This document provides information on mycoplasma and actinomycetes. It discusses that mycoplasma are the smallest free-living microbes that lack cell walls and can cause respiratory infections like atypical pneumonia. Actinomyces are soil bacteria that can cause cervicofacial actinomycosis in humans through dental infections. Nocardia are acid-fast soil bacteria that can cause pulmonary or disseminated nocardiosis through inhalation or skin inoculation. Laboratory diagnosis involves culture, staining, biochemical testing and PCR for mycoplasma and actinomycetes. Treatment involves macrolides or other antibiotics.