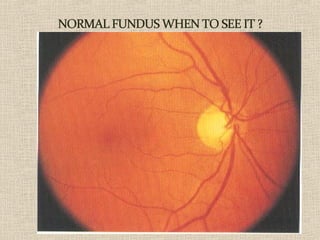
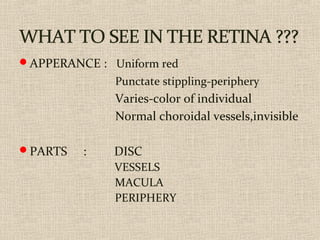
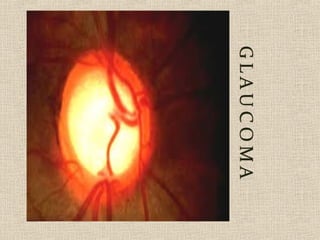
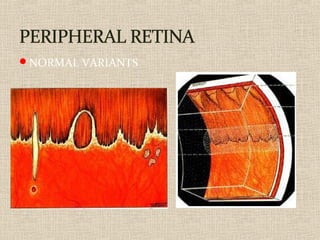
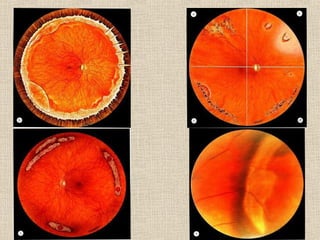
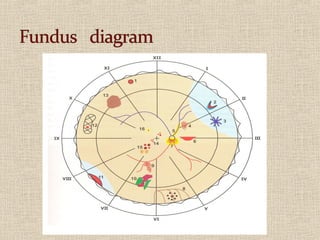
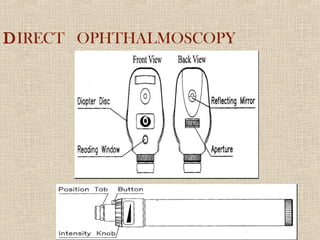
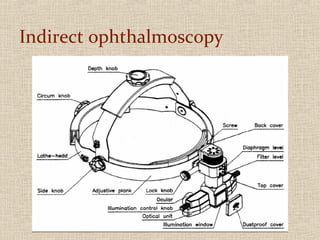
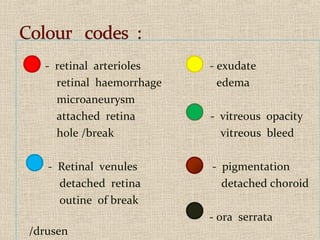
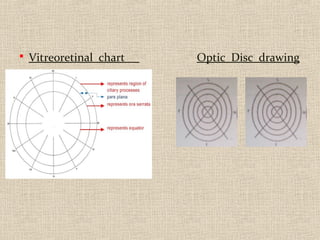
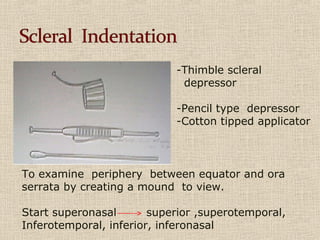
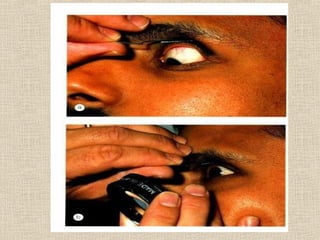
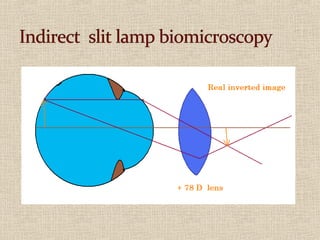
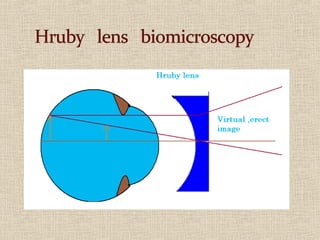
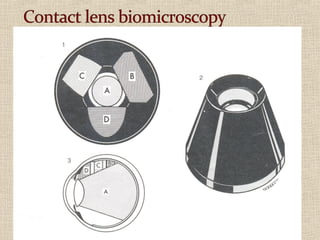
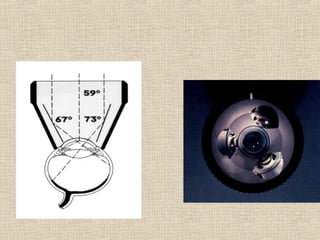
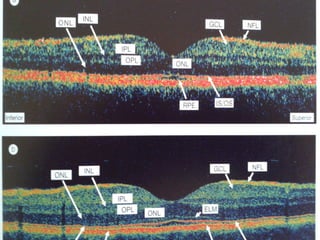
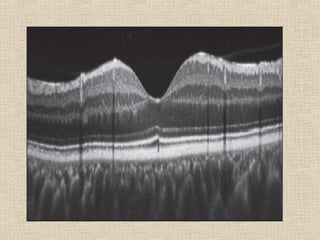
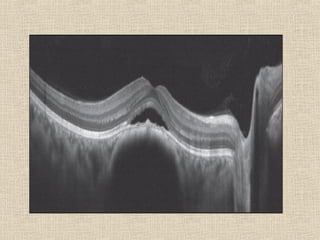
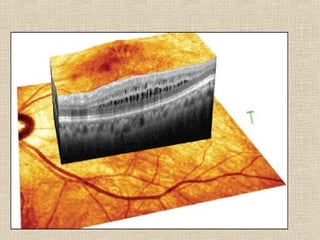
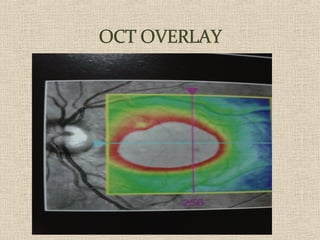
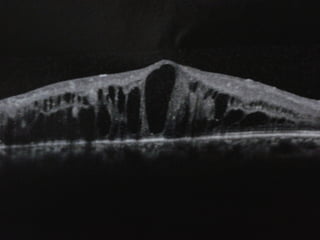
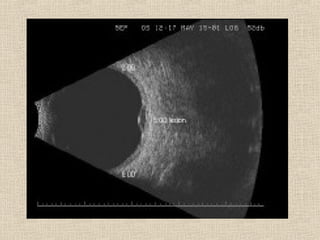
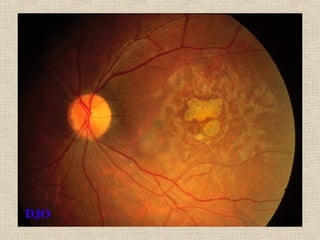
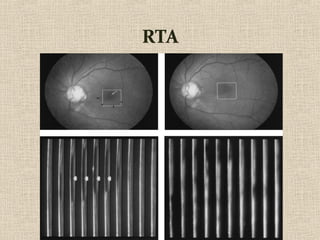
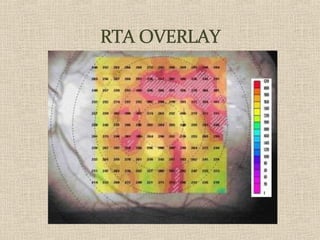
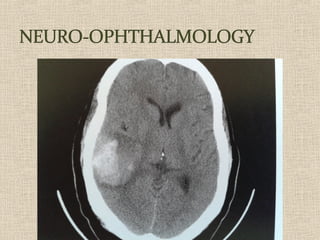
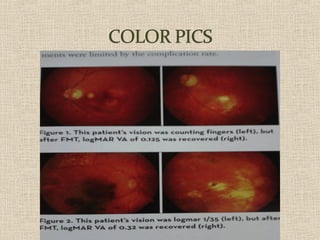
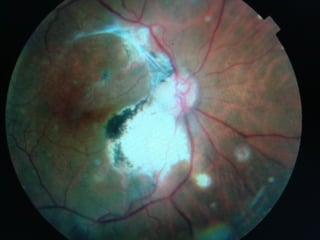
This document discusses fundus examination and its importance in ophthalmology. Fundus examination can detect signs of circulatory, metabolic, and neurological disorders. It is used to identify and locate retinal and optic nerve defects caused by eye disease or trauma, examine the extent of abnormalities to plan treatment, and evaluate treatment success. The document describes different methods of performing fundus examination including direct ophthalmoscopy, indirect ophthalmoscopy, and indirect slit lamp biomicroscopy. It provides examples of common fundus findings and conditions that can be assessed via this examination.