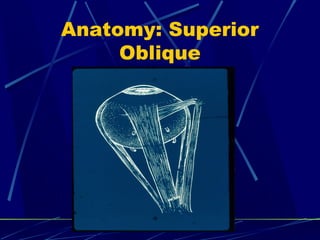
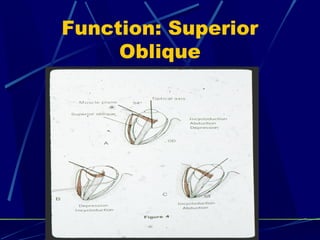
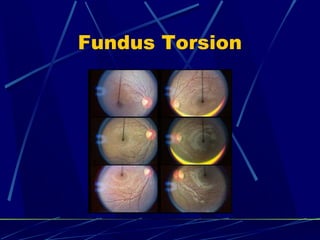
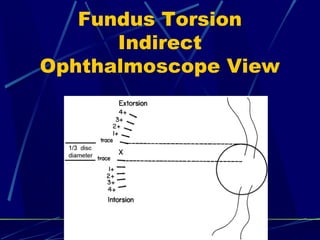
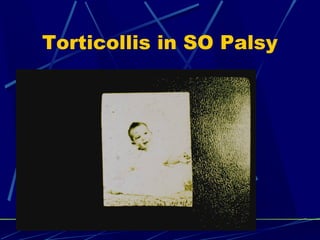
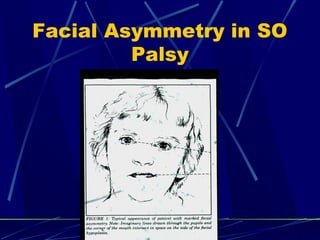
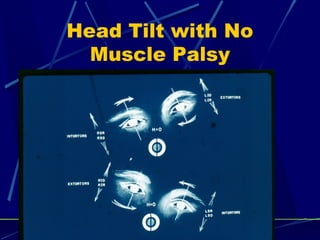
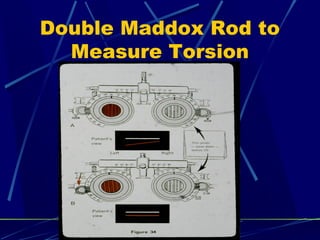
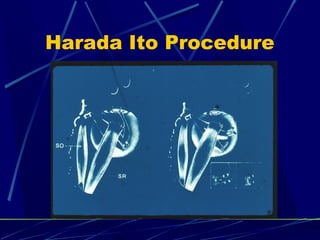
This document discusses the diagnosis and management of superior oblique palsy. It begins by describing the anatomy and function of the superior oblique muscle. Superior oblique palsy can result in hypertropia, excyclotorsion, and esotropia that are greater in certain gazes. Causes may be congenital or acquired from trauma or vascular issues. Diagnosis involves evaluating eye movements, diplopia, and head tilt. Non-surgical treatment includes patching or prisms while surgery involves weakening the antagonist inferior oblique muscle or tucking the superior oblique tendon. The goal of treatment is to expand the field of single vision while minimizing complications.