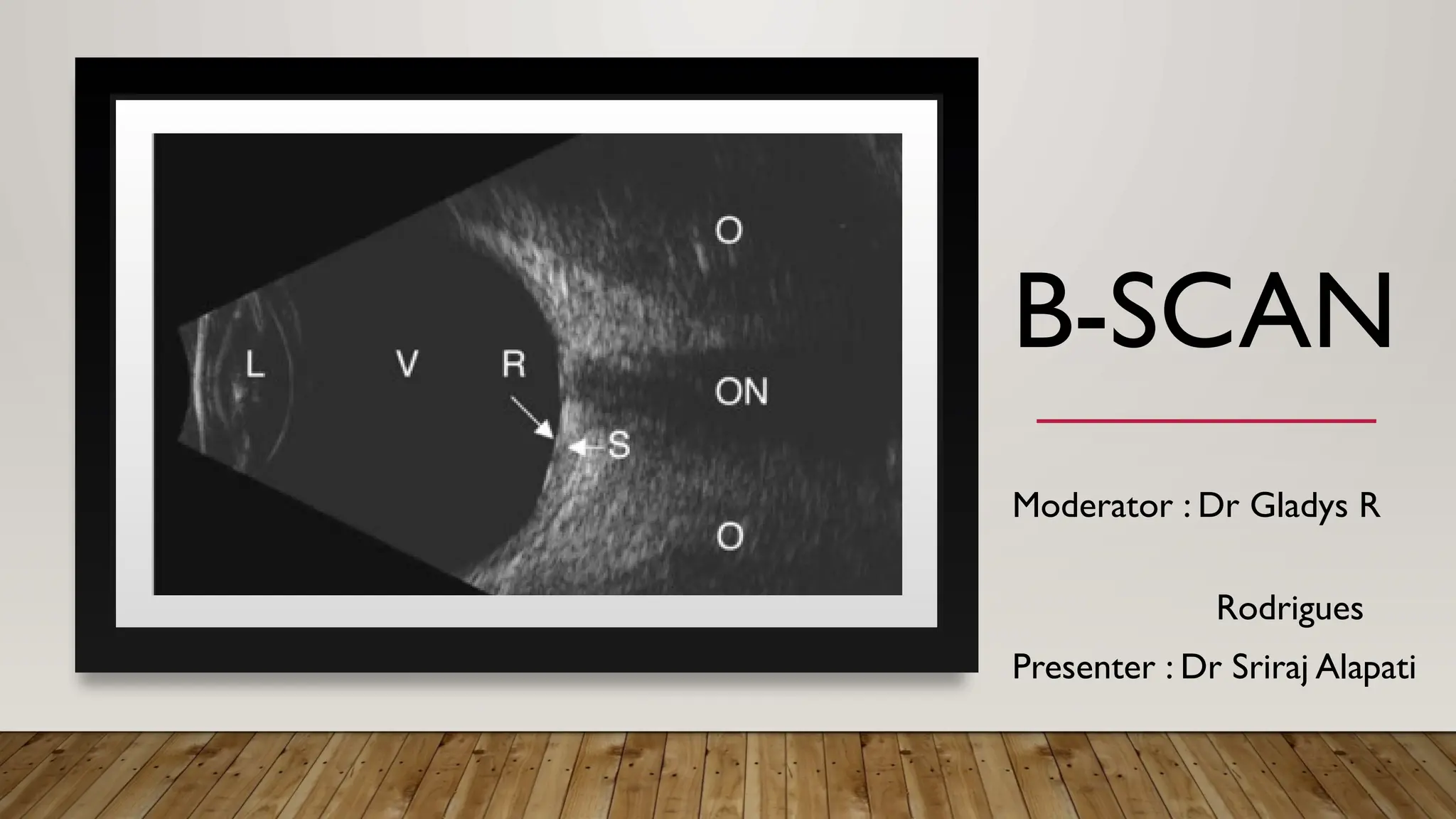
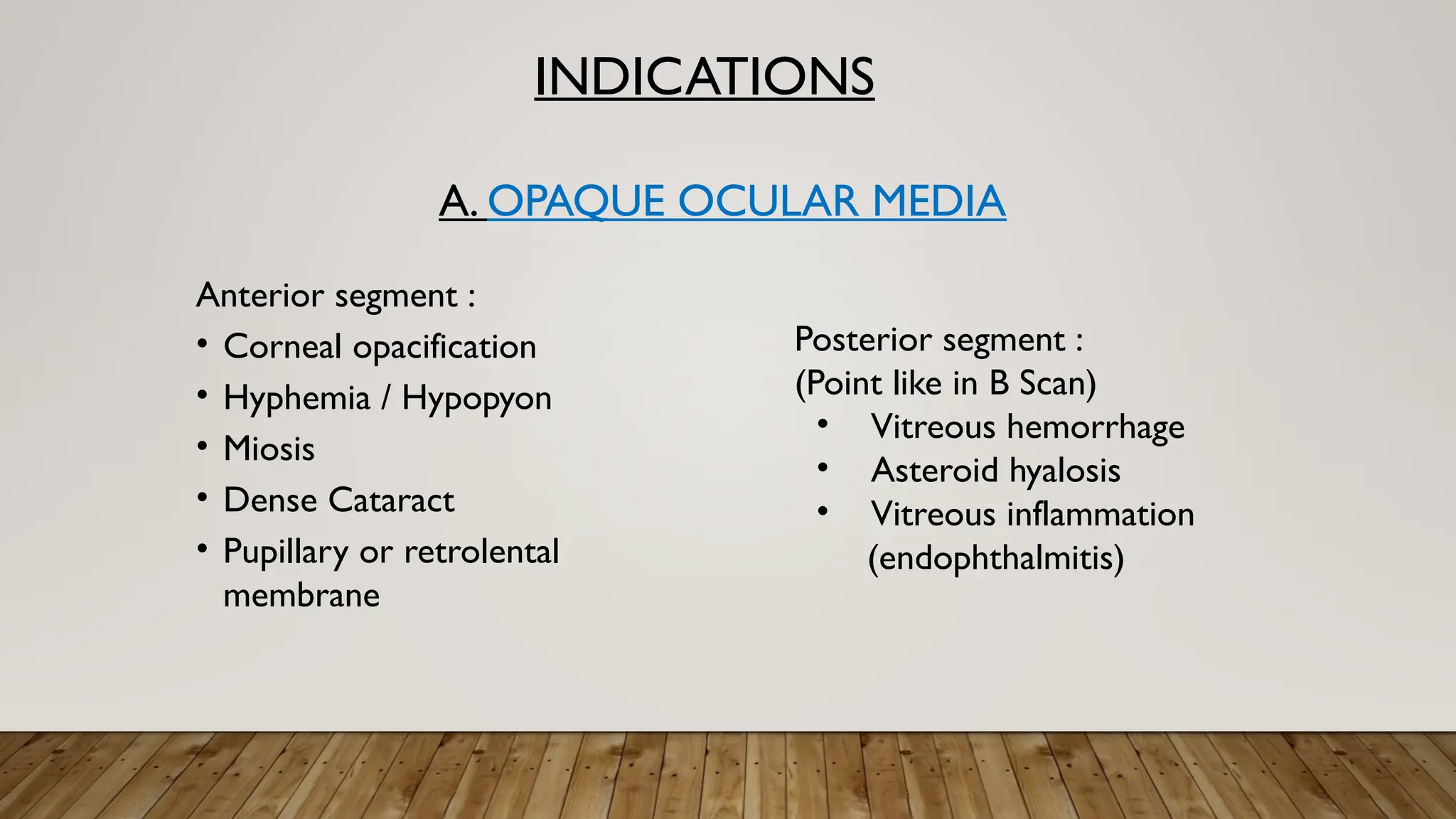
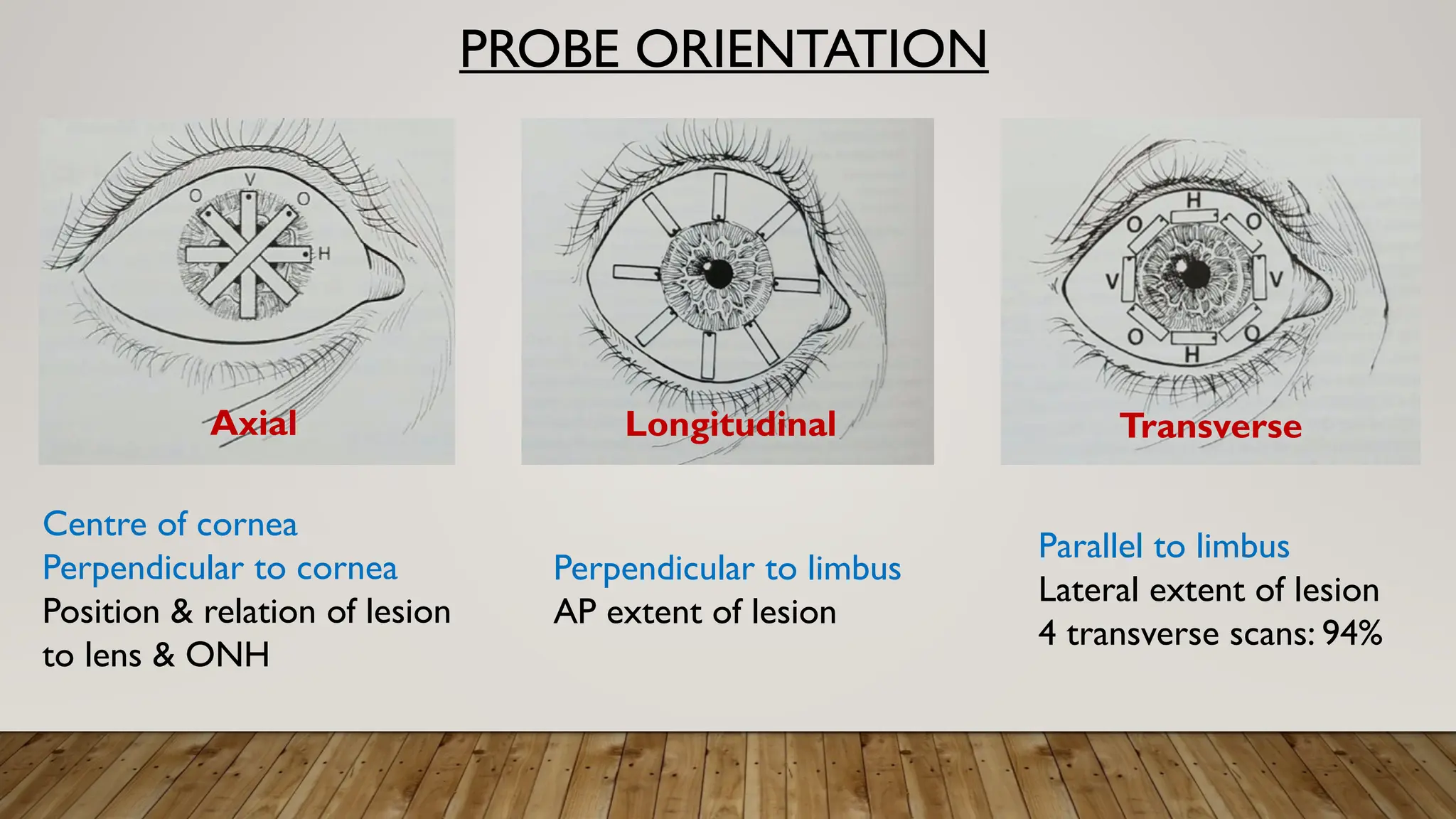
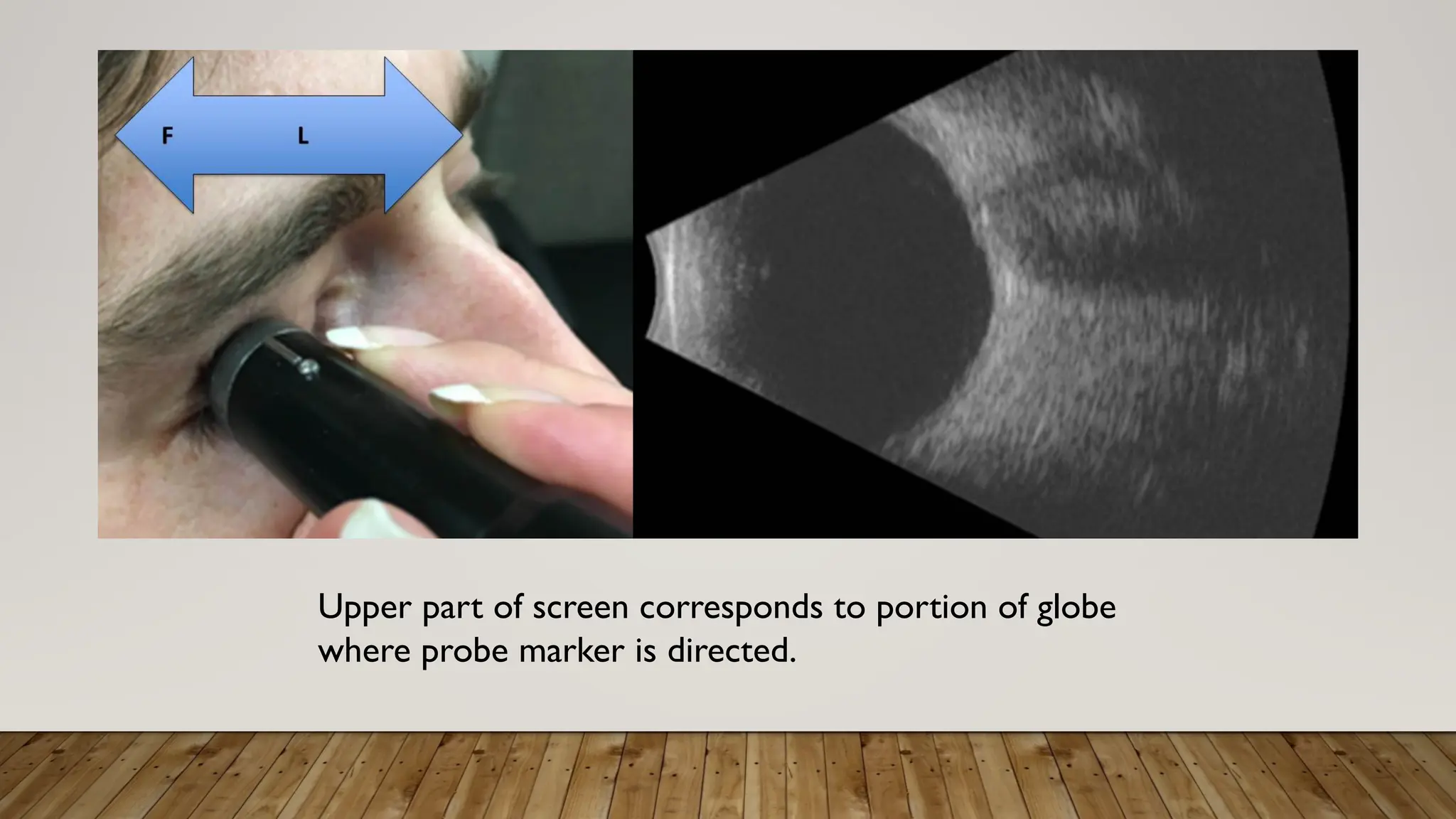
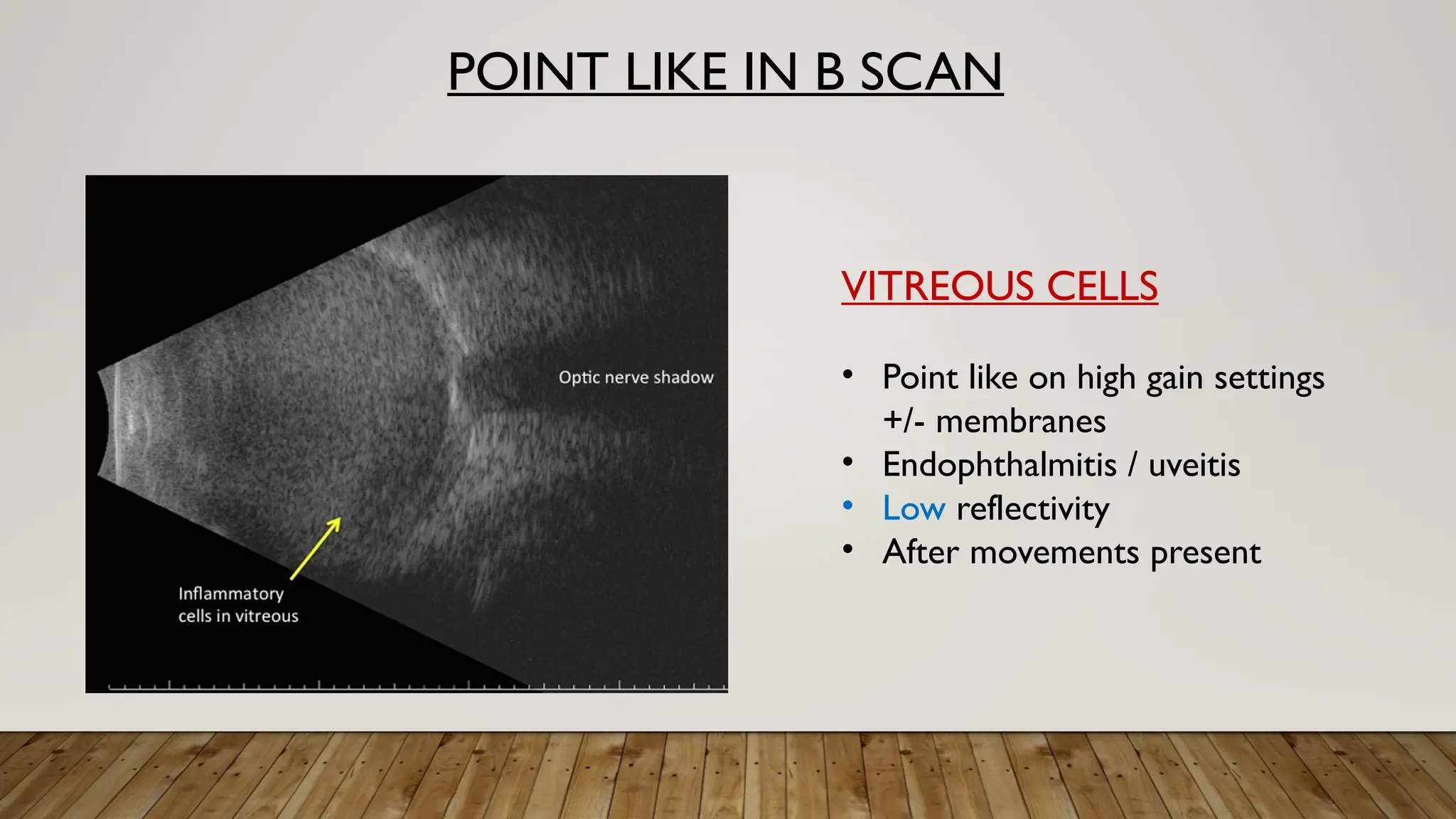
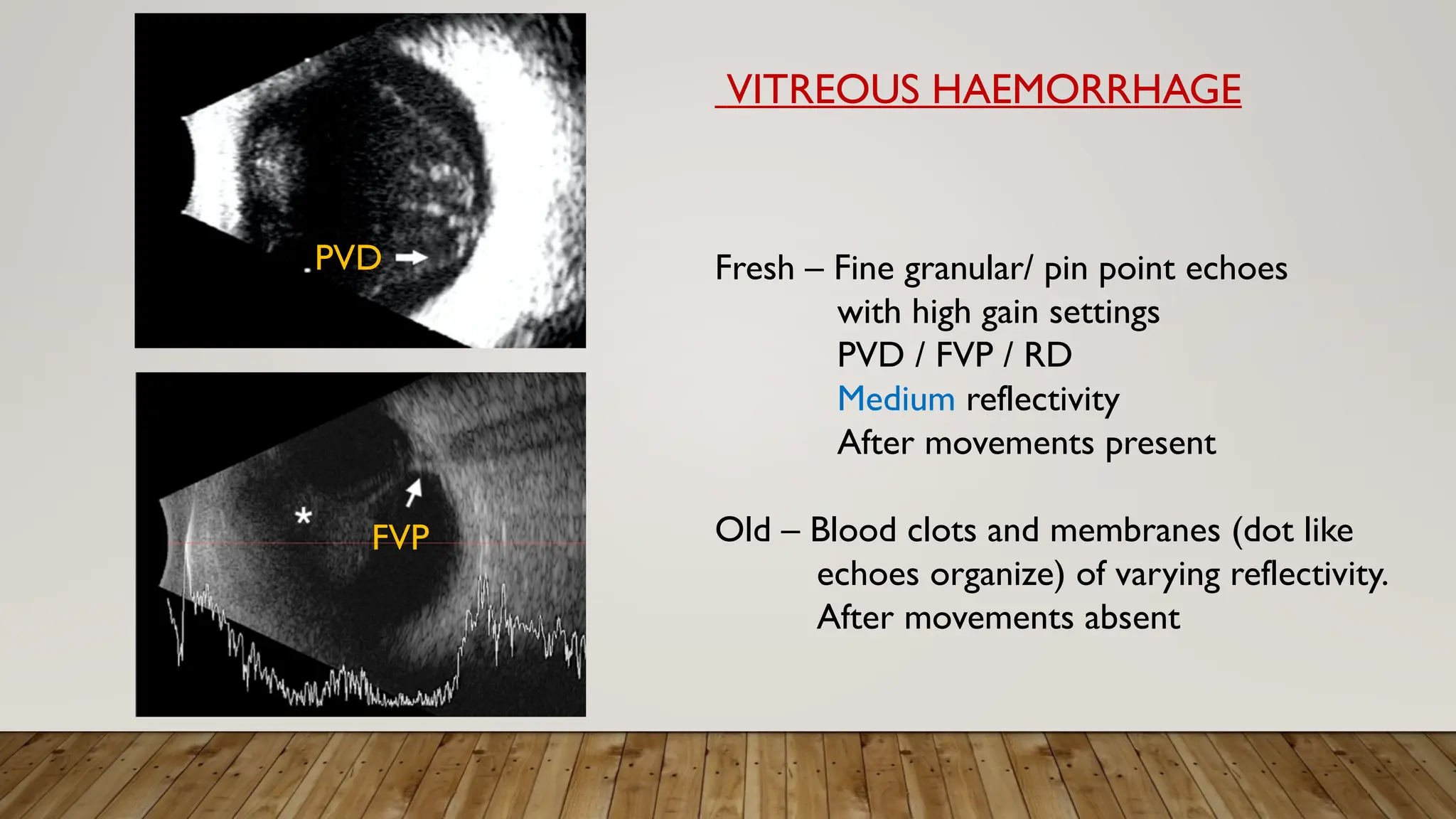
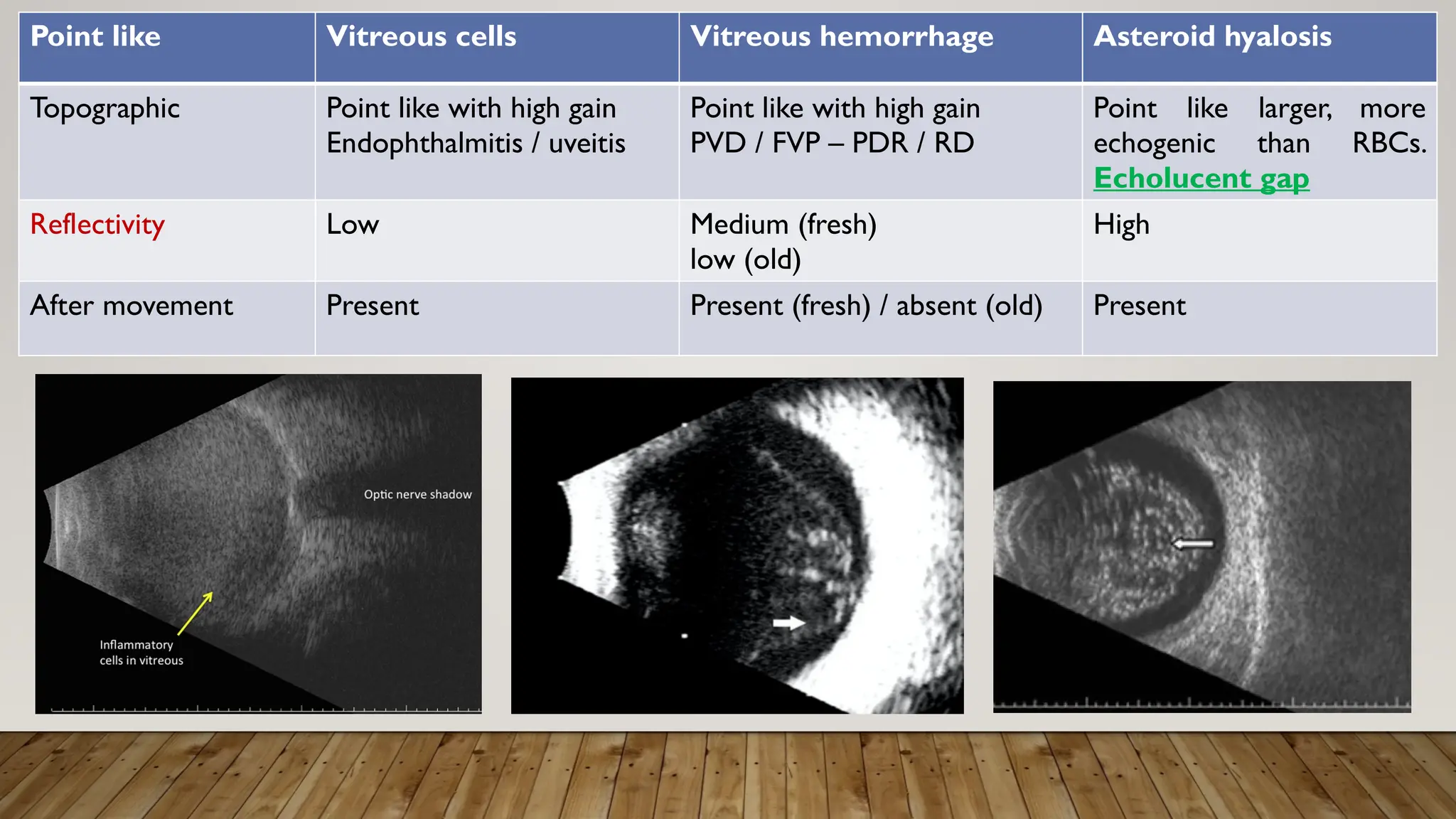
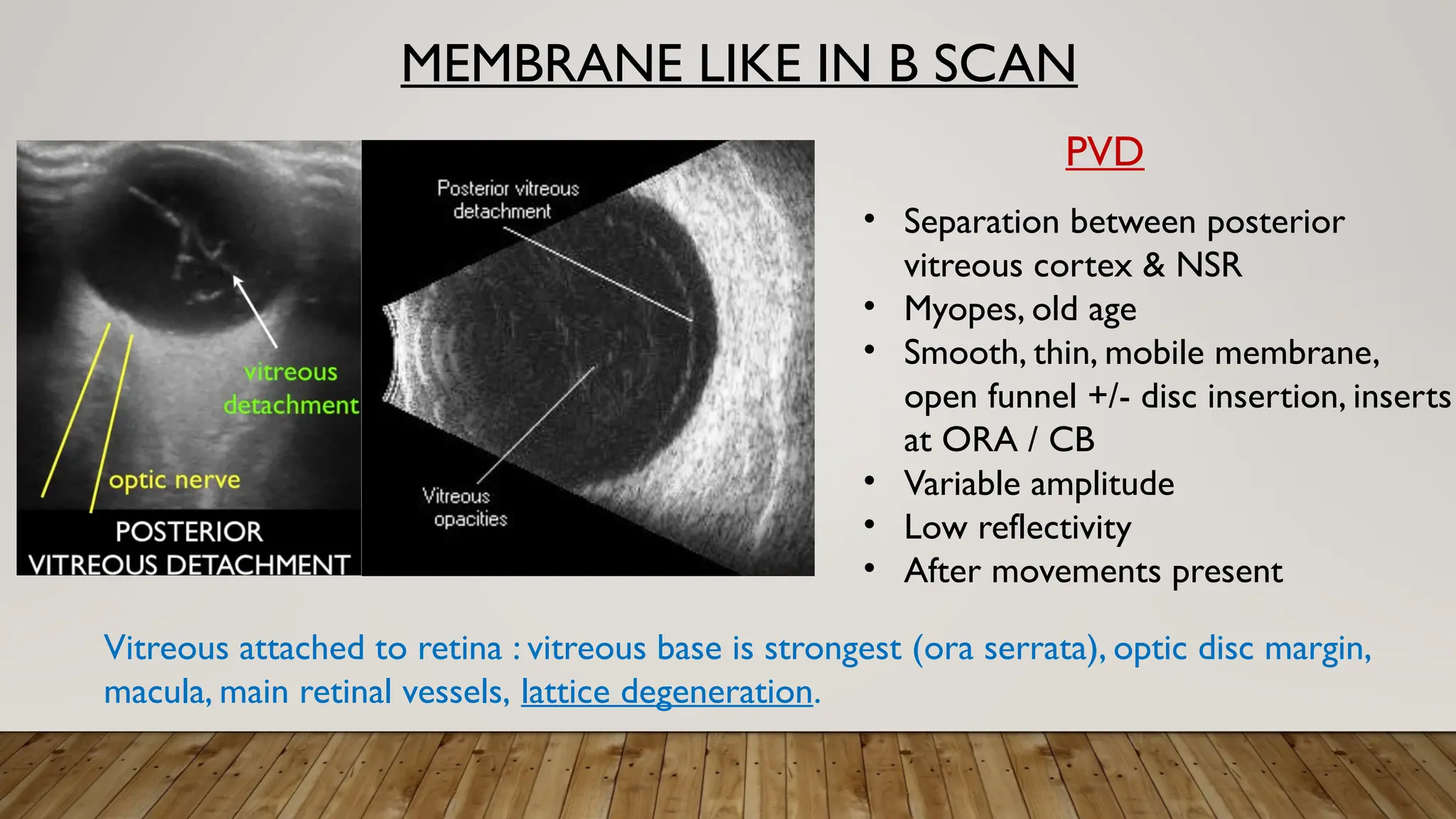
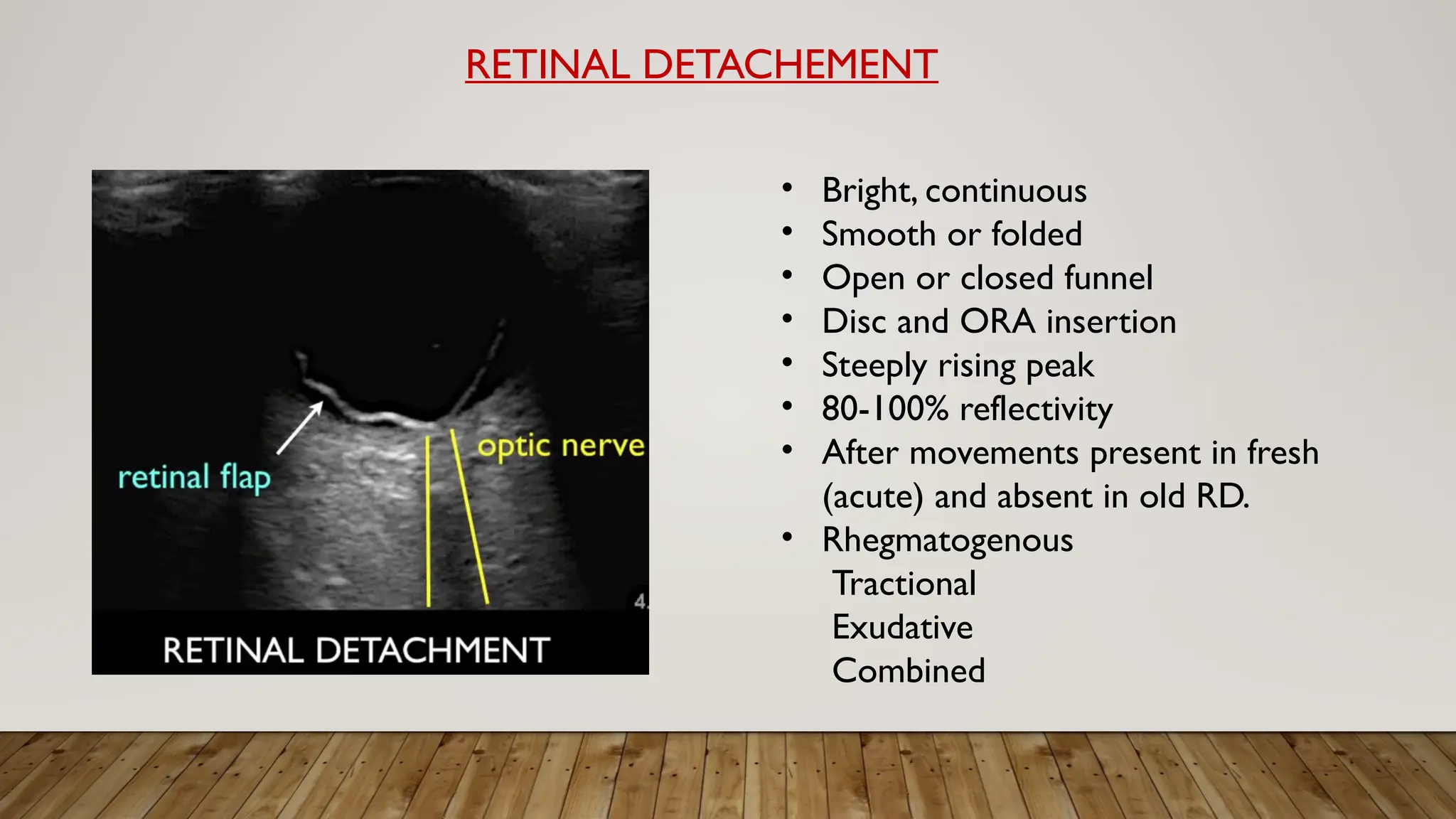
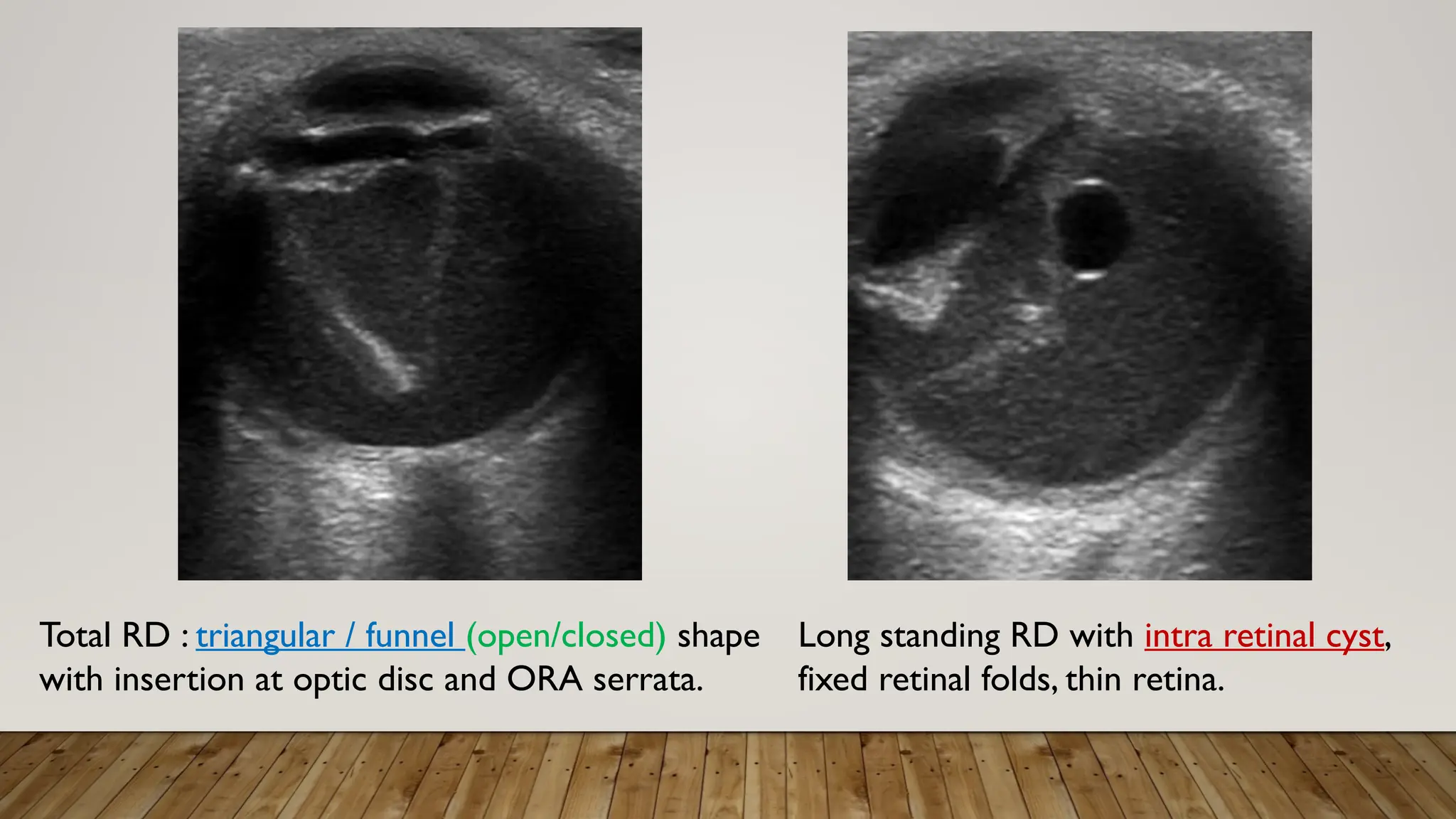
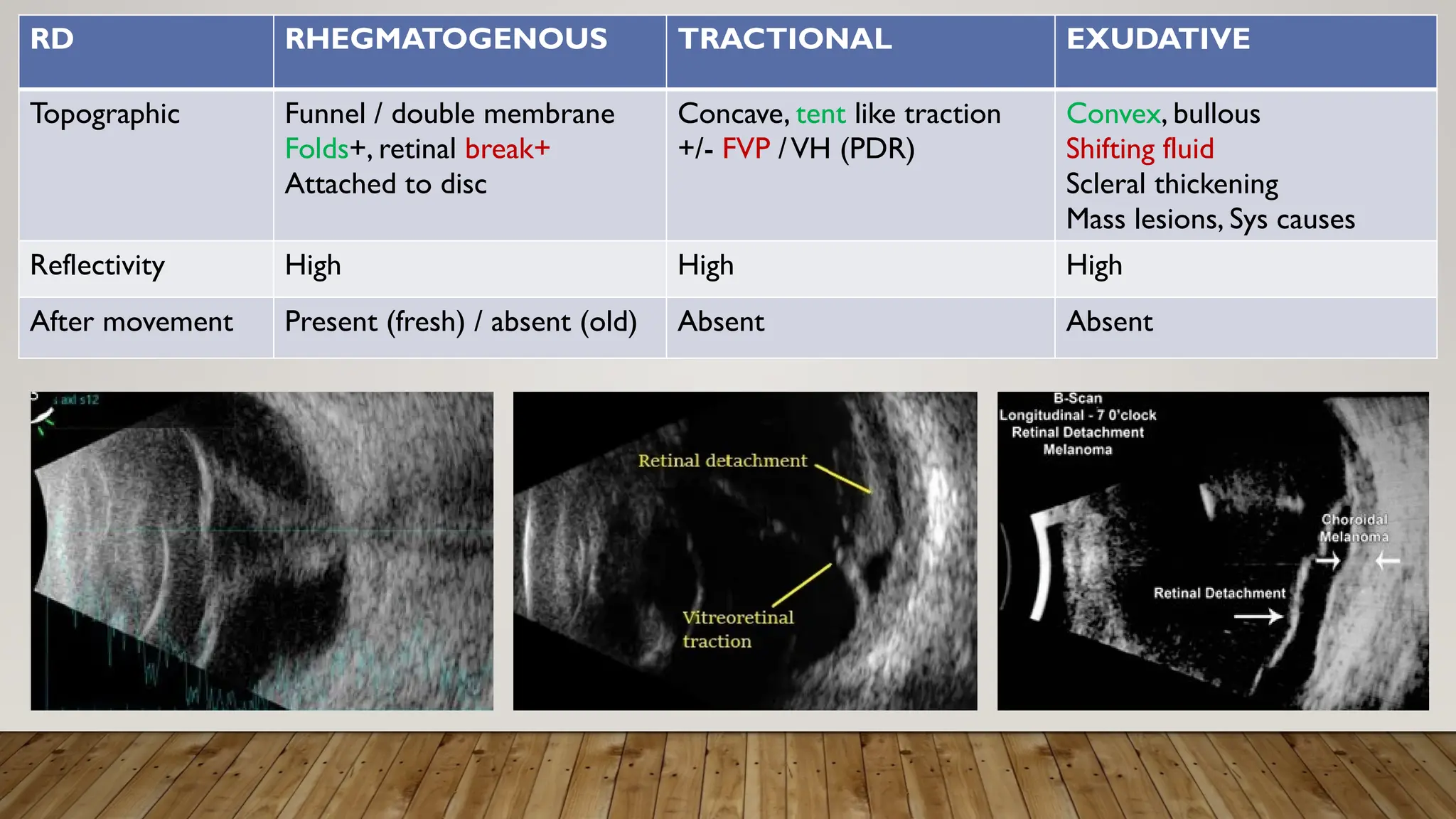
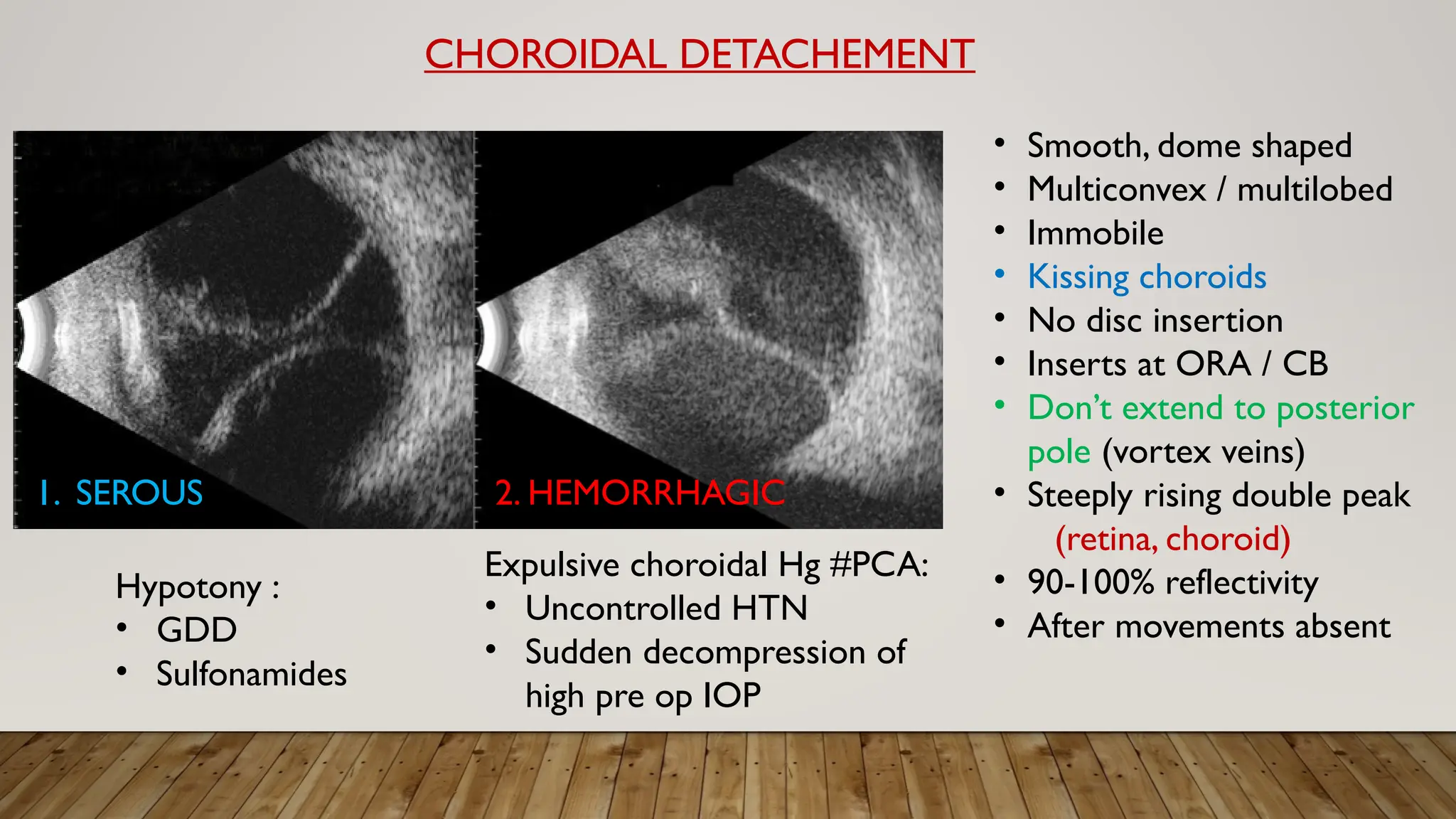
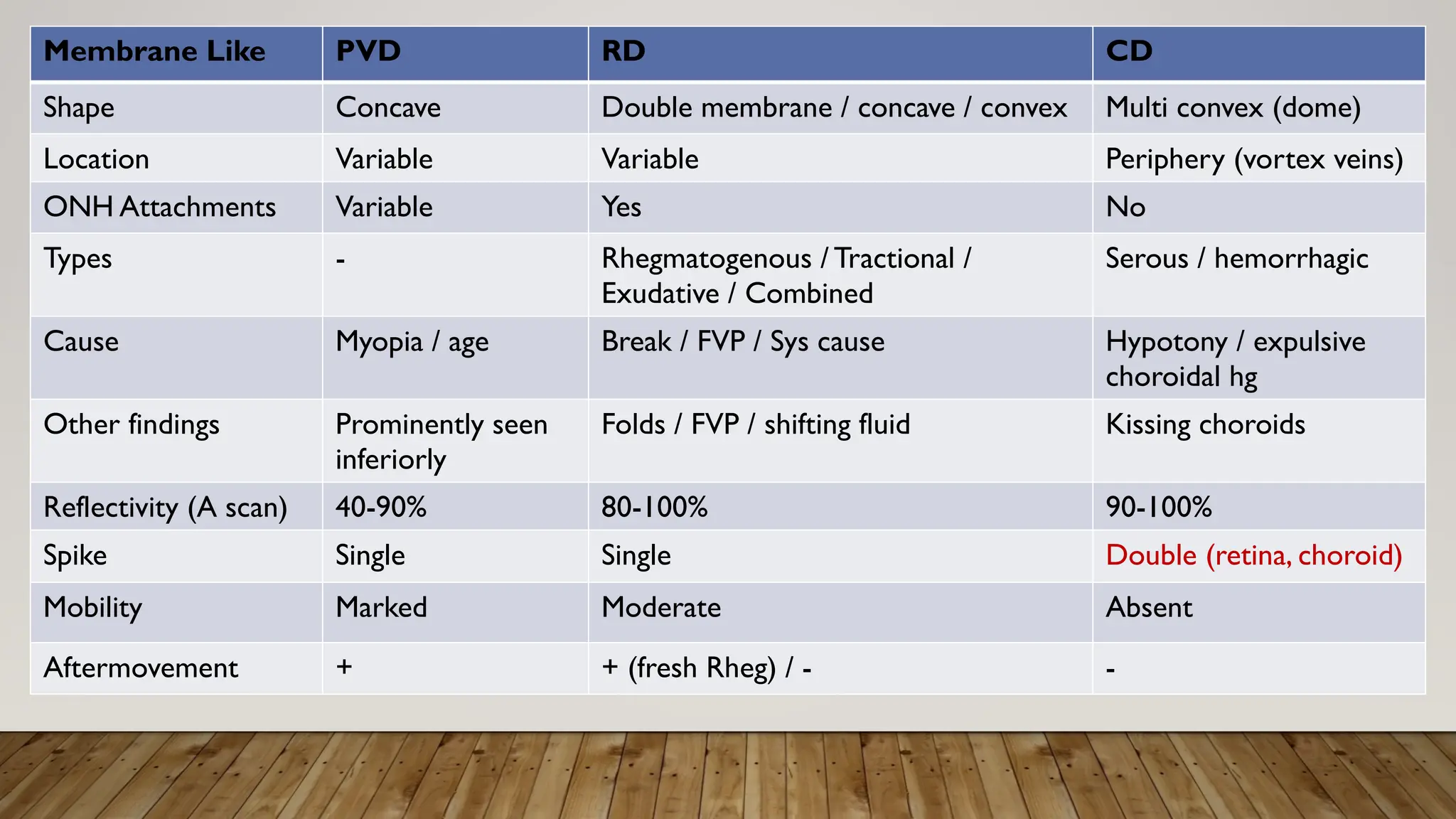
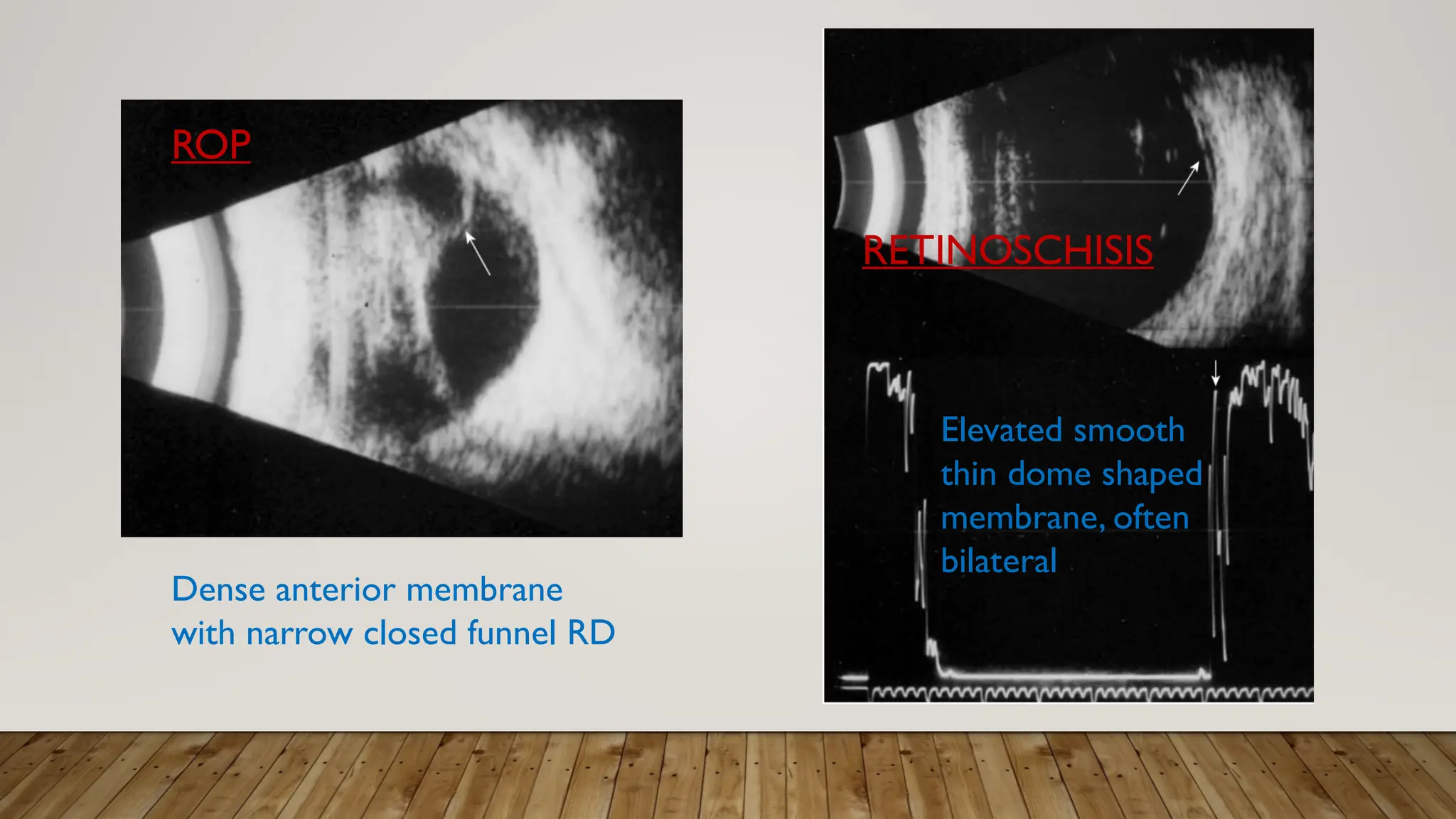
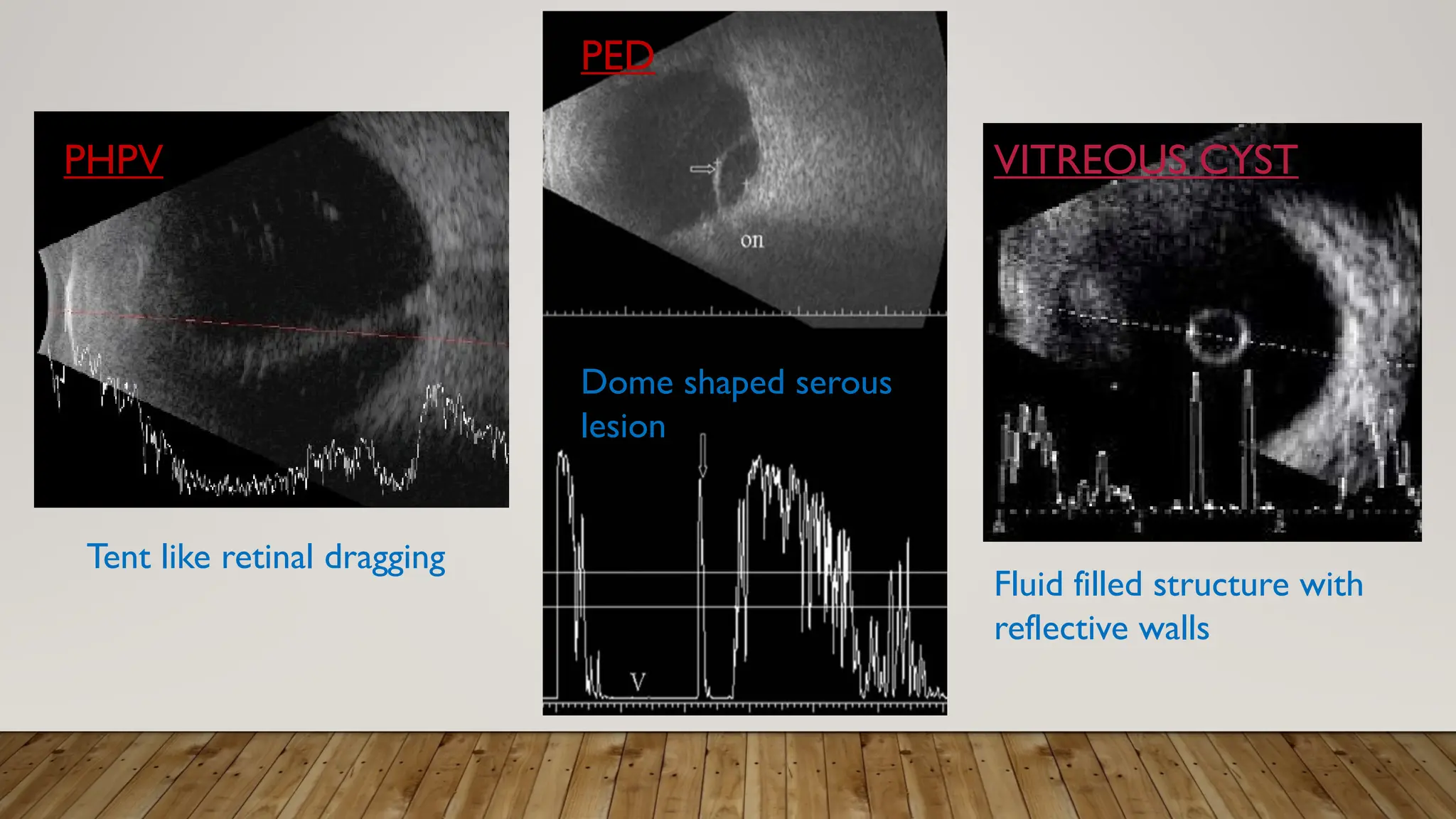
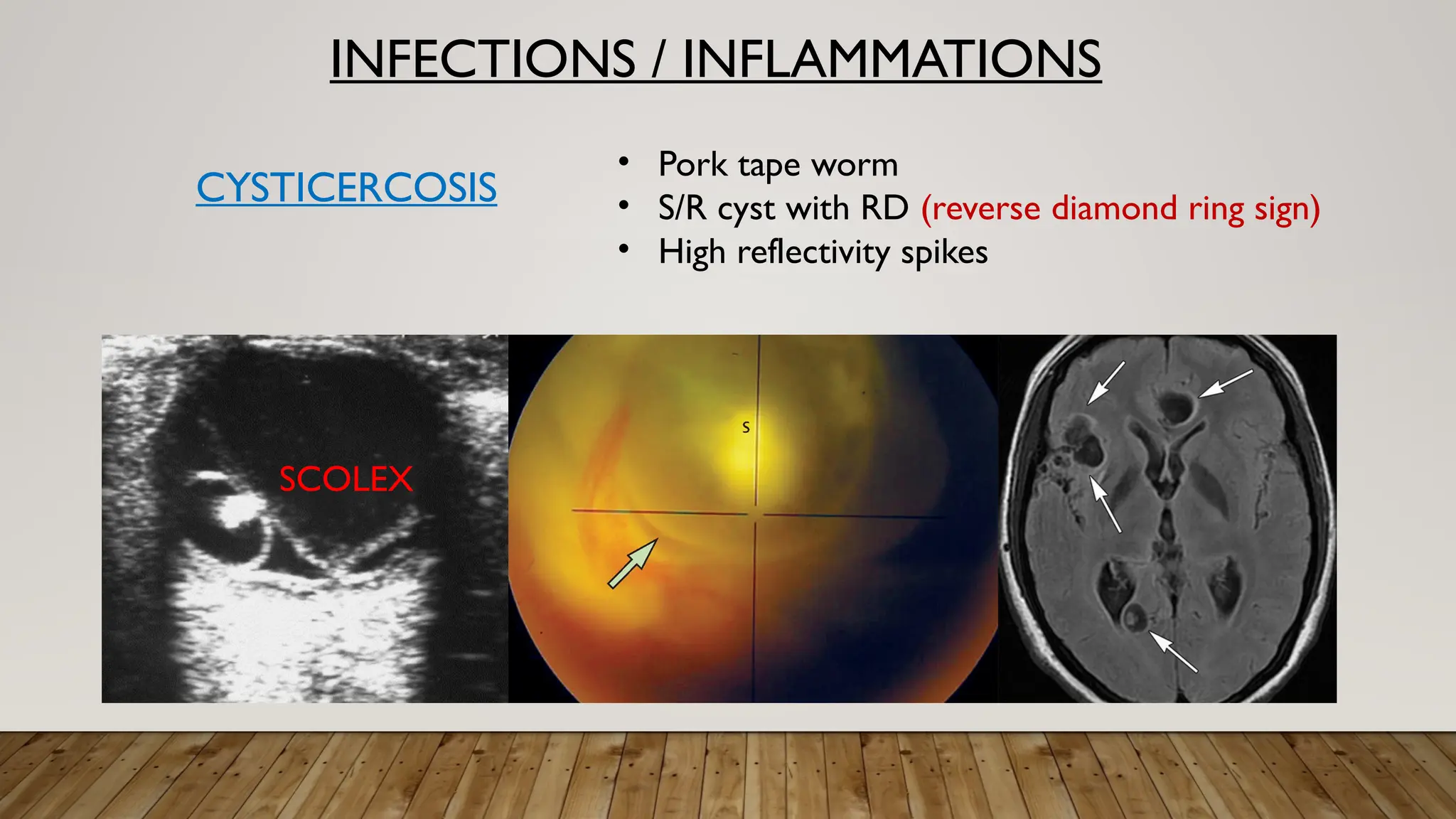
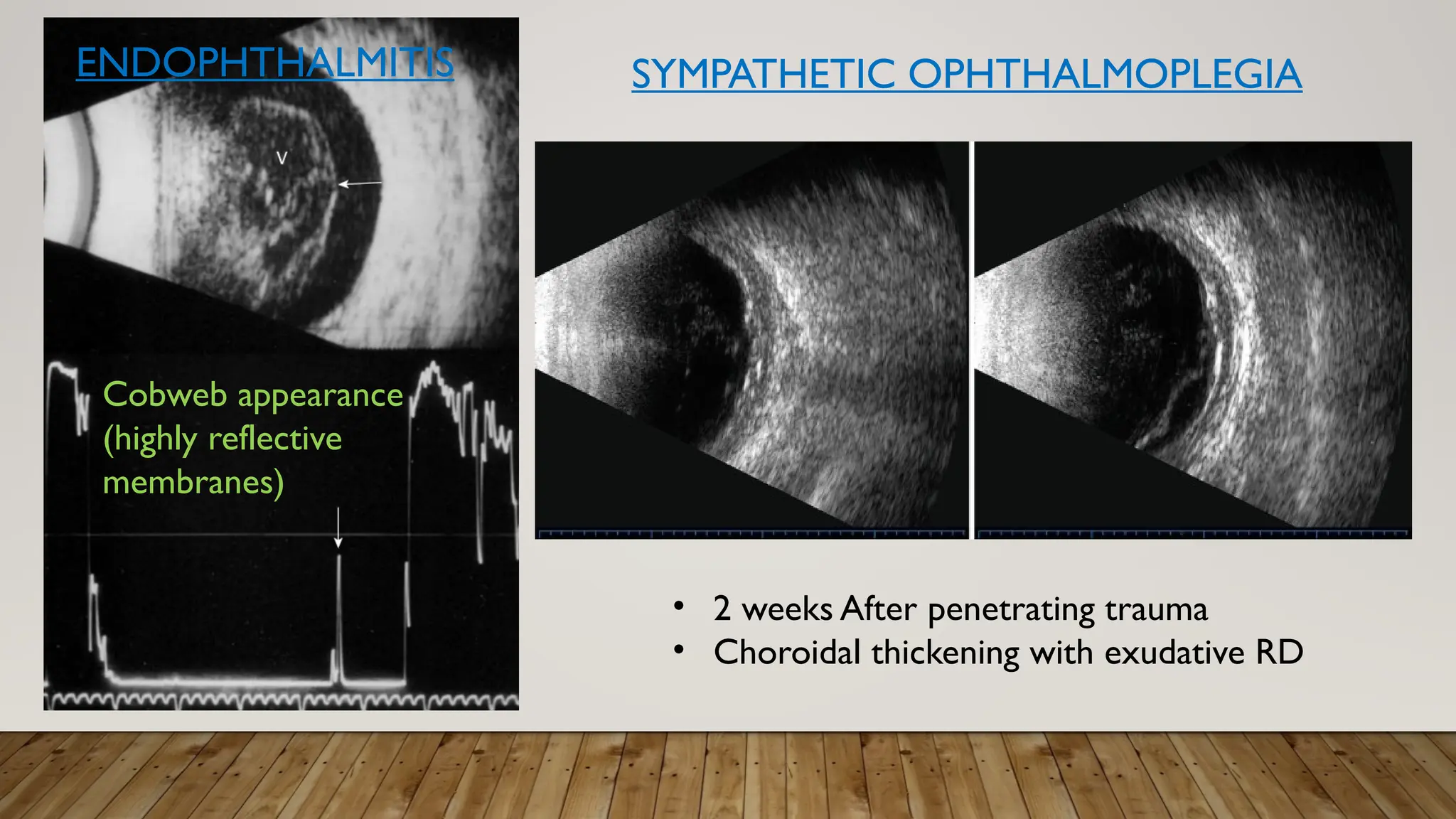
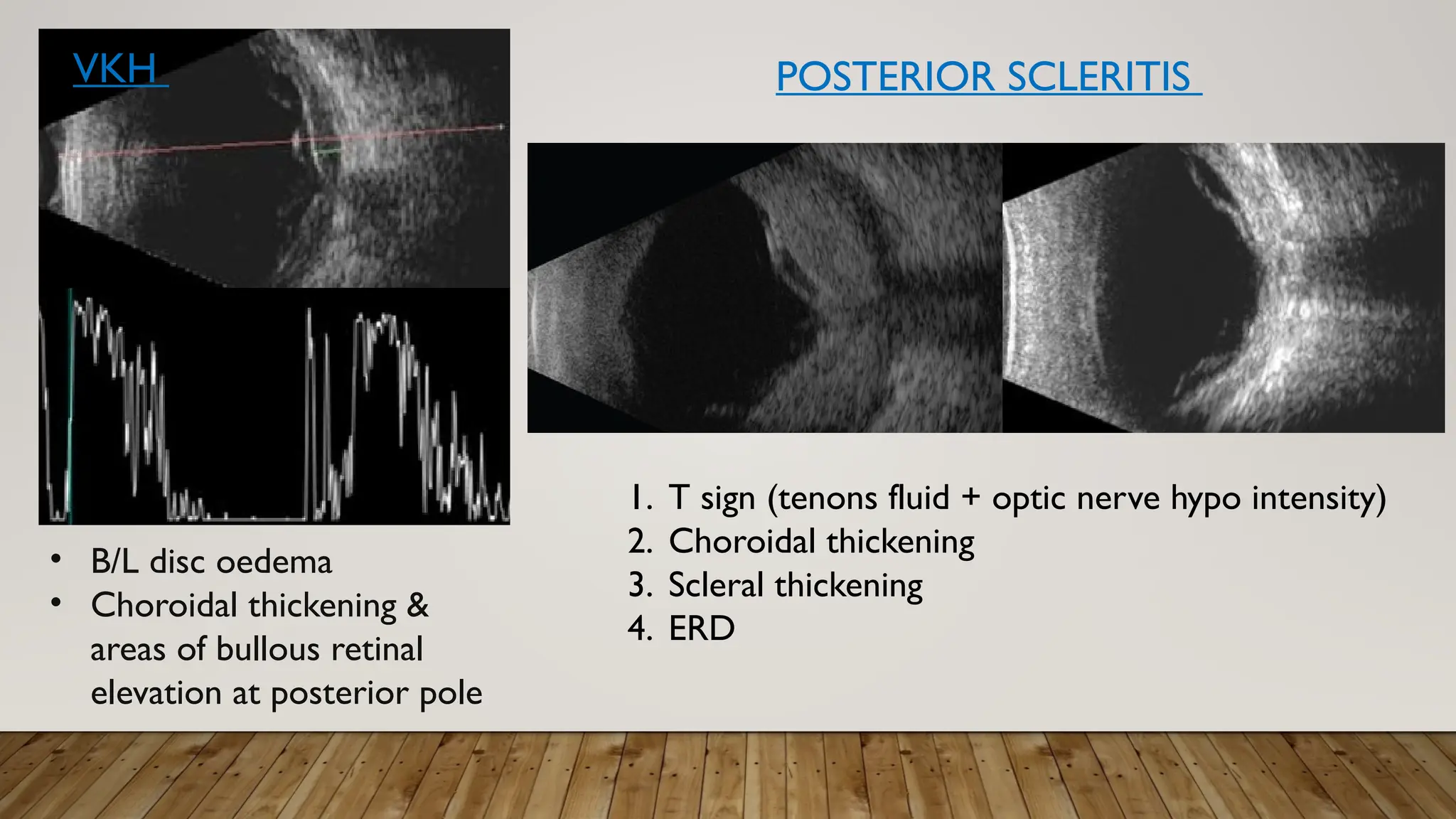
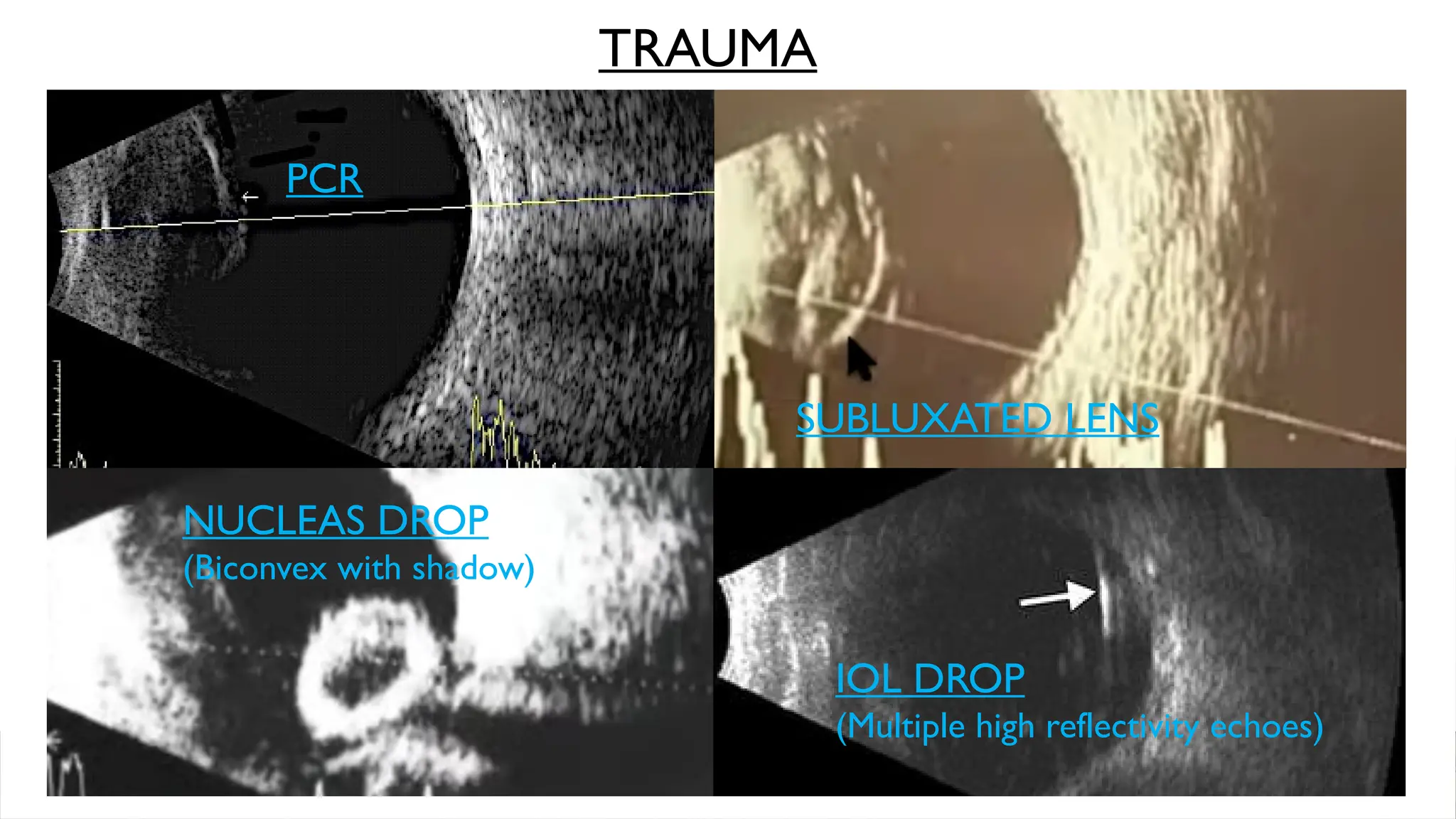
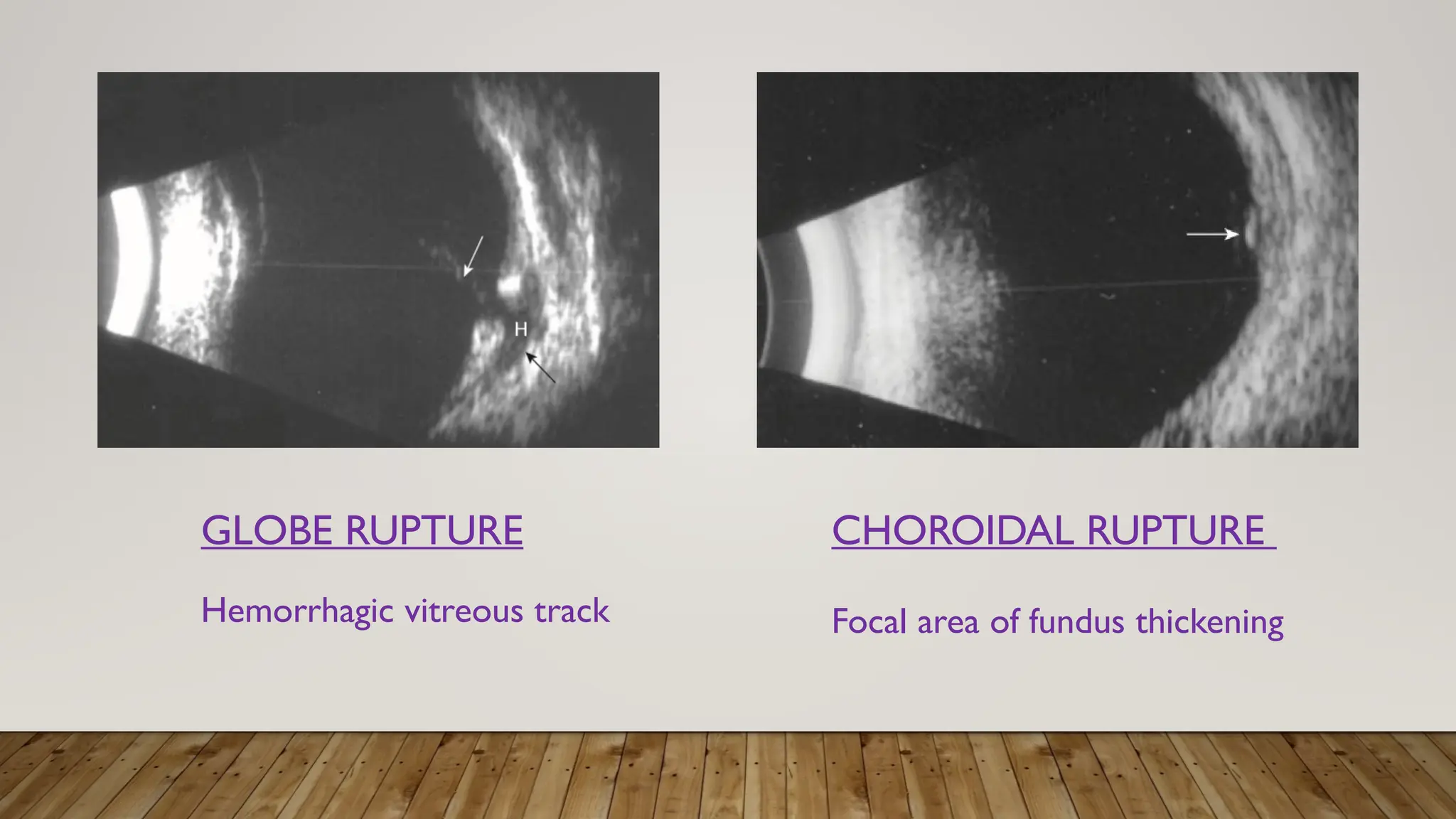
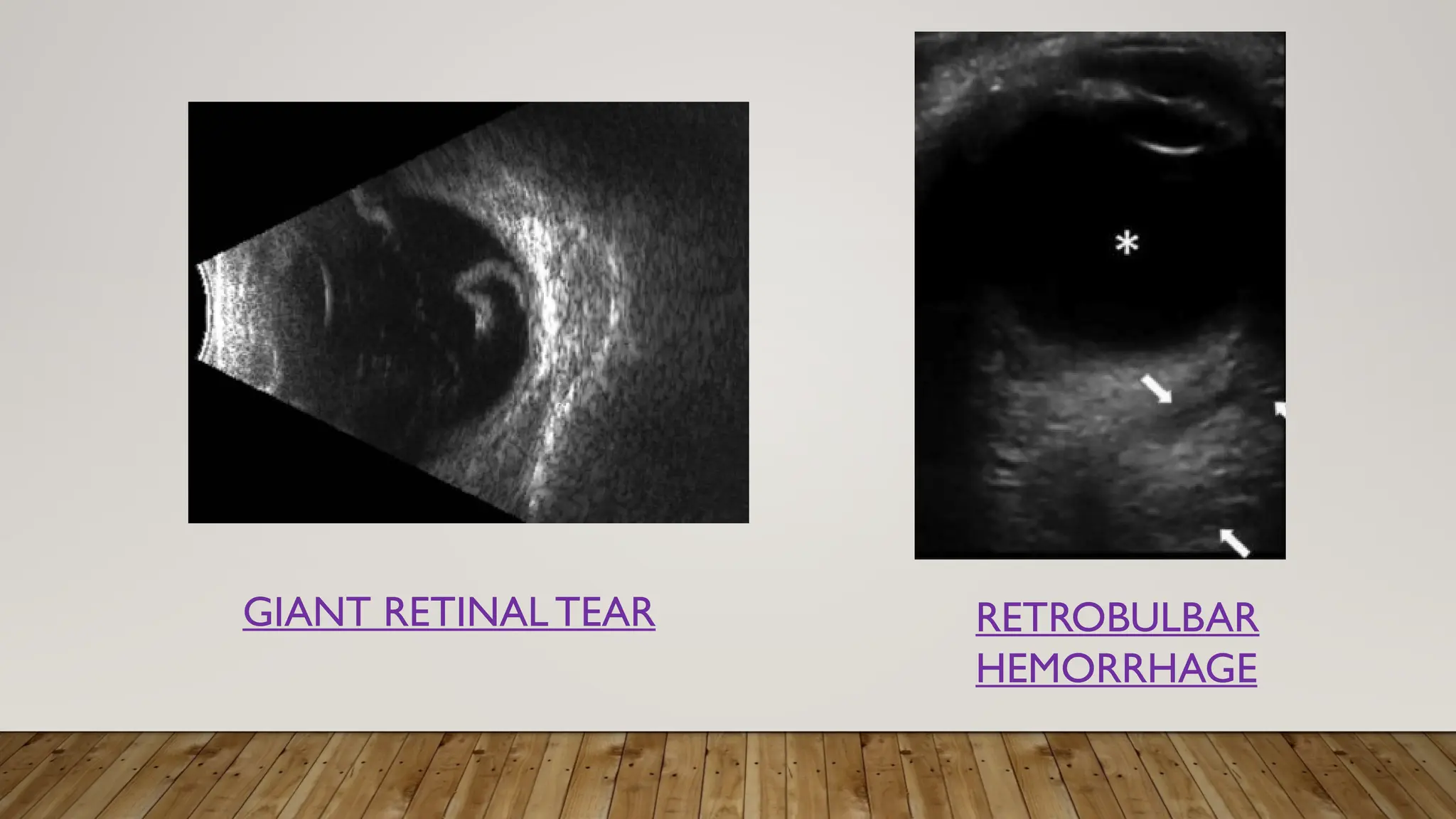
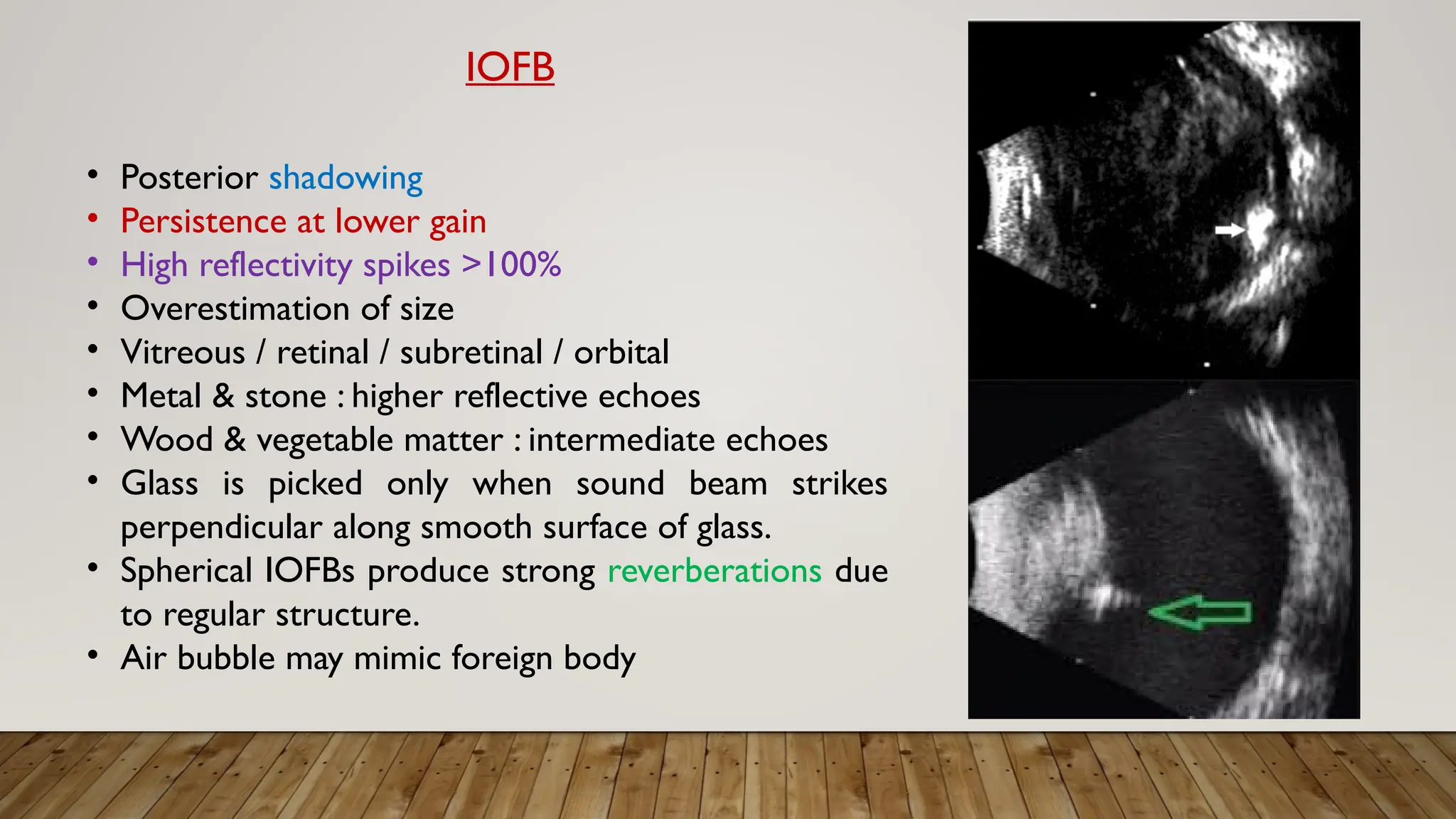
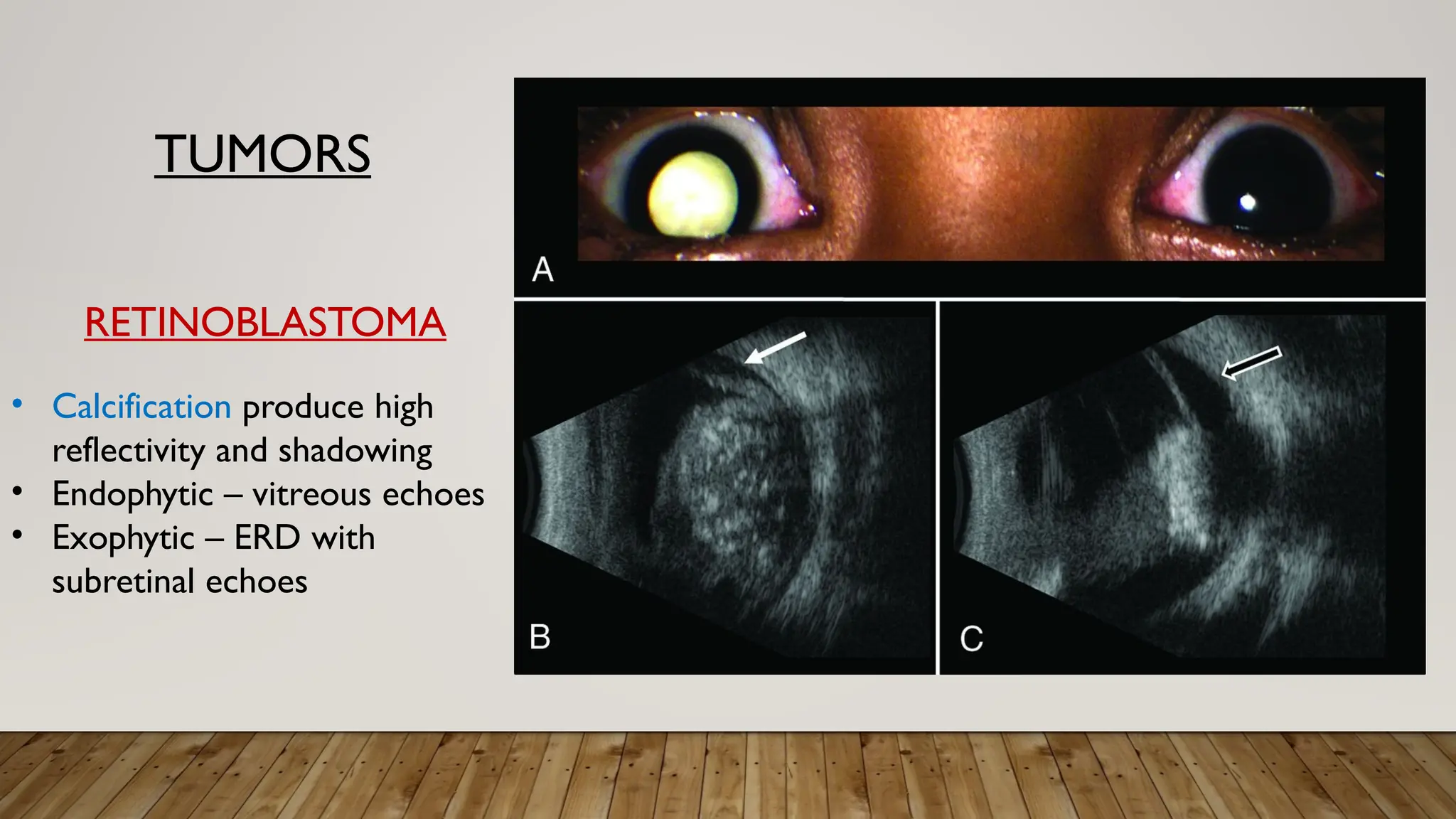
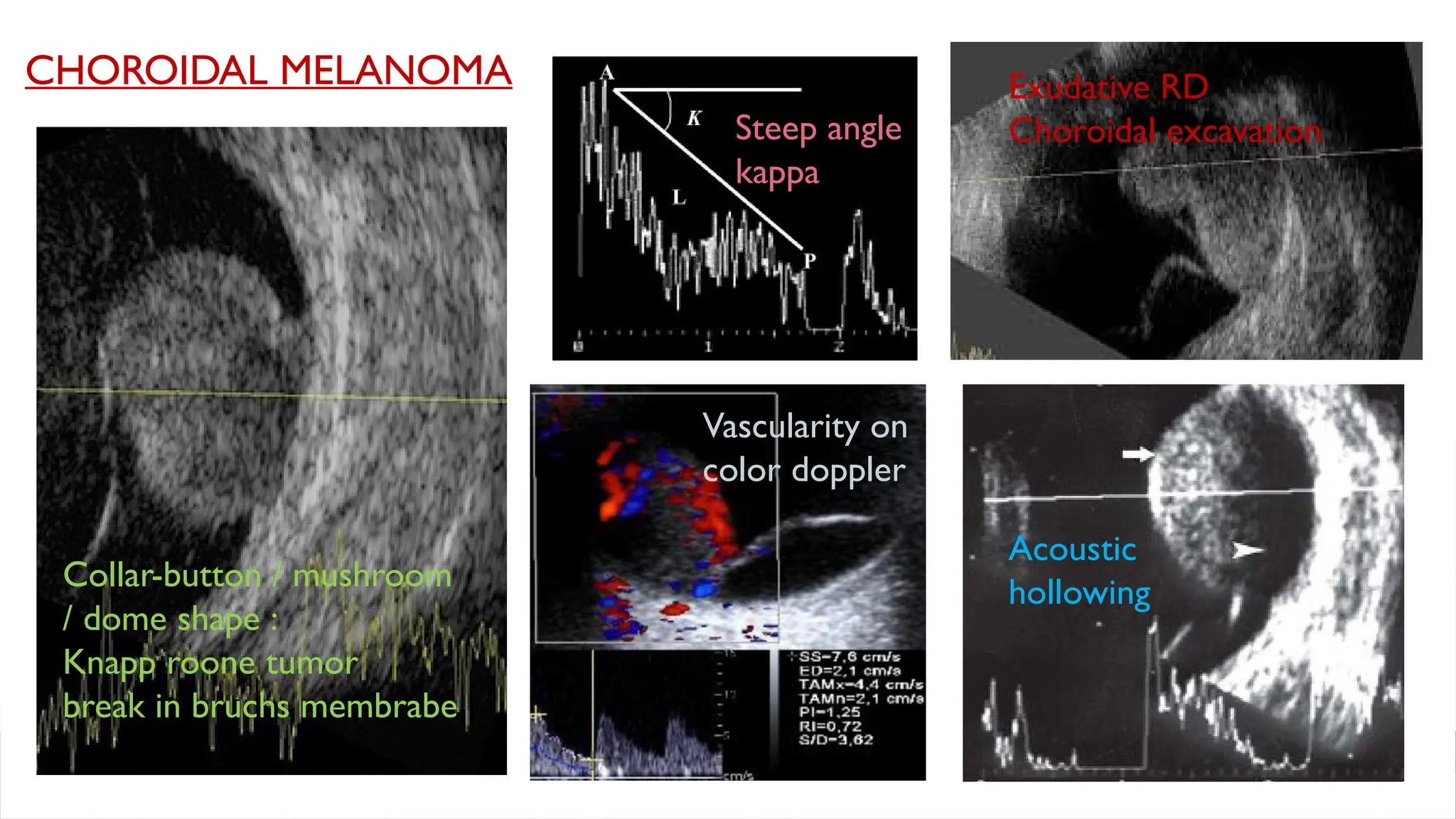
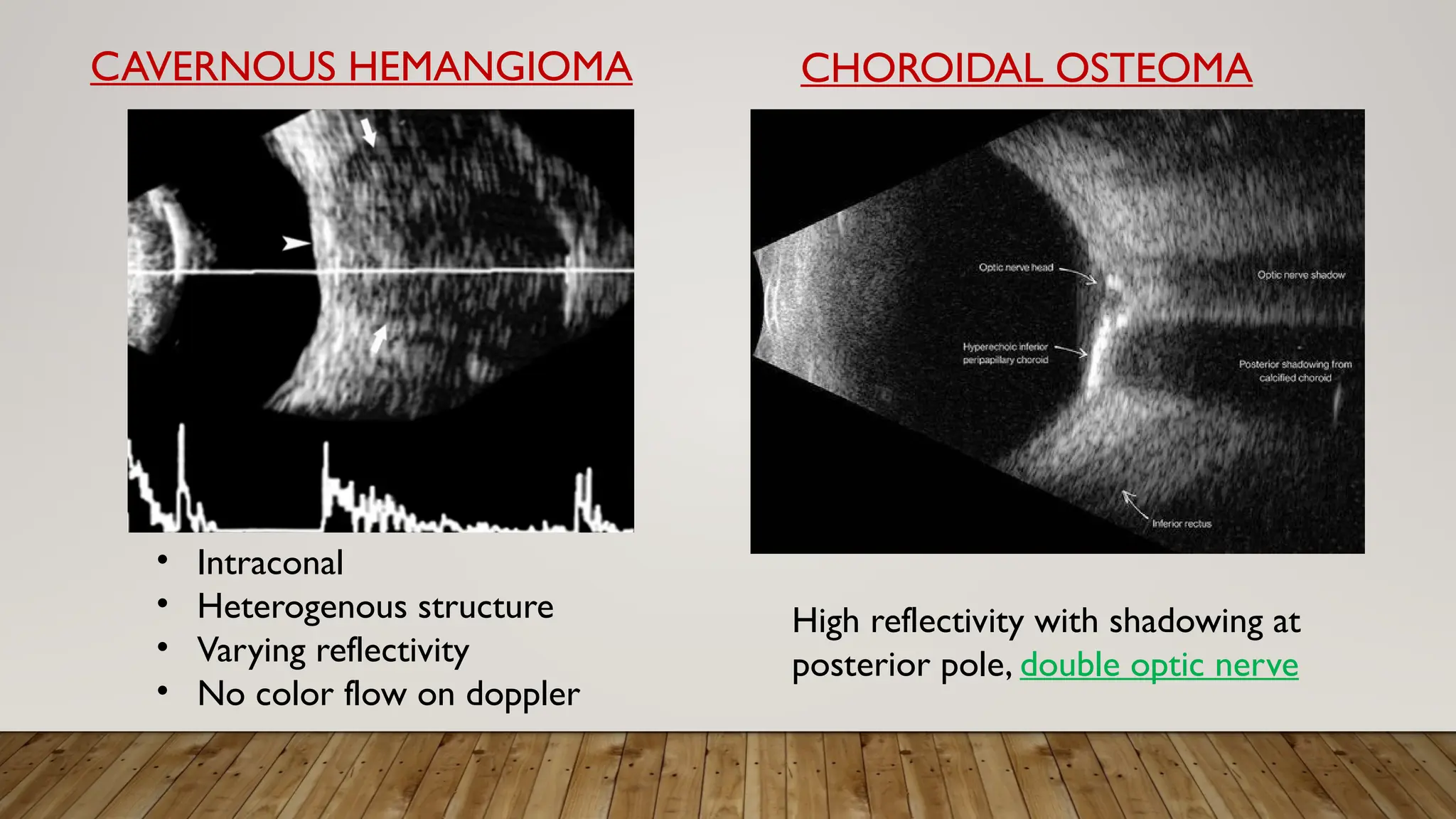
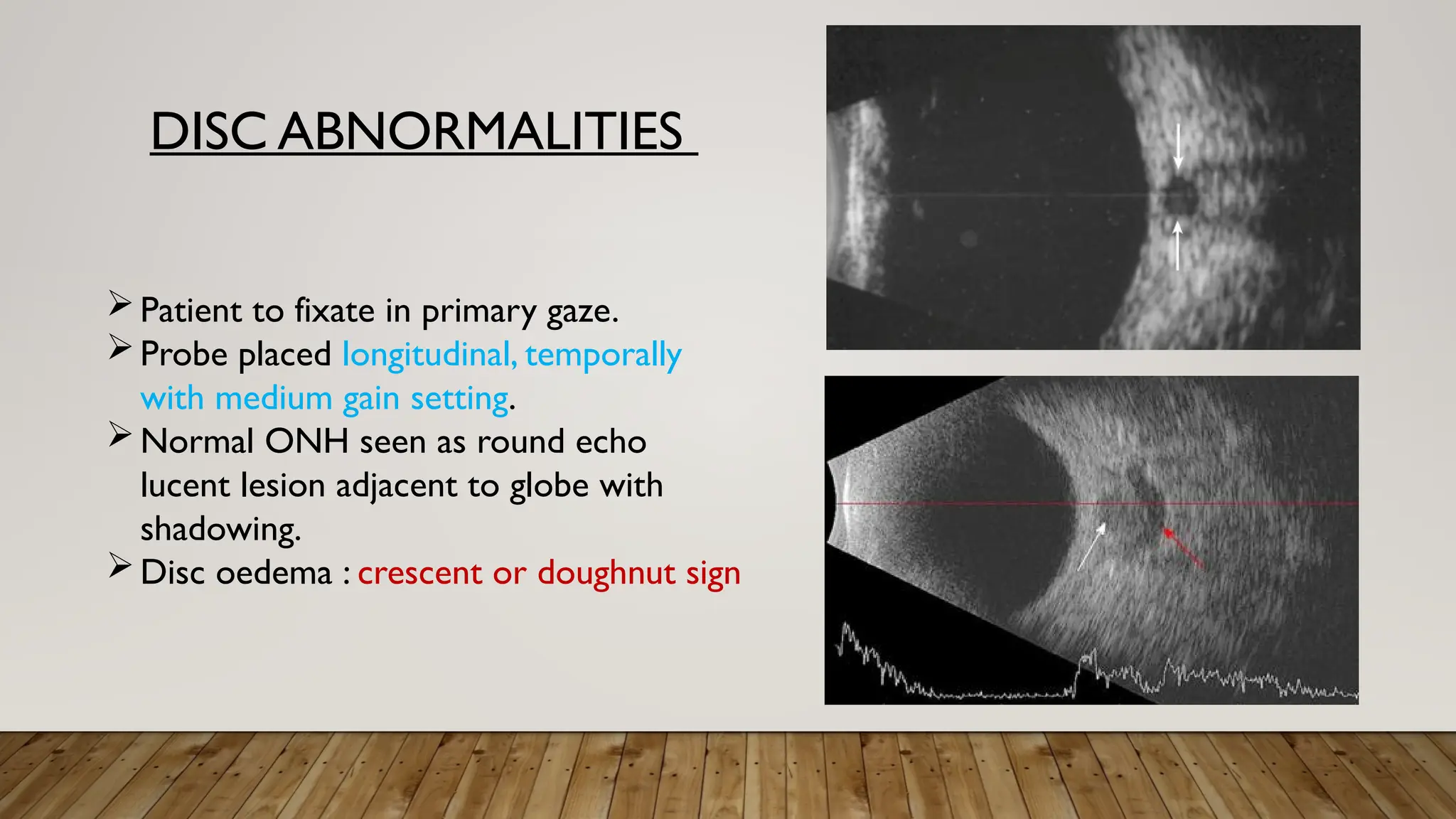
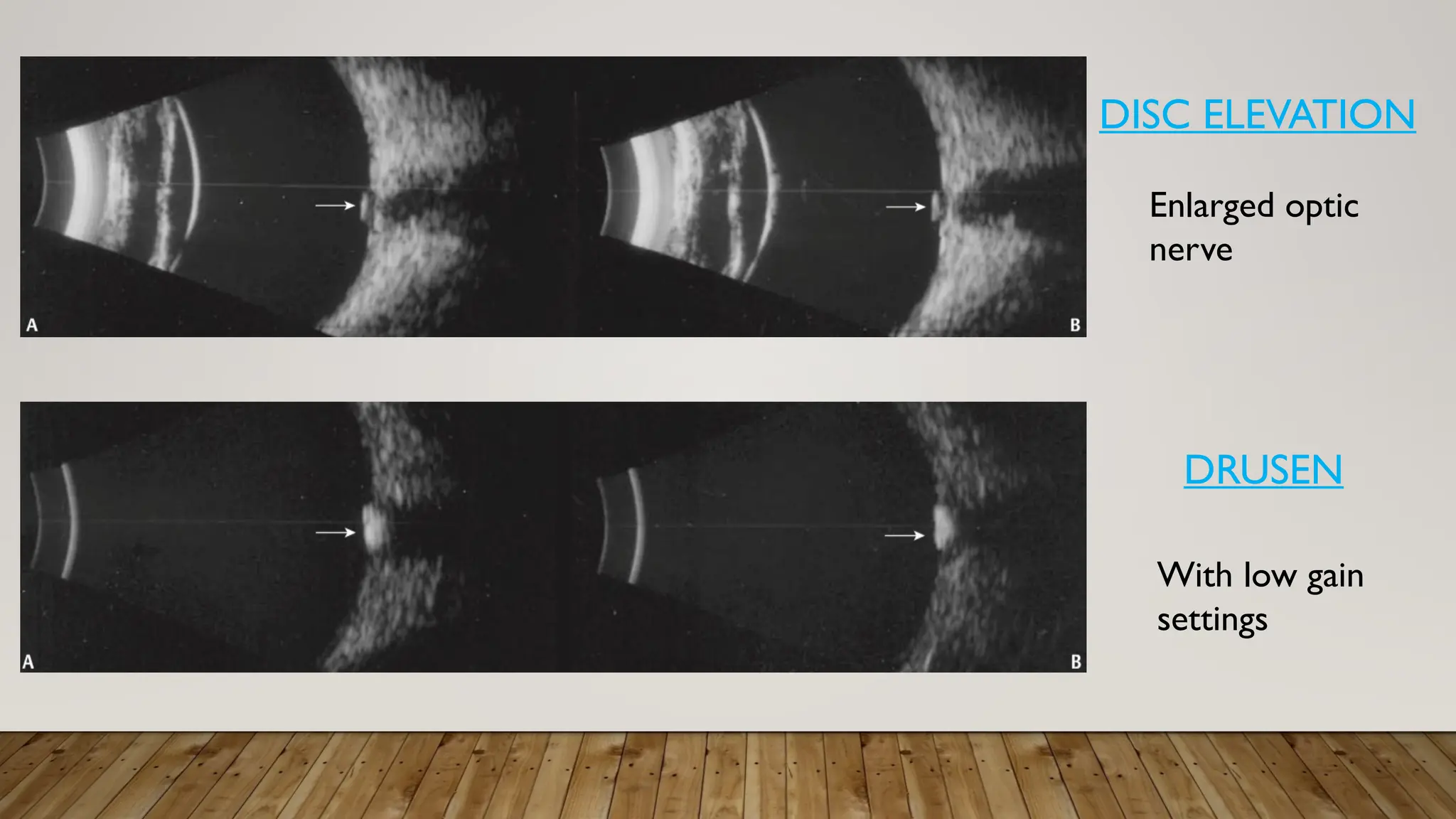
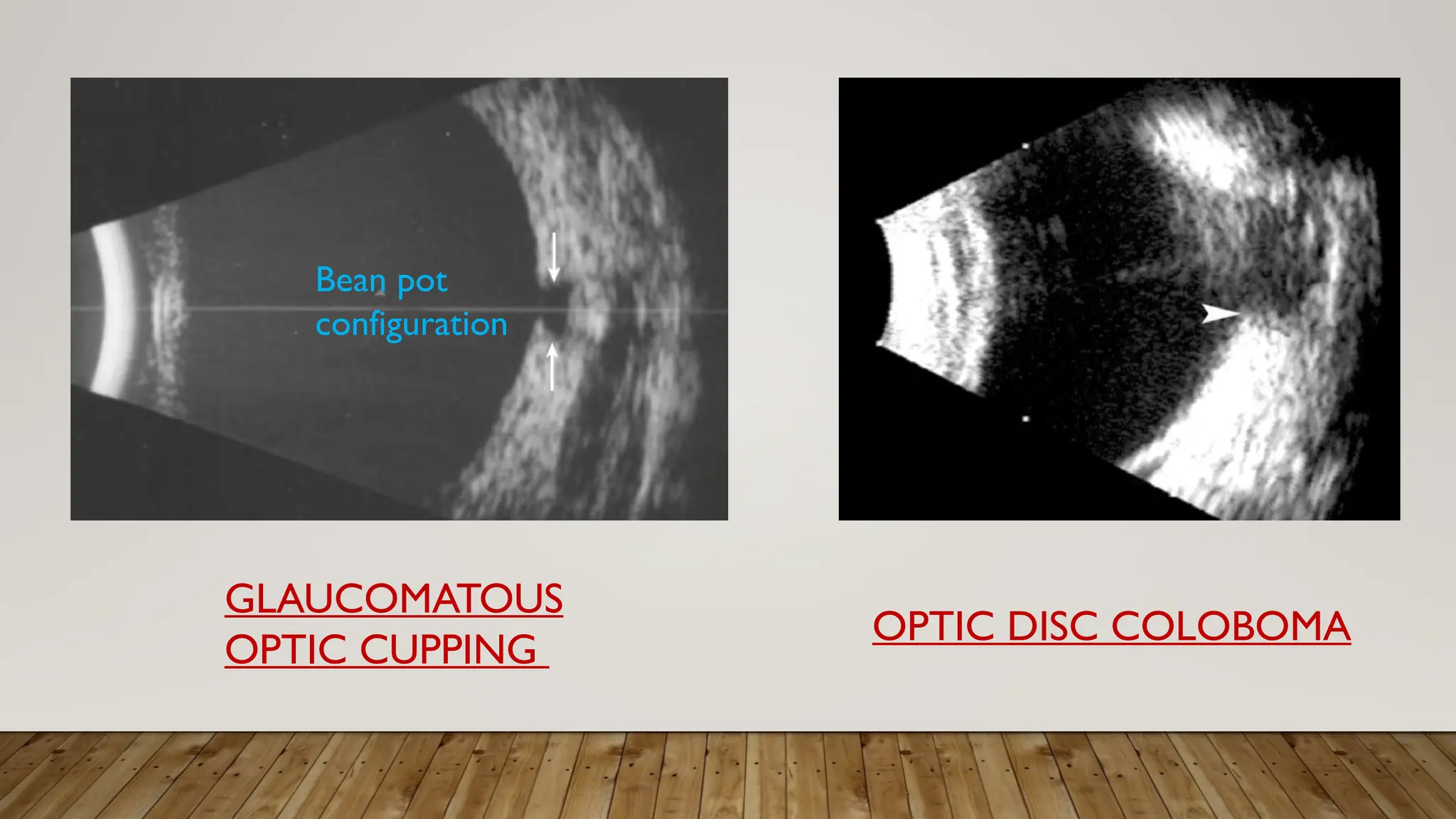
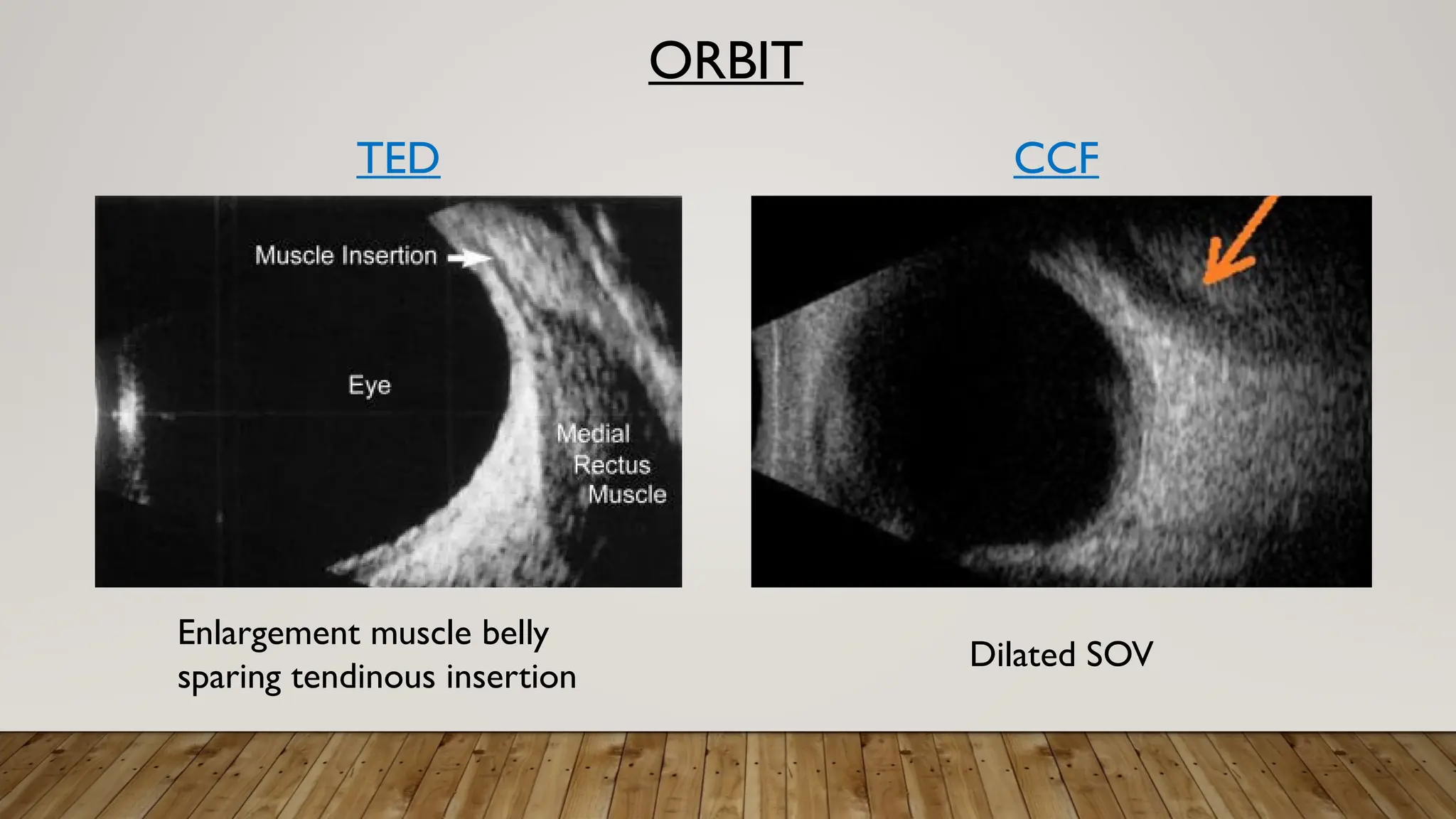
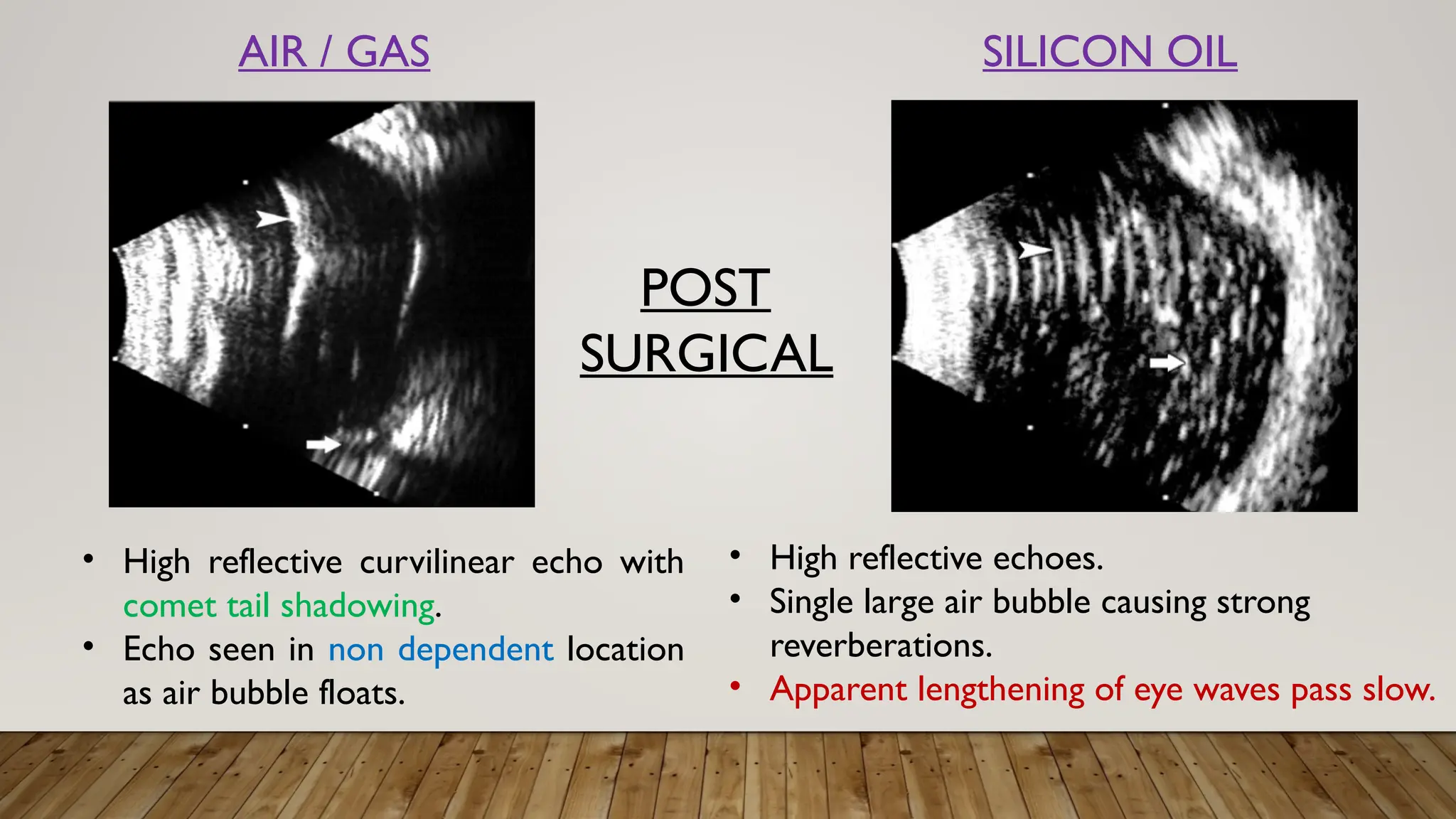
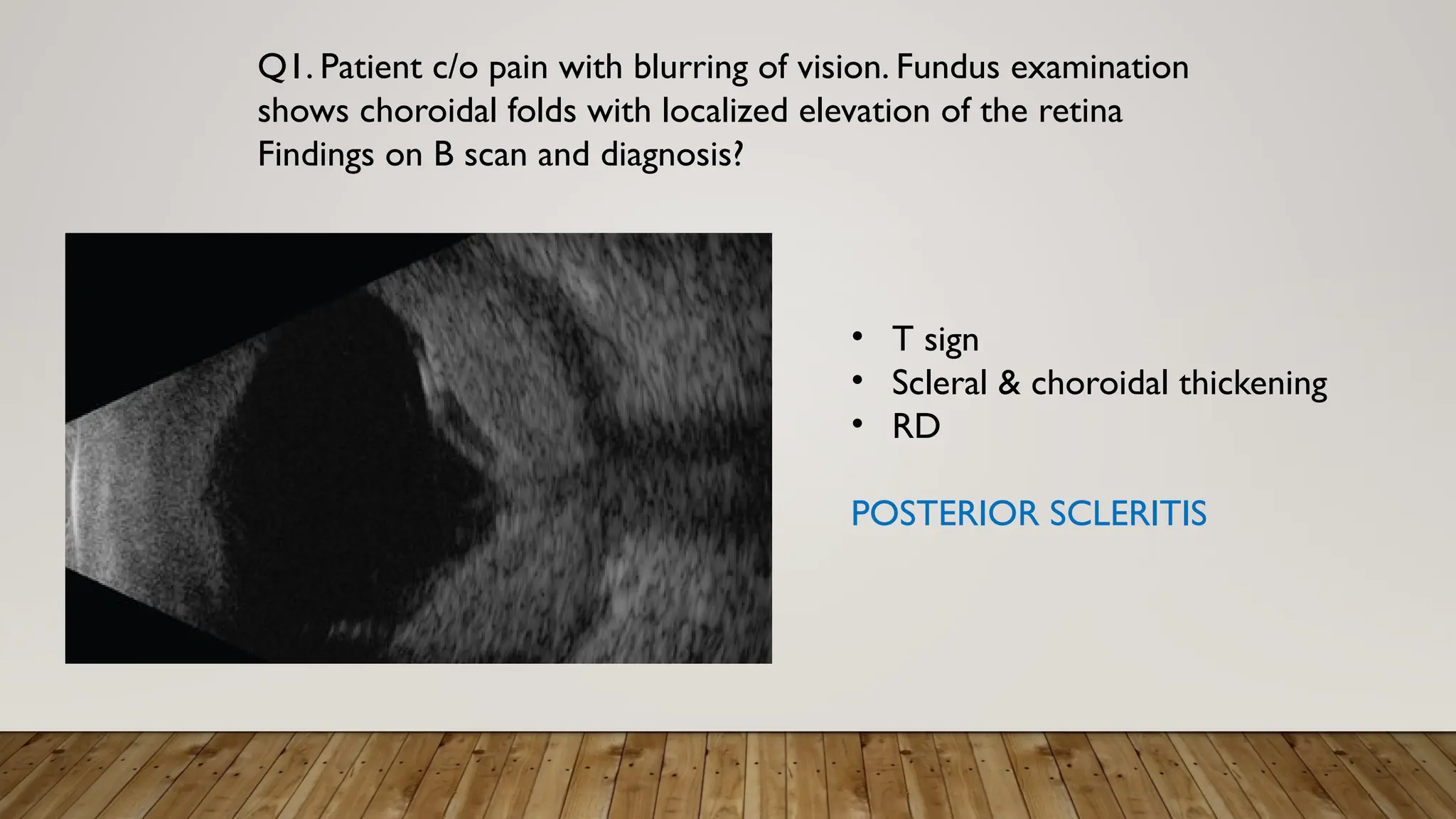
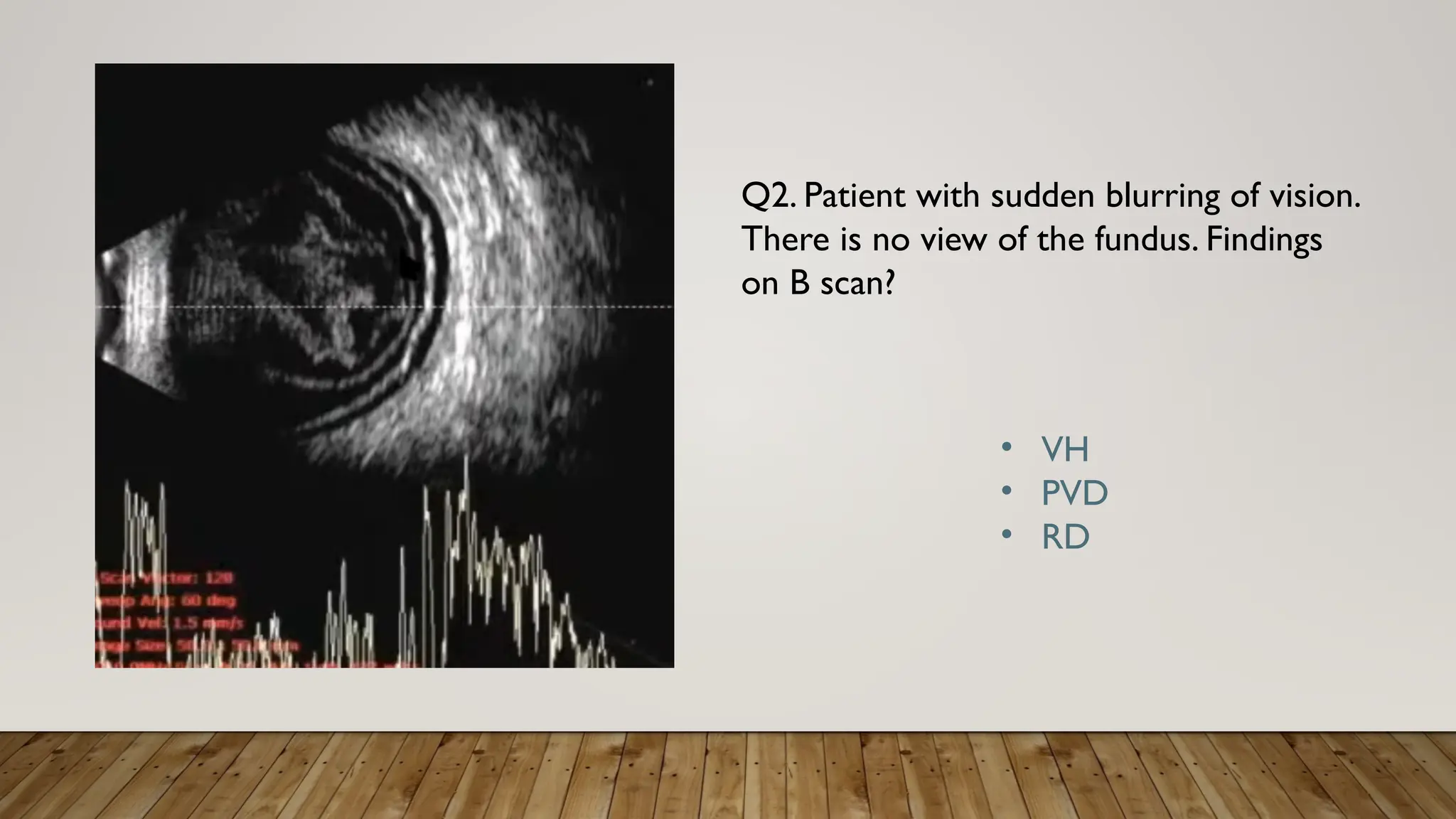
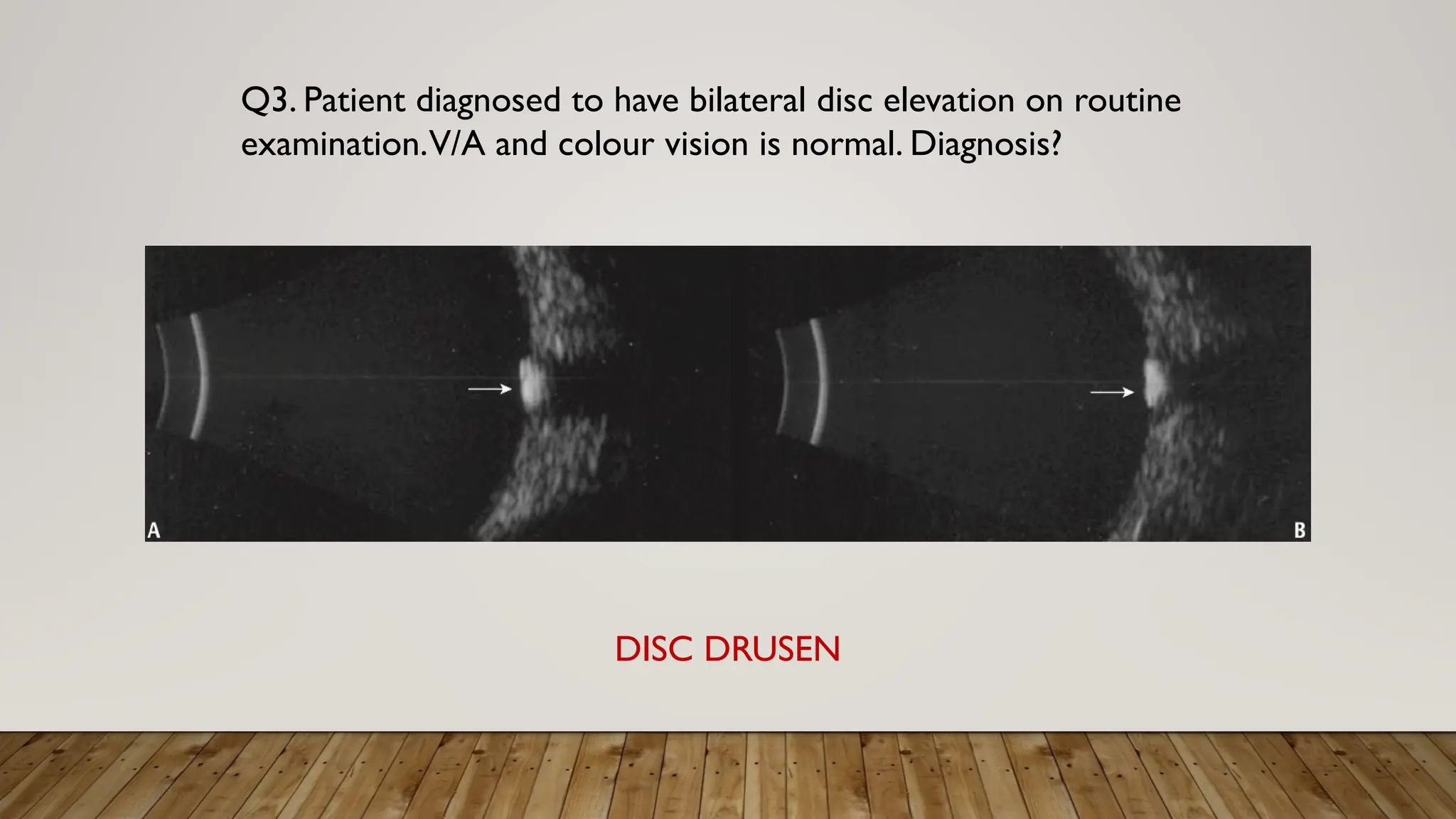
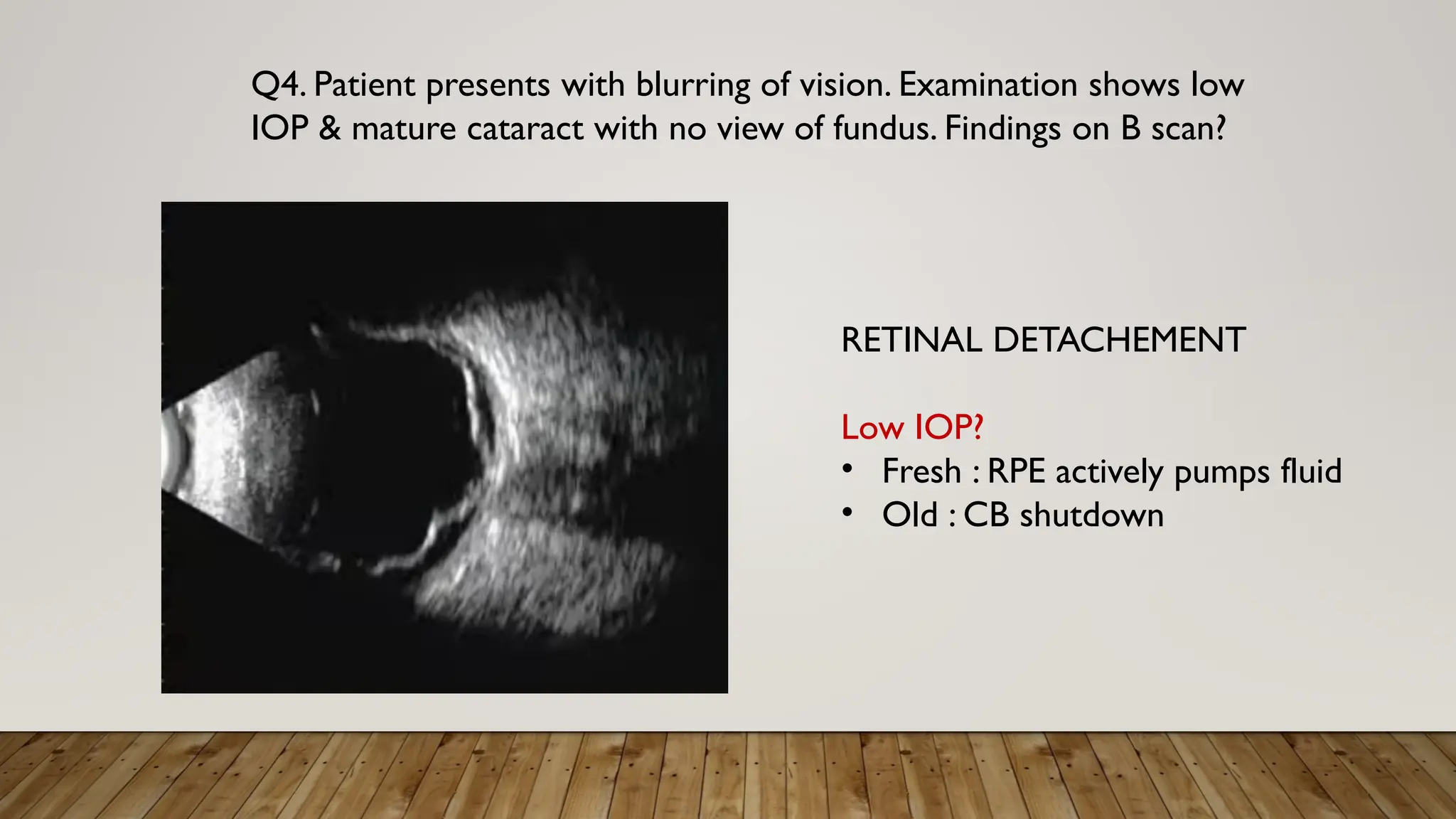
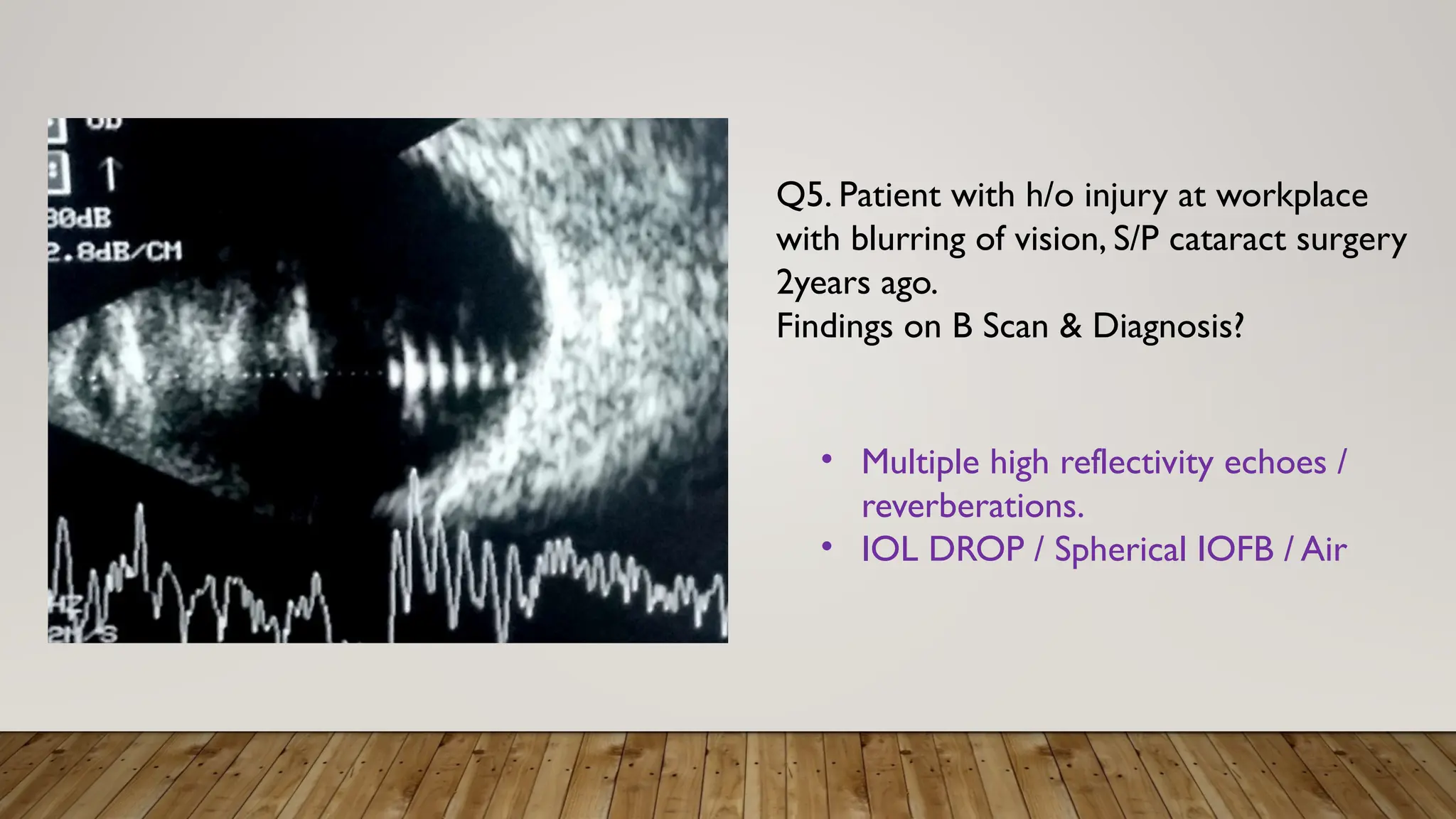
The document discusses the use of B-scan ultrasound in ophthalmology, detailing its role in complementing clinical examination and the distinctions between high and low frequency B-scans. It highlights various ocular conditions assessed through B-scan, including the evaluation of opaque and clear ocular media, vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, tumors, and post-surgical complications. The document also outlines methods for lesion description, reflection characteristics, and possible diagnoses based on B-scan findings.