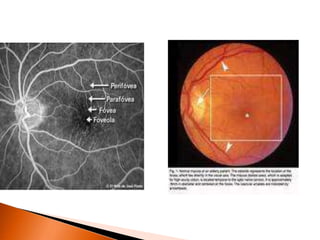
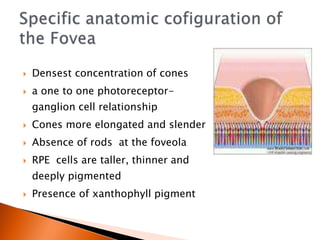
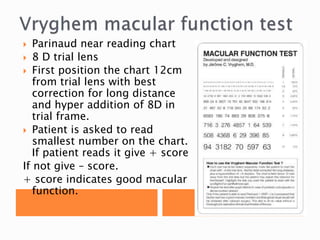
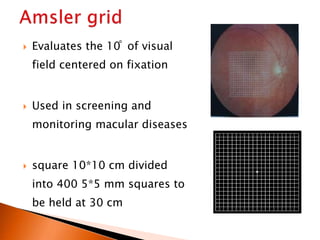
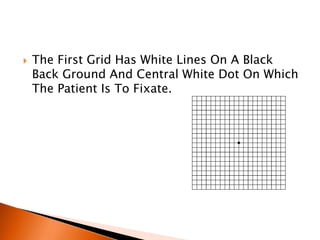
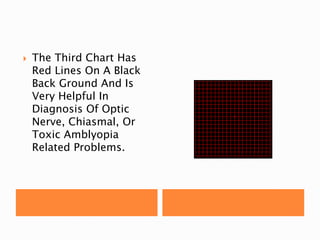
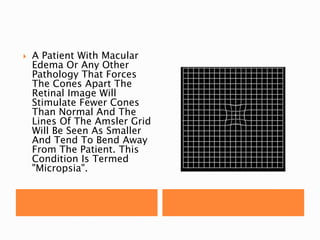
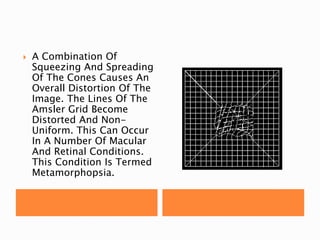
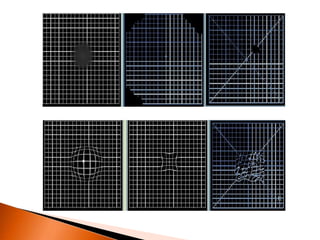
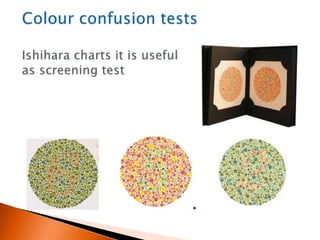
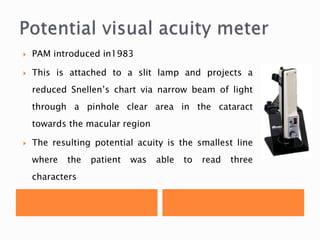
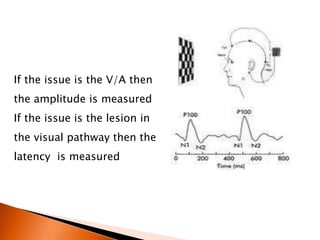
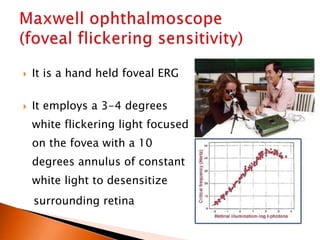
The document discusses various tests used to evaluate macular function, including both subjective and objective tests. Subjective tests include visual acuity tests, Amsler grid testing, color vision tests, and photostress testing. Objective tests mentioned include visual evoked potentials (VEP), electroretinography (ERG), and optical coherence tomography (OCT). The advantages and limitations of different tests are provided.