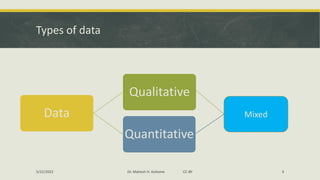
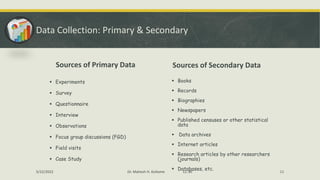
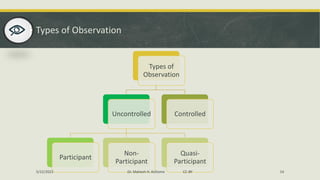
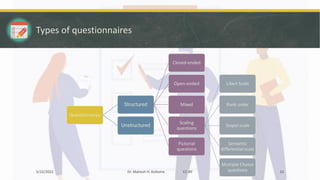
The document discusses various data collection methods, tools, and techniques. It begins by defining data collection as the process of gathering and measuring information on variables of interest in a systematic way. It then covers the main types of data: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed. For each type, it provides examples and features. It also distinguishes between primary and secondary data collection. The document then examines specific methods like surveys, interviews, observation, and focus groups. It provides details on each, including types of tools and potential issues. In summary, the document offers an overview of key concepts and approaches to collecting data for research purposes.