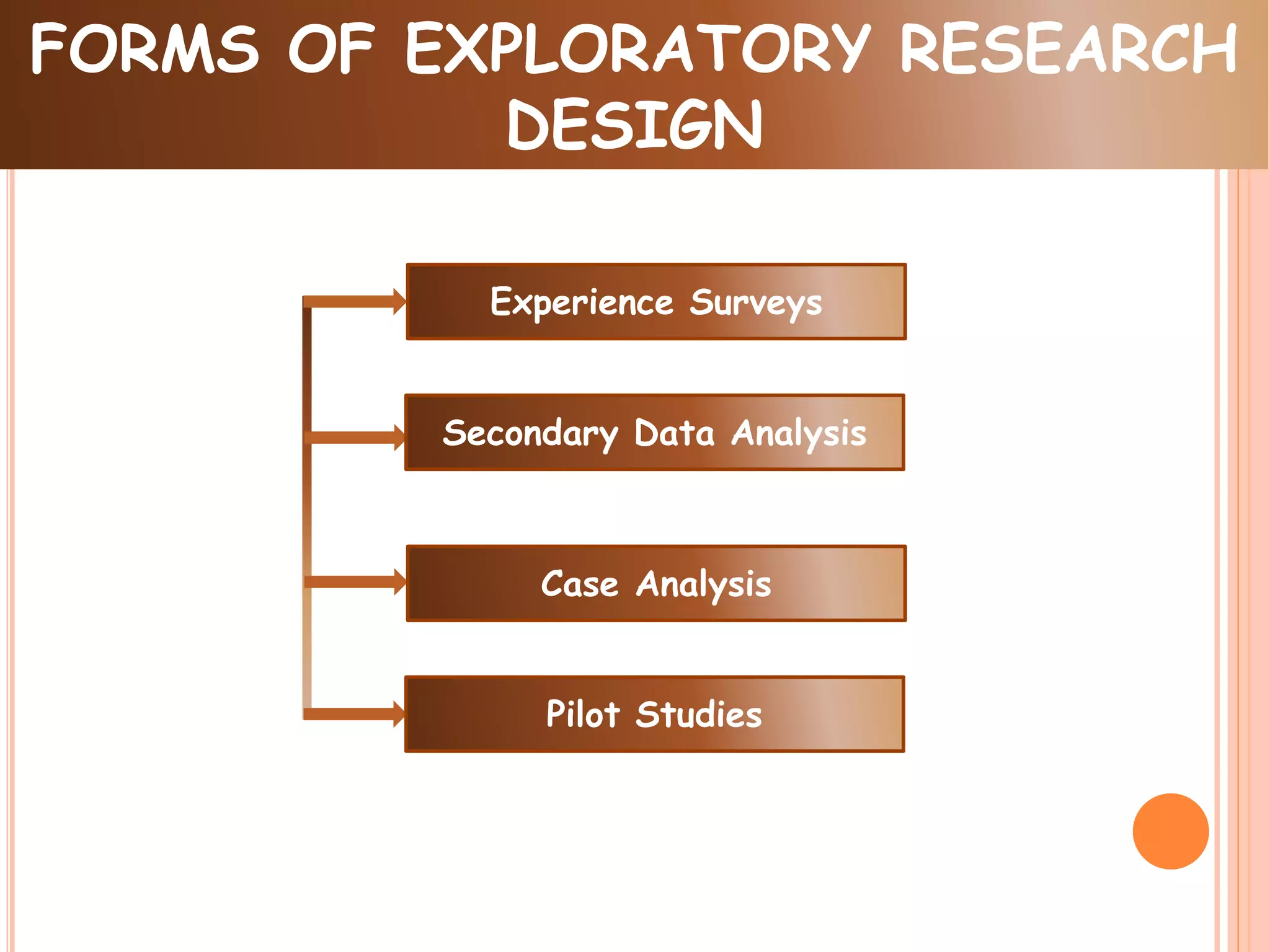
Exploratory research design, also known as formative research, is used when the researcher is unfamiliar with the problem. It aims to discover new ideas and insights through flexible and unstructured methods like literature reviews, experience surveys, and case analyses. These methods help define the problem and form hypotheses for further investigation through more structured research.