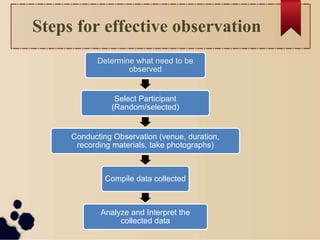
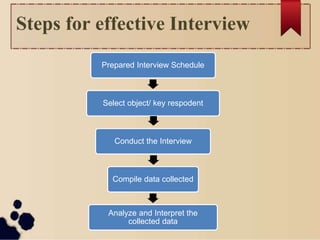
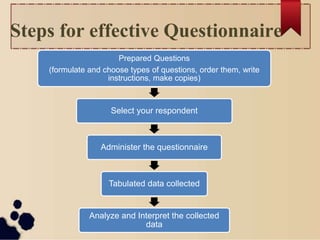
The document discusses various methods for collecting data in research. It describes primary and secondary data collection. Some key methods covered include observation, interviews, questionnaires, schedules, and surveys. For each method, it provides details on the process, types, advantages, and disadvantages. The goal of the document is to outline different approaches for gathering information needed to conduct research.