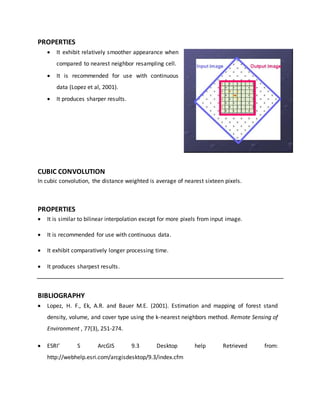
Resampling is defined as deriving pixel values for a new image from an existing image. There are two main types of resampling: nearest neighbor and bilinear interpolation. Nearest neighbor assigns the value of the nearest pixel in the input image to pixels in the output image, producing blocky results best used for discrete data. Bilinear interpolation takes the weighted average of the nearest four pixels, producing smoother results best used for continuous data. Cubic convolution is similar but uses sixteen nearest pixels, providing the sharpest results but longest processing time and is best for continuous data.