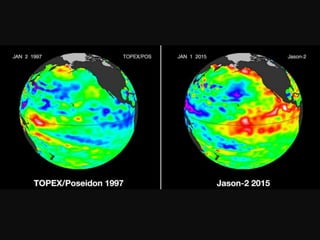
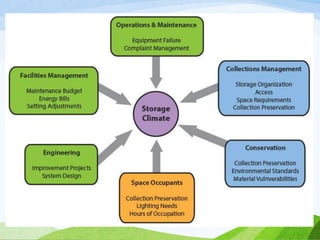
The document discusses climate change, defining it as significant long-term changes in climate measures such as temperature and precipitation. It provides historical data showing an increase in global temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels, emphasizing the impacts on ecosystems and human communities. Additionally, it highlights the Kyoto Protocol's aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and presents statistics on carbon emissions from various countries.