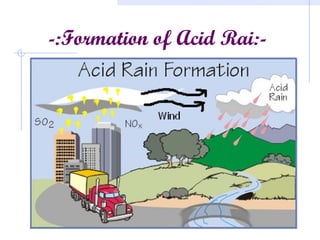
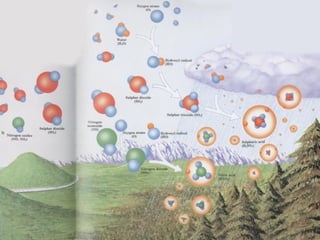
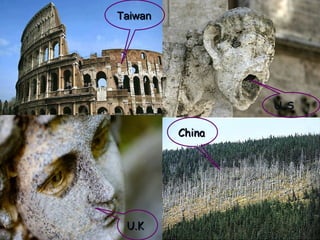
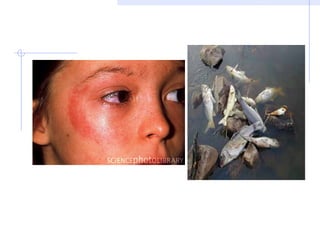
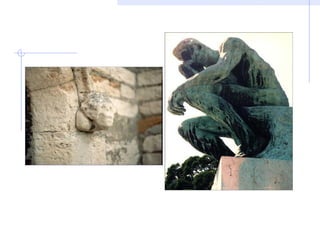
Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulfur and nitrogen compounds from human sources like fossil fuel burning. It makes rainwater acidic and harms aquatic life, forests, and infrastructure. Areas with granite bedrock and those downwind of industrial regions are most affected. To reduce acid rain, emissions must be decreased through cleaner energy sources and regulated smokestack emissions. Affected ecosystems can also be treated by adding limestone to neutralize acidity.