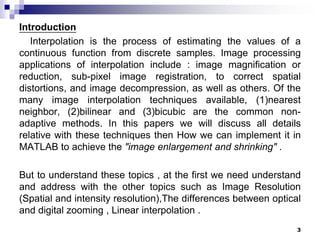
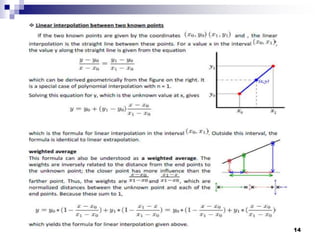
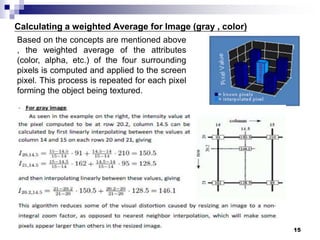
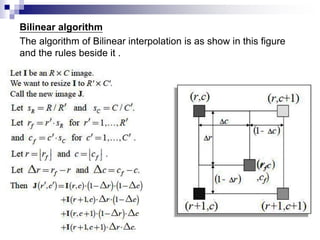
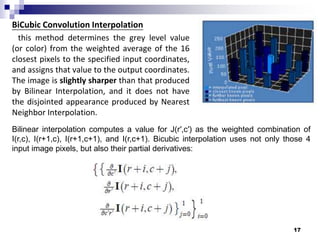
Digital image concepts and interpolation techniques for optical and digital zoom are discussed. There are three main types of interpolation used for resizing images: nearest neighbor, bilinear, and bicubic. Nearest neighbor is the simplest but produces the lowest quality, while bicubic is the most complex but highest quality. Optical zoom uses lens magnification before sensing, whereas digital zoom interpolates after sensing, resulting in lower quality than optical zoom. Interpolation methods assign pixel values to new locations during resizing based on weighting patterns around the original pixel values.