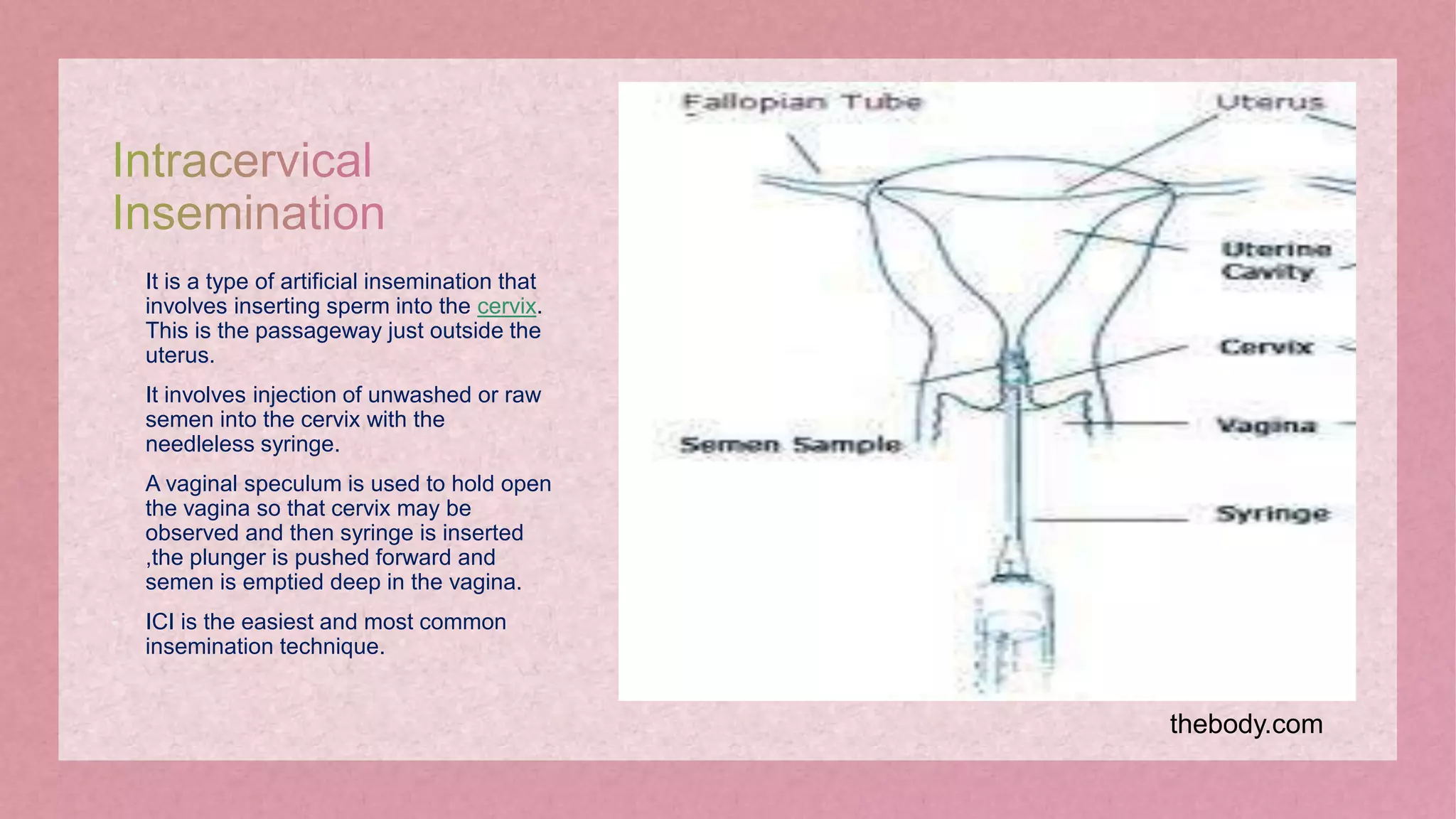
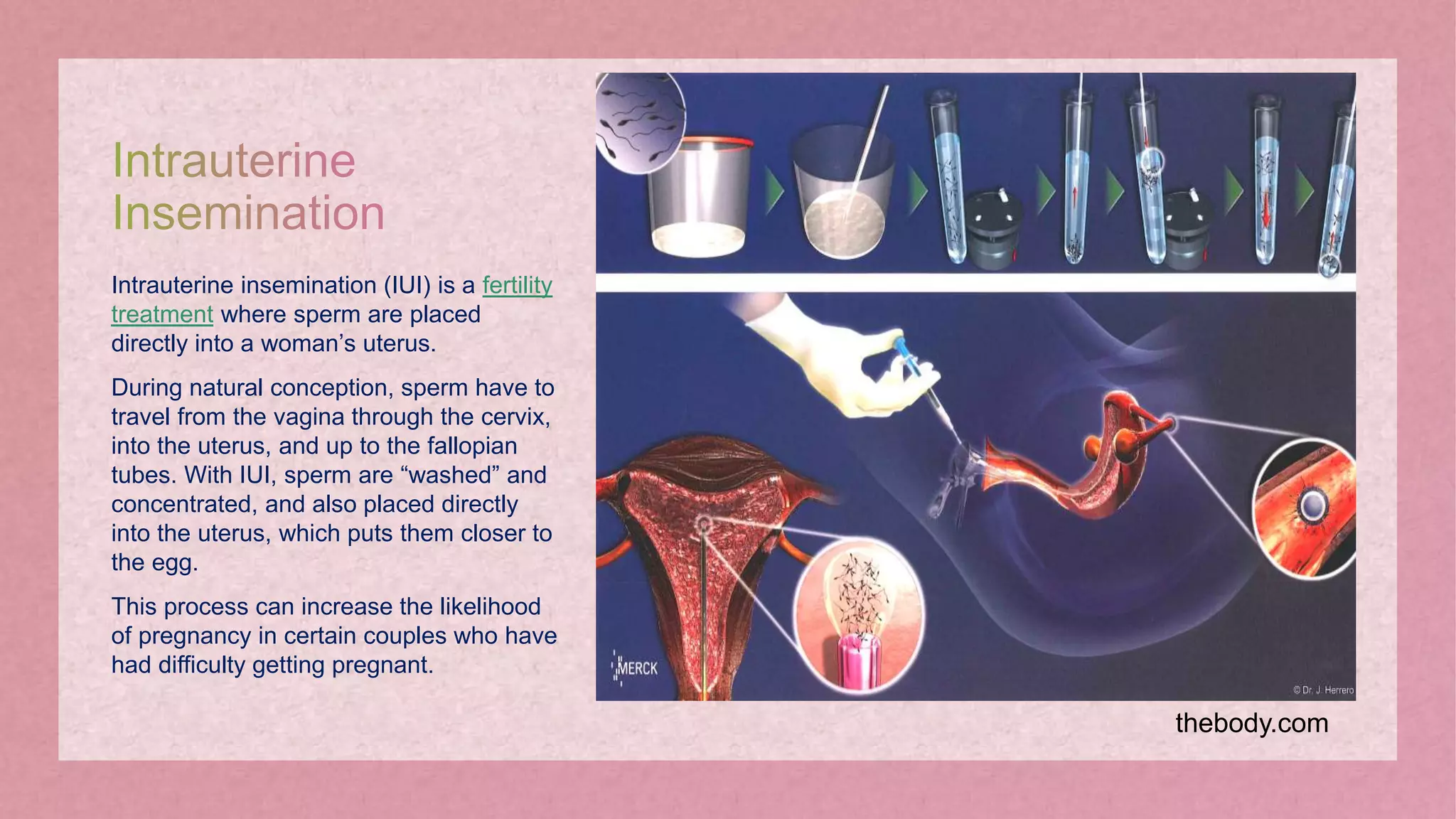
The document discusses assisted reproductive technology (ART) as a method to assist with infertility through techniques like in vitro fertilization and artificial insemination. It outlines historical development, factors affecting conception, and various ART procedures, along with their advantages and implications. Additionally, the document raises ethical considerations surrounding ART, emphasizing the importance of the child's welfare in such interventions.