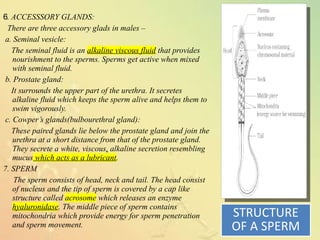
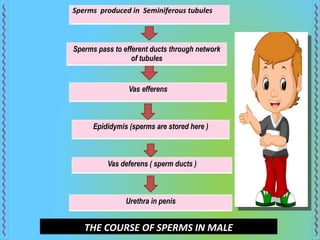
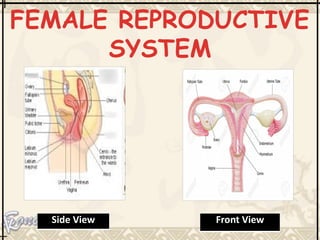
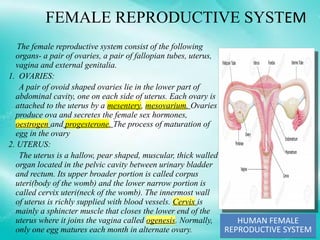
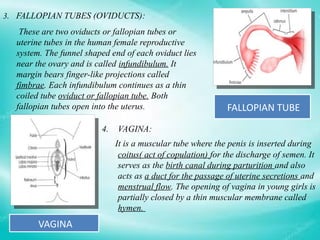
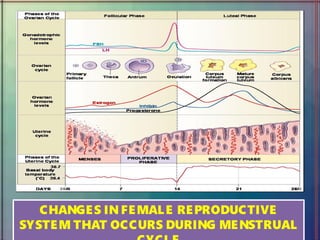
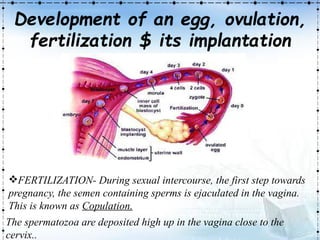
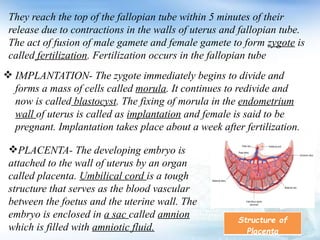
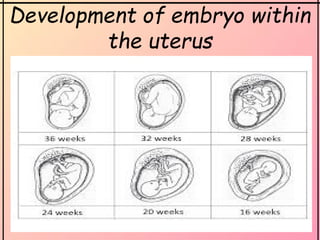
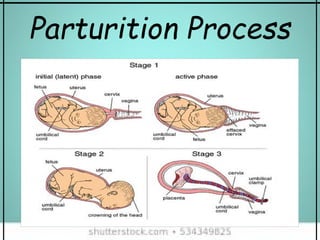
The document provides an overview of the human reproductive system, detailing the anatomy and functions of both male and female reproductive organs. It explains the processes of fertilization, pregnancy, and the menstrual cycle in human females, highlighting key phases and hormonal influences. Additionally, it includes information about the development of embryos and the role of the placenta during pregnancy.