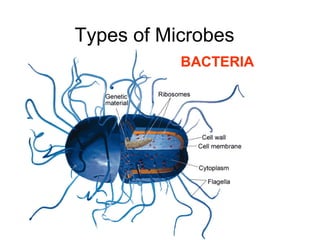
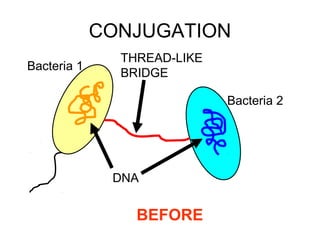
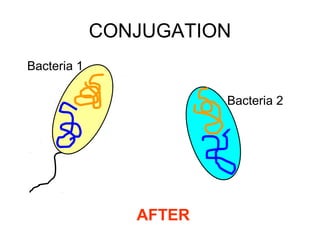
Bacteria come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They can be spherical, spiral, or rod-shaped. Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission where a single parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Some bacteria can also undergo sexual reproduction through conjugation where DNA is transferred between two bacteria through a bridge. Bacteria have different ways of obtaining food including photosynthesis, breaking down chemicals, or consuming other organisms or organic matter. They can survive unfavorable conditions by forming hardy endospores. Bacteria play both helpful and harmful roles in nature such as producing oxygen, recycling nutrients, causing disease, and spoiling food.