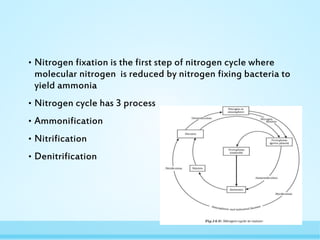
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen is converted from its stable dinitrogen form in the atmosphere into ammonia. This process is essential because plants cannot use atmospheric nitrogen. It is carried out by nitrogen-fixing bacteria that contain the nitrogenase enzyme complex. There are two types of biological nitrogen fixation - symbiotic fixation occurs through root nodules in legumes formed via their association with Rhizobia bacteria, and asymbiotic fixation by free-living bacteria and cyanobacteria in soil. Nitrogen fixation requires a large amount of energy, so it is tightly regulated by various mechanisms at the genetic level and through feedback inhibition when fixed nitrogen is abundant.








![• Its redox centres has 2 MO, 32 Fe and 30 S per tetramer
• And it has 2 binding site for reductase
• About half of the iron and sulphur is present as 2 bridged pairs of 4Fe
– 4S centres called as P cluster
• P cluster – consists 2[ 4Fe – 4S] clusters linked through additional
sulphide ion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitrogenfixation-170410144314/85/Nitrogen-fixation-10-320.jpg)