1. Renal injuries occur in 3% of all trauma admissions and are most commonly caused by blunt trauma such as motor vehicle accidents.
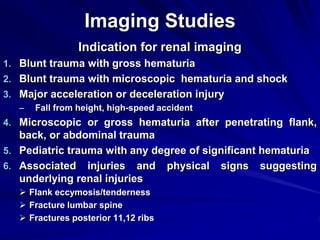
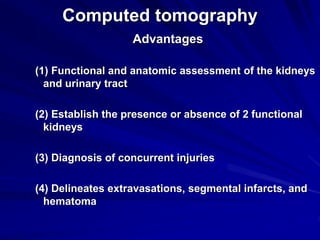
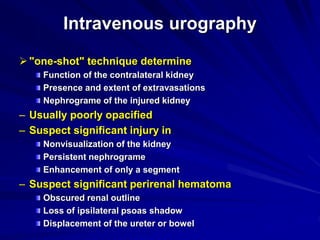
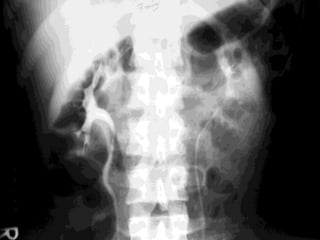
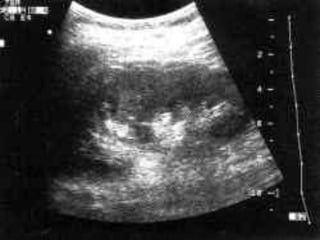
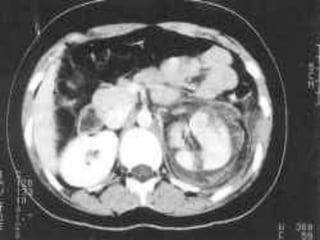
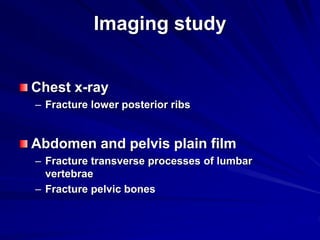
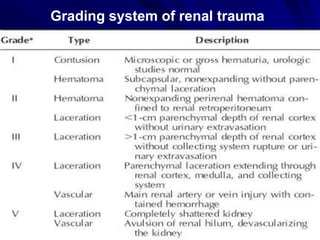
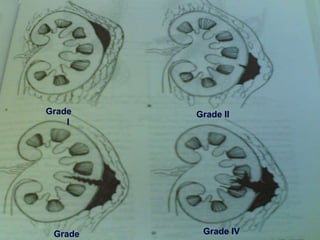
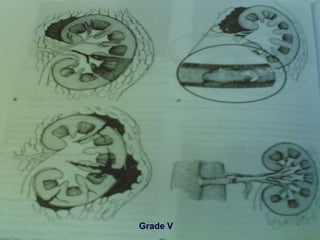
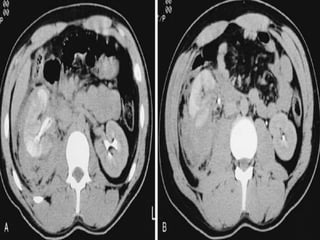
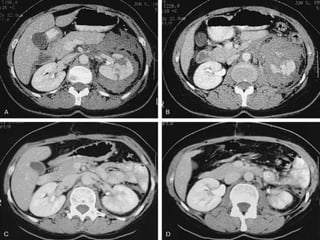
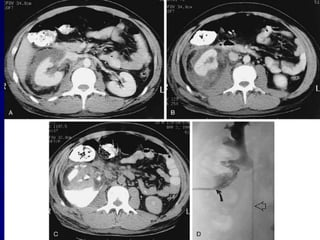
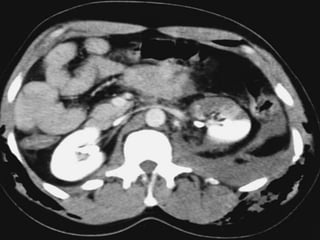
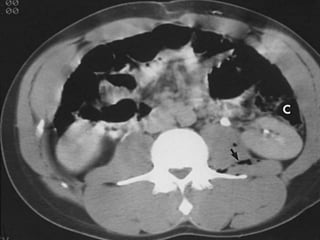
2. Evaluation of renal trauma involves clinical assessment of hematuria and imaging studies such as CT scan or IVU to grade the injury severity. Mild injuries (Grades I-II) can often be managed non-operatively.
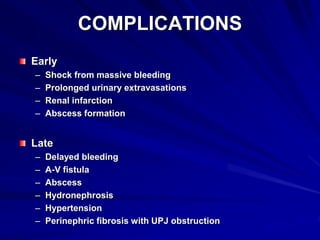
3. Treatment depends on injury grade and patient stability. The majority (98%) of renal injuries can now be managed non-operatively with bed rest and monitoring. Operative exploration is only indicated for expanding hematomas or high grade injuries with vascular involvement.