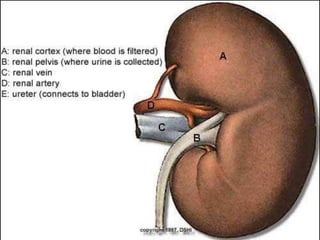
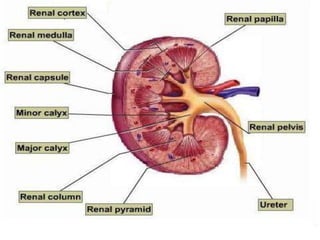
The document discusses urinary tract stones (calculi) including their formation, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Key points:
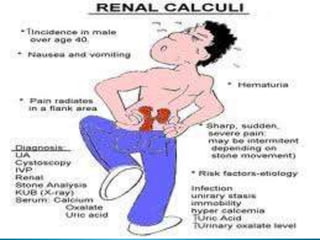
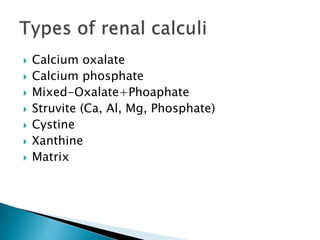
- Stones form when urinary concentrations of minerals like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid increase.
- Symptoms include sharp pain (renal colic) radiating from the back to the groin as stones pass through the urinary tract.
- Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT scans, X-rays, and ultrasounds to detect radiopaque stones.
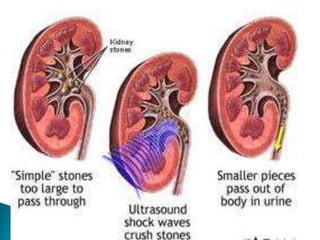
- Treatment depends on stone size but may include shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or open surgery to remove stones. Recurrence rates after treatment remain high.