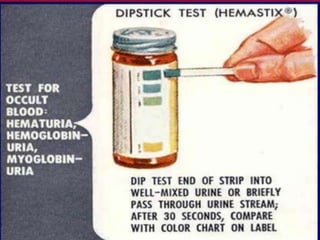
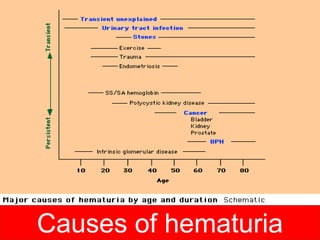
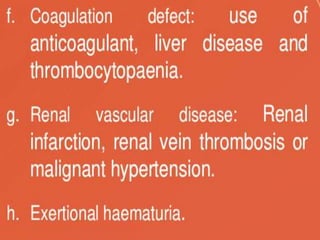
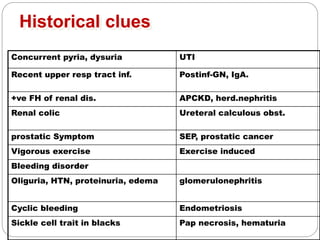
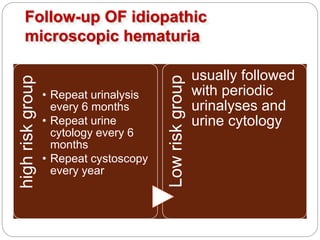
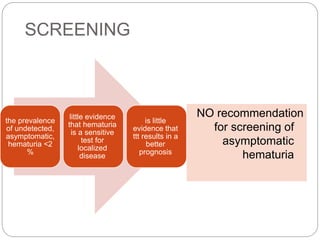
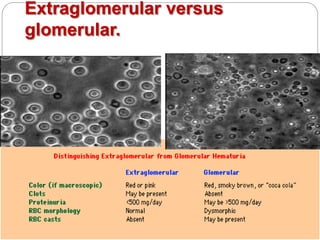
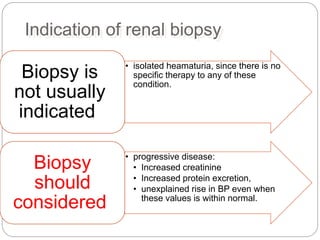
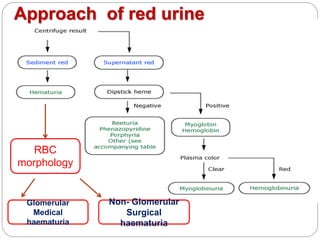
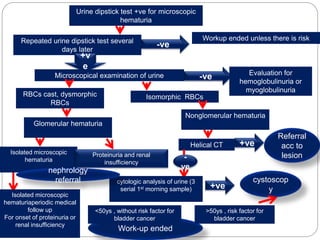
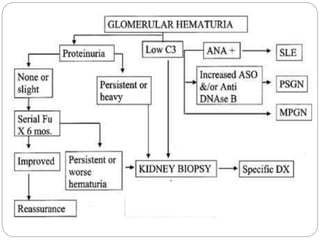
This document discusses hematuria, or the presence of red blood cells in urine. It defines gross hematuria as visible red or brown urine, and microscopic hematuria as 3 or more red blood cells per high-powered field in urine samples. The causes, patterns, and workup of hematuria are described. Transient microscopic hematuria is common and often does not require extensive evaluation unless the patient is over 50 or has other risk factors. Evaluation of persistent hematuria may involve urine analysis, cystoscopy, imaging tests, and renal biopsy depending on findings.