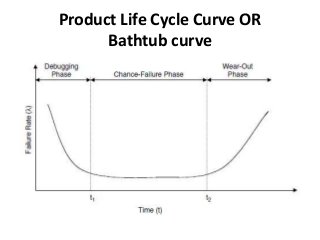
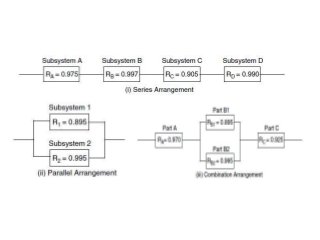
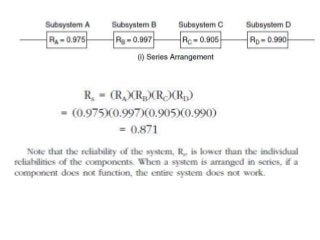
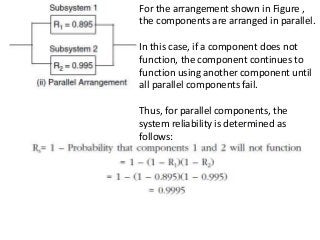
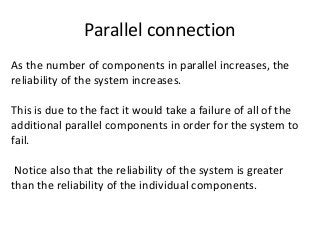
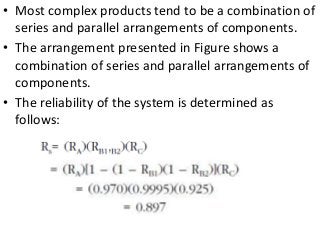
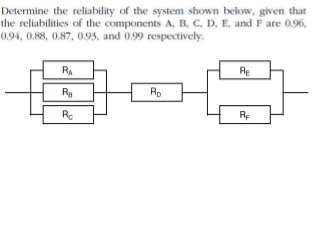
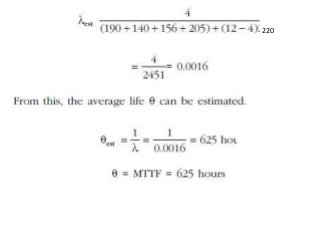Reliability is the probability that a product will perform its intended function satisfactorily for a prescribed period of time when used under specified environmental conditions. Failures can occur due to design flaws, overstressing, wear and tear, variation, wrong specifications, or misuse. As products increase in complexity with more features and components, reliability challenges also increase. Reliability is measured through failure-terminated, time-terminated, and sequential tests which examine factors like failure rate, mean life, and availability. The arrangement of components as series, parallel, or a combination also impacts overall system reliability.