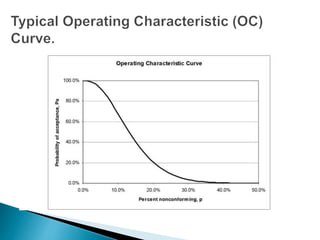
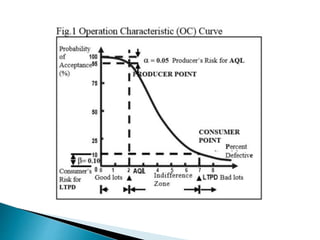
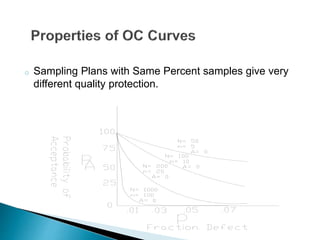
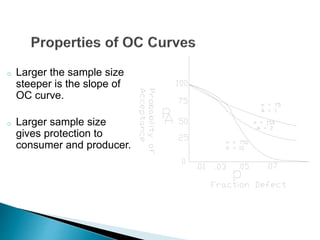
This document discusses operational characteristic (OC) curves, which are graphs used in quality control to determine the probability that a production lot will be accepted based on the percentage of non-conforming items found during sampling inspections. The key points covered include:
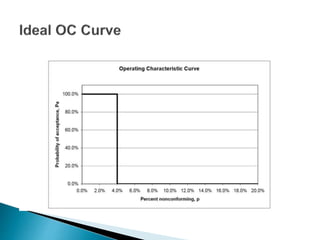
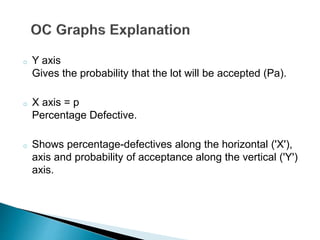
- The components of an OC curve including probability of acceptance (Pa) on the y-axis and percentage of defective items (p) on the x-axis.
- The different types of OC curves (A and B) which depend on whether the lot size is finite or infinite.
- Important points on the curve including the acceptable quality level (AQL) and rejectable quality level (RQL).
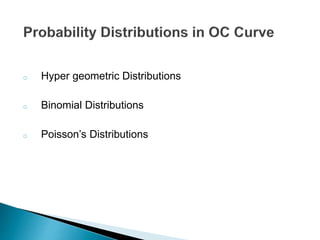
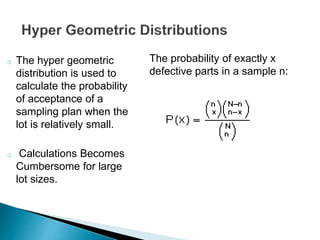
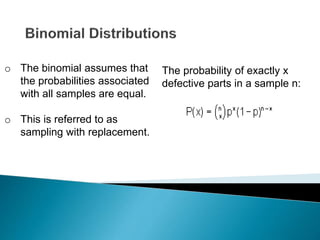
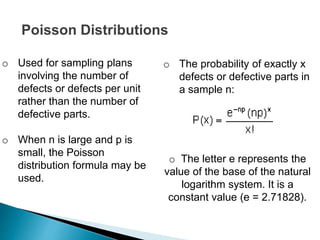
- The probability distributions used to model different sampling plans