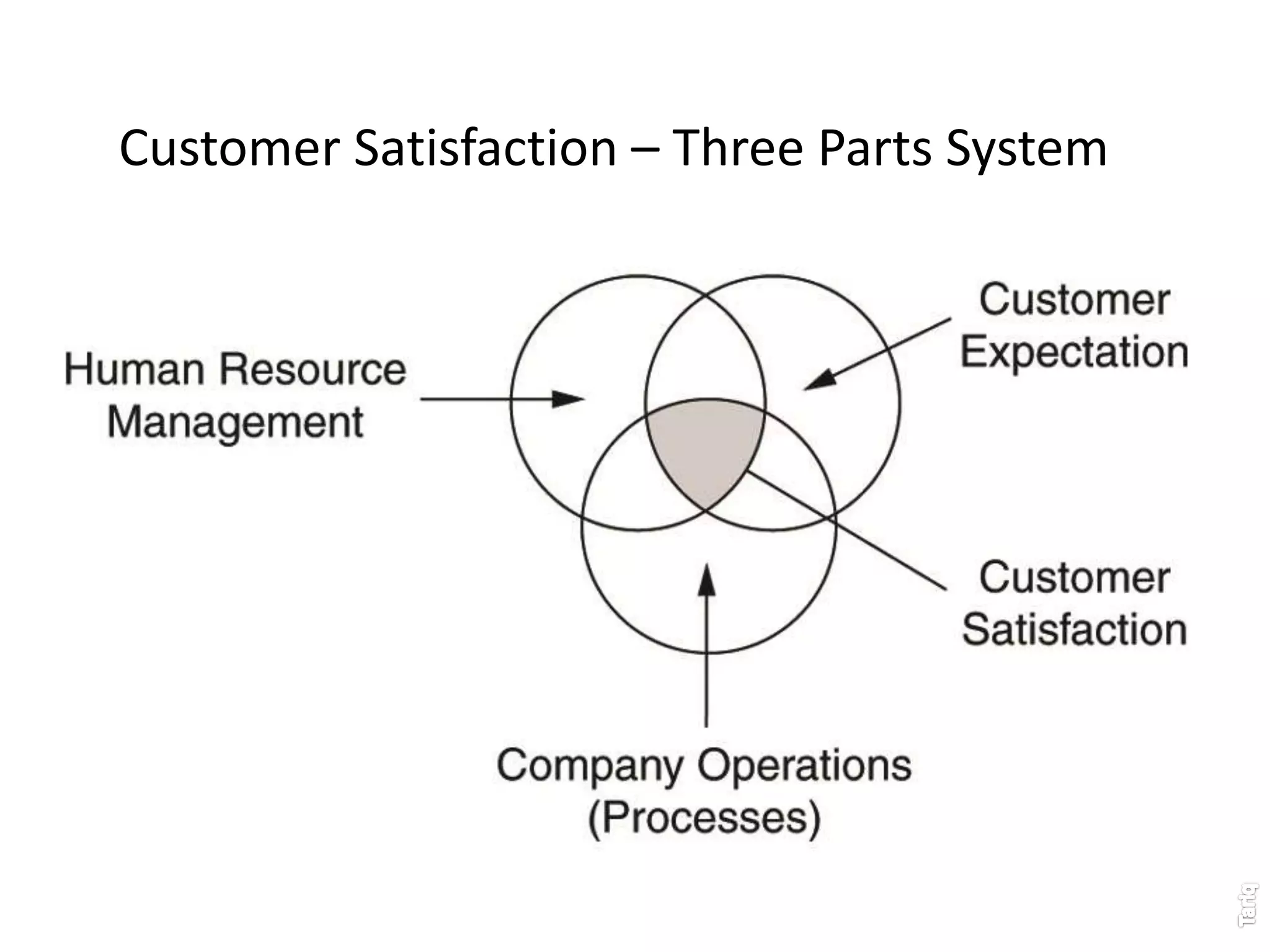
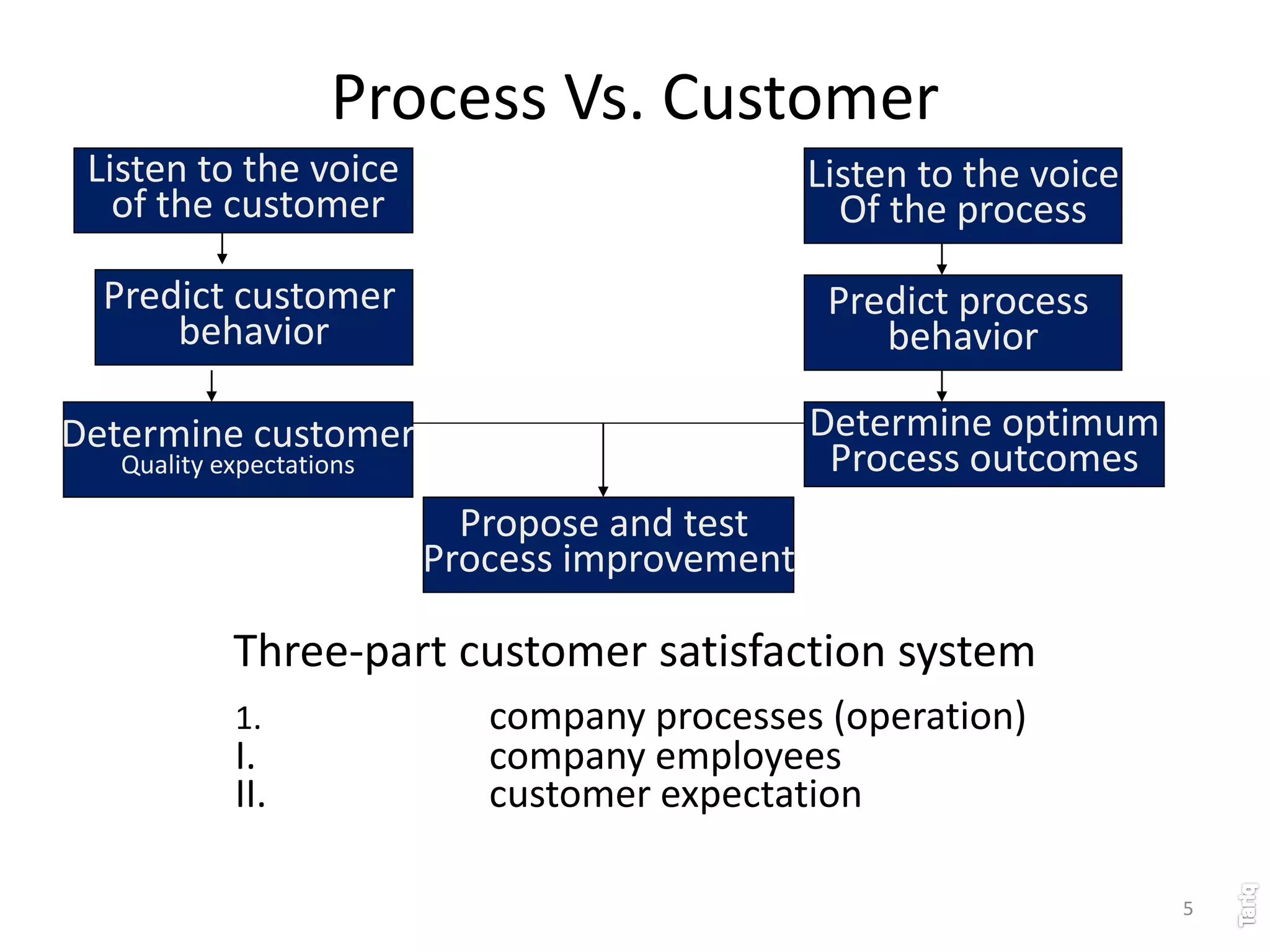
The document discusses the principles of total quality management (TQM) with a focus on customer satisfaction, emphasizing the importance of understanding both internal and external customer needs. It outlines a three-part customer satisfaction system that integrates employee input, service standards, and proactive relationship management to enhance quality and loyalty. The document also highlights the need for effective measurement of customer satisfaction and the critical role of employee engagement in achieving quality improvement.