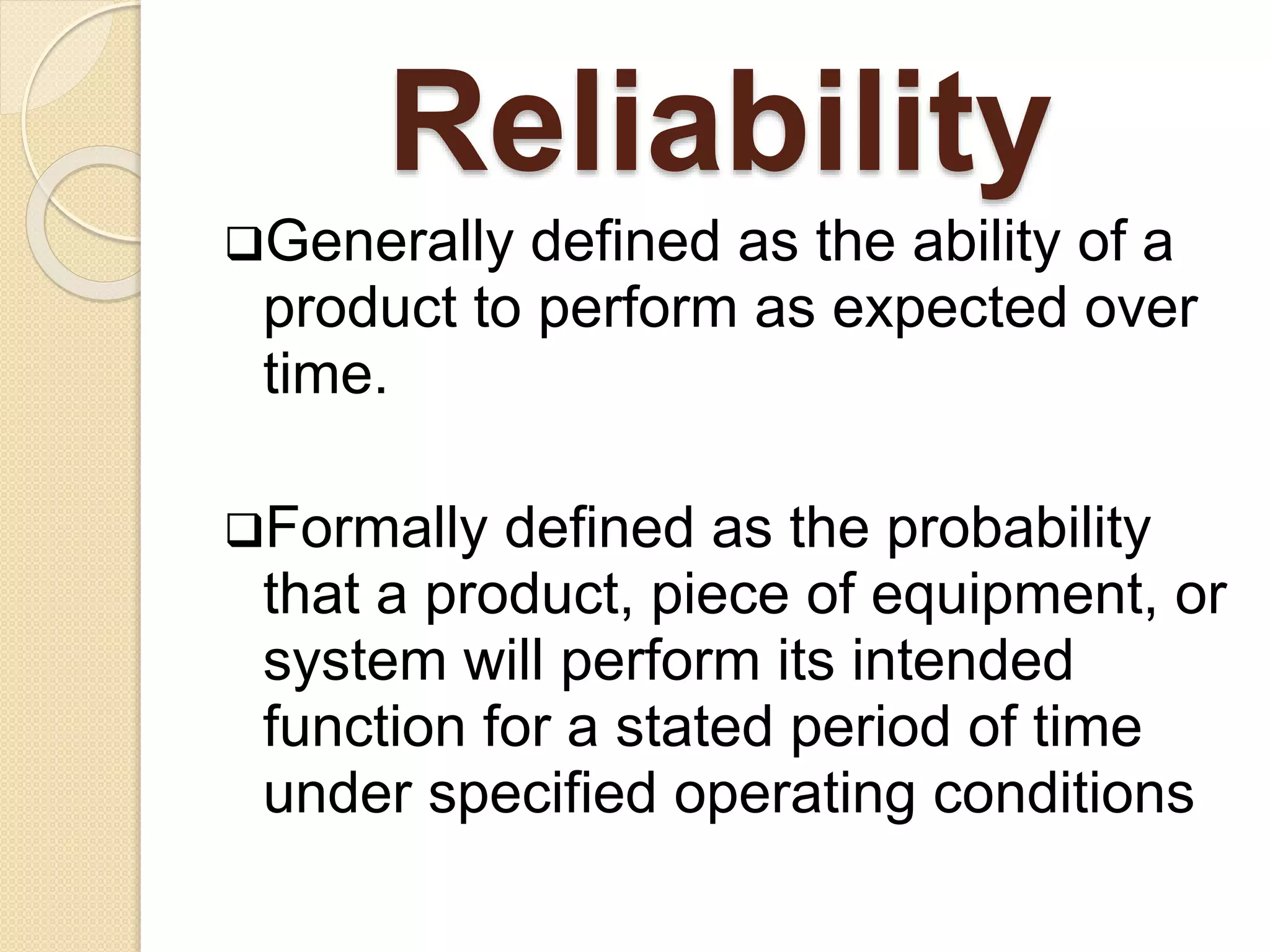
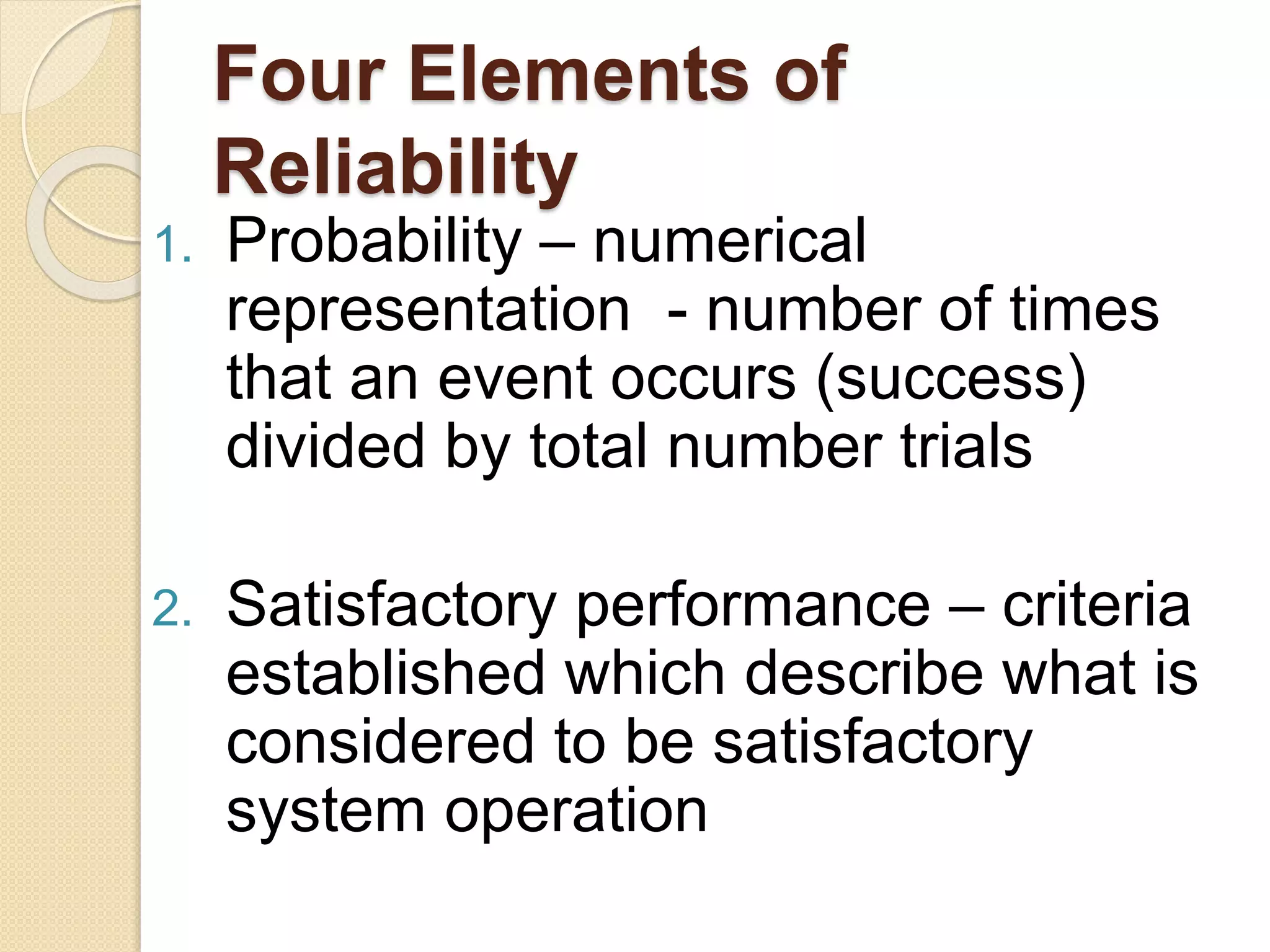
This document discusses the concept of reliability in engineering. It defines reliability as the ability of a product to perform as expected over time under specified operating conditions. There are four elements of reliability: probability of satisfactory performance, specified time period, and specified operating conditions like temperature, vibration, etc. Reliability is influenced by factors like the numerical probability value, intended function of the product, expected life, and environmental conditions. The document outlines key aspects of reliability management, design, production, and transportation that influence a product's reliability.