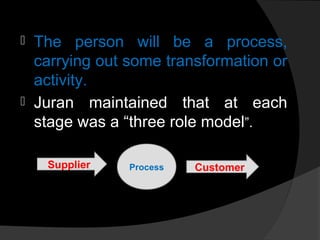
Joseph Juran made many contributions to quality management, including developing the concept of the internal customer and cost of quality. He is known for establishing the "Juran Trilogy" which outlines three processes for quality management - quality planning, quality control, and quality improvement. The trilogy shows how organizations can improve by better understanding the relationships between planning, controlling, and improving quality processes and business results. Juran also proposed 10 steps for quality improvement projects and emphasized the concept of breaking through problems by understanding the journey from symptom to cause and from cause to remedy.