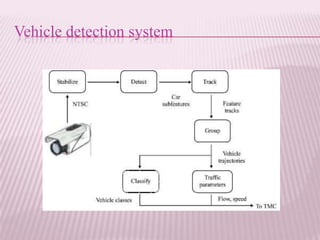
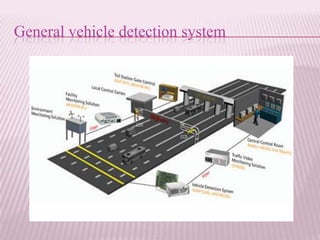
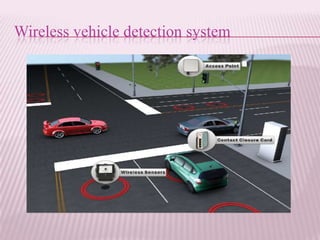
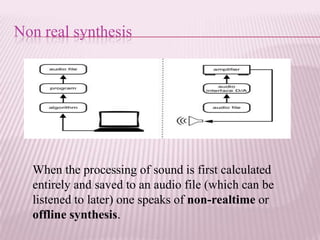
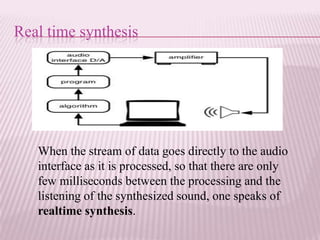
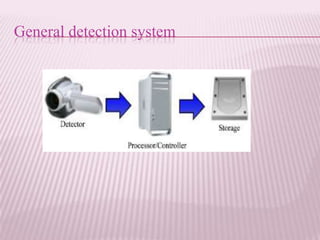
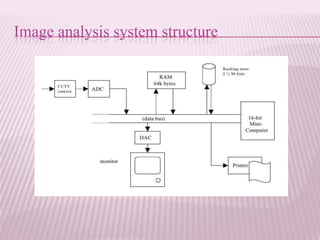
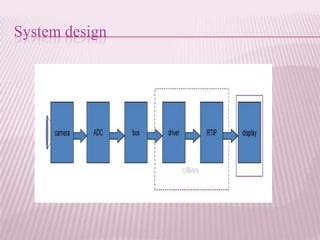
This document provides an overview of real-time image processing. It begins with introducing real-time image processing and how it differs from ordinary image processing by having deadlines and predictable response times. The document then discusses the requirements for a real-time image processing system including high resolution video input, low latency, and high processing performance. It also covers applications such as mobile robots and human-computer interaction. In the end, it provides definitions of real-time image processing in both the perceptual and signal processing senses.