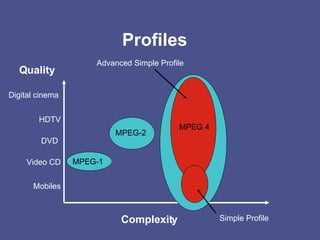
MPEG 4 is an object-based multimedia format that allows for low bitrate compression and transmission of audio-visual content such as video, speech, audio, and graphics. It supports scalable compression from mobile phone quality up to HDTV, as well as interactive capabilities. MPEG 4 compression uses various coding methods tailored to different object types and allows objects to be combined into scenes.