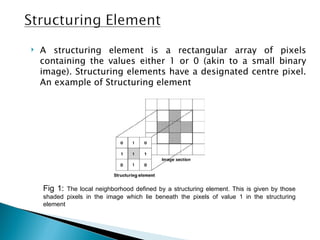
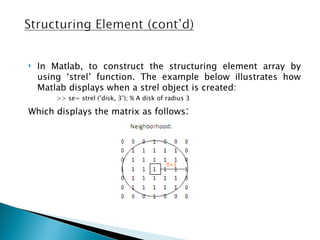
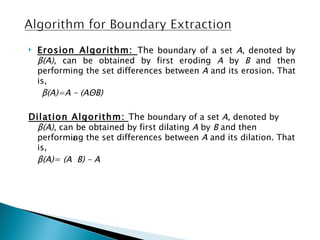
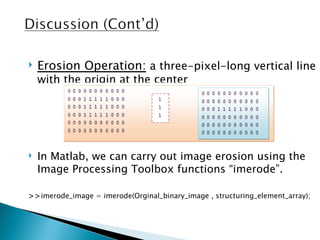
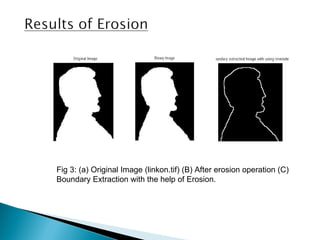
The document discusses boundary extraction techniques in image processing using mathematical morphology, specifically focusing on dilation and erosion operations. It provides definitions, mathematical formulas, and examples of MATLAB implementations for both operations, including how to create structuring elements and perform boundary extraction. Additionally, it refers to relevant literature and resources for further study in digital image processing.