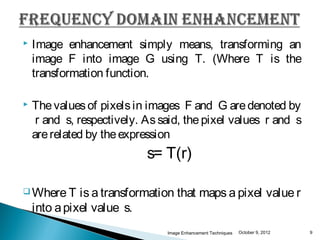
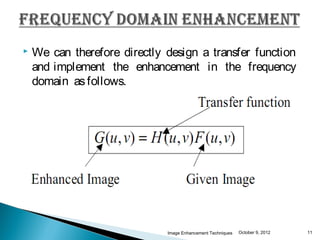
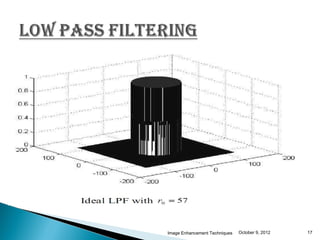
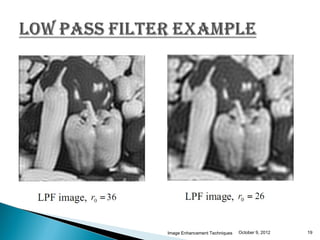
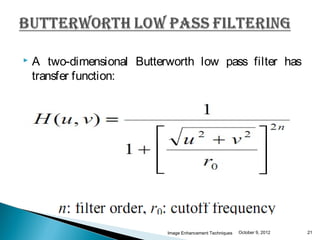
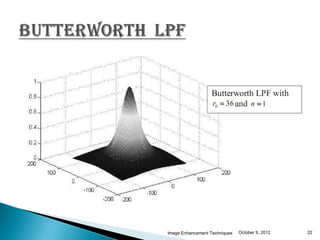
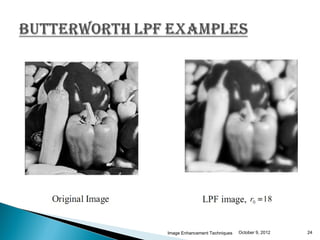
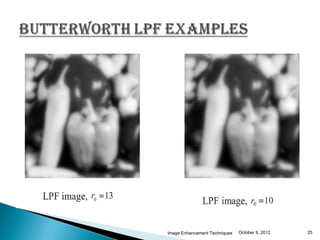
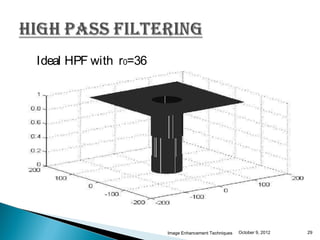
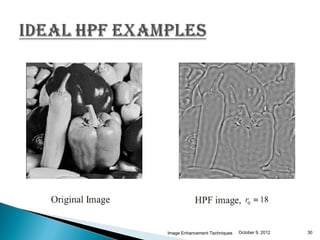
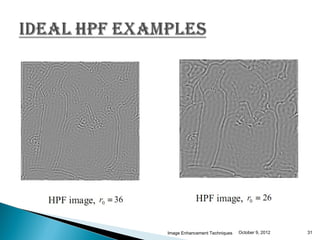
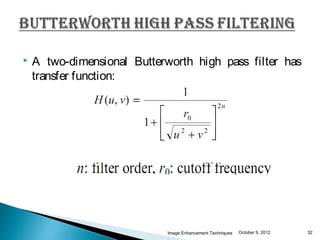
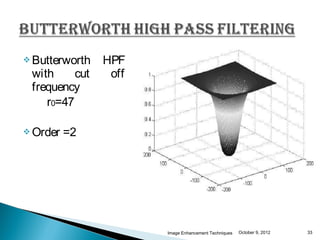
The document discusses various techniques for enhancing digital images, including spatial domain and frequency domain methods. It describes how frequency domain techniques work by applying filters to the Fourier transform of an image, such as low-pass filters to smooth an image or high-pass filters to sharpen it. Specific filters discussed include ideal, Butterworth, and Gaussian filters. The document provides examples of applying low-pass and high-pass filters to images in the frequency domain.