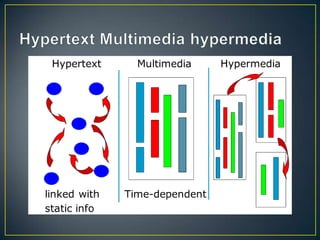
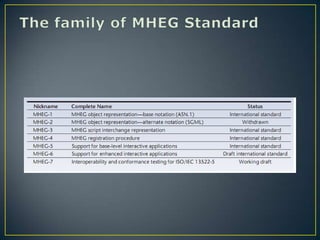
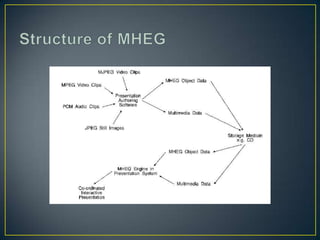
The document discusses MHEG (Multimedia and Hypermedia Experts Group), an ISO standard for defining multimedia presentations that can run across different hardware platforms. It describes the evolution of MHEG standards over time from MHEG-1 to MHEG-7, with each version adding new capabilities like interactivity (MHEG-3) or support for client-server applications (MHEG-5). MHEG defines classes, properties, and a framework to structure multimedia objects and presentations in a platform-neutral way so they can be viewed on different machines.