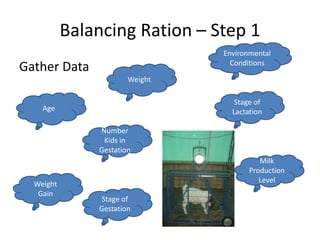
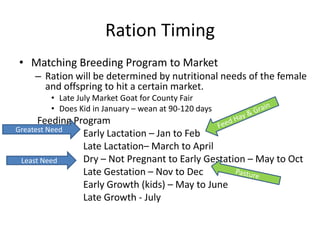
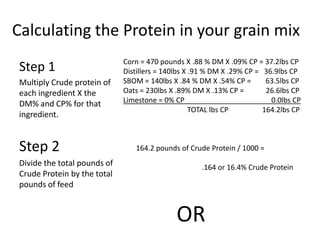
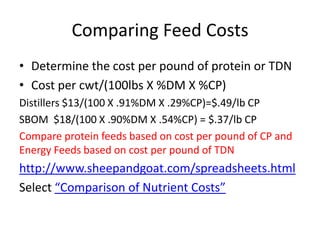
This document discusses balancing rations for small ruminants. Balancing rations ensures nutritional requirements are met in a cost effective way to maximize performance and profits. The key steps involve gathering data on animal needs based on factors like age, stage of production, and environmental conditions. Feeds are then selected based on availability and costs. Critical times like late gestation and early lactation when needs are highest are identified. Animal requirements are determined using resources like the NRC guidelines. Rations are then balanced to meet the identified protein and energy needs in a least cost manner. Software tools can help in calculating balanced rations.