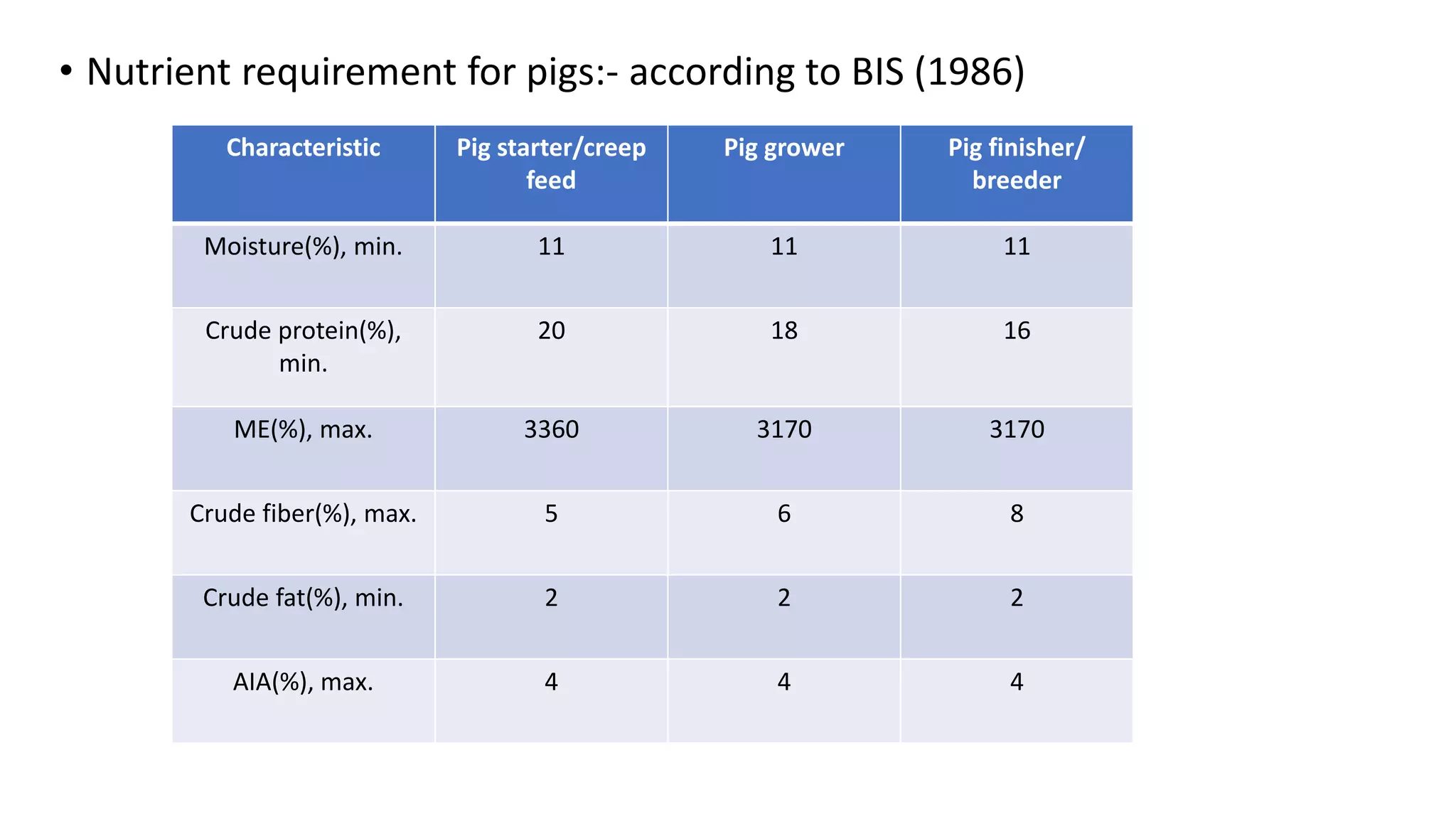
This document discusses feeding systems and nutrient requirements for swine. It describes the three main feeding systems for pigs as extensive/scavenging, semi-intensive/semi-scavenging, and intensive. It outlines the nutrient requirements for pigs at different growth phases according to sources like NRC and BIS. The document provides recommended ingredient compositions for starter, grower, and finisher diets. It also discusses feeding recommendations for different pig stages like creep feeding, weaning, gestating and lactating sows, and use of unconventional feedstuffs in pig rations.