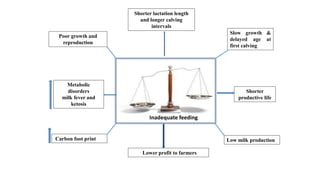
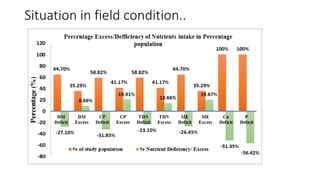
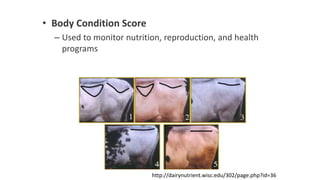
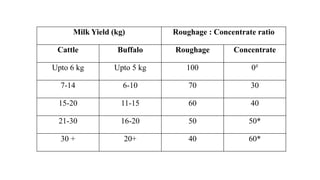
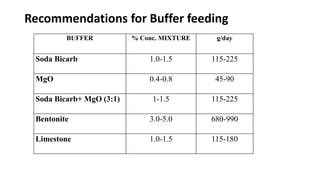
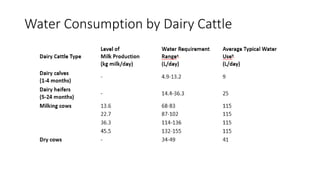
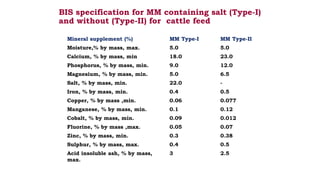
1. Proper ration formulation for dairy animals is important to optimize their milk production, reproduction and health. Rations should meet the animals' nutrient needs during different stages and account for factors like milk yield, body weight and forage quality.
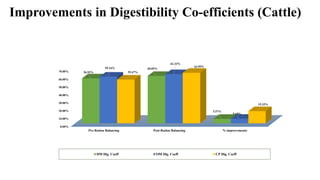
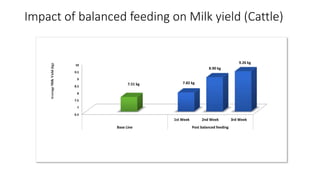
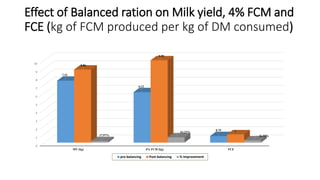
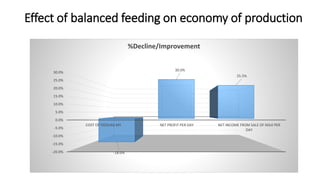
2. Balanced rations can improve digestibility, increase milk yield and fat-corrected milk, enhance feed efficiency and reduce production costs. Special care is needed when formulating rations for high producing animals and those in transition periods.
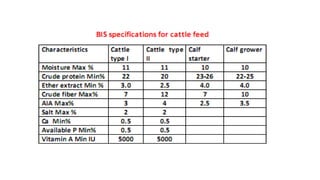
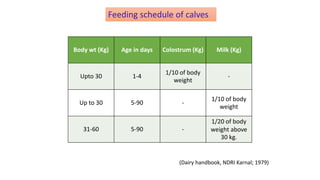
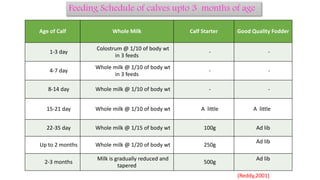
3. Feeding calves requires proper colostrum and liquid feeding initially, followed by transition to solid feed like calf starter to support growth and rumen development. A structured feeding schedule tailored to the calf's age and needs optimizes its