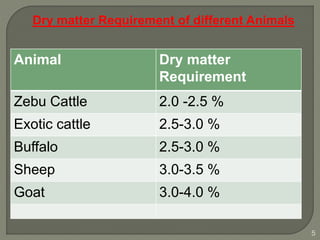
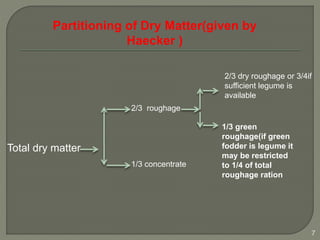
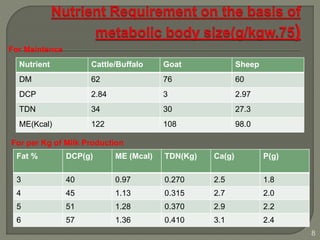
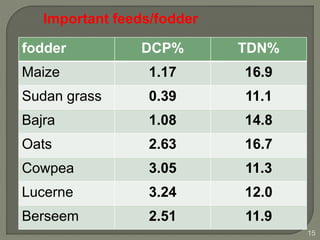
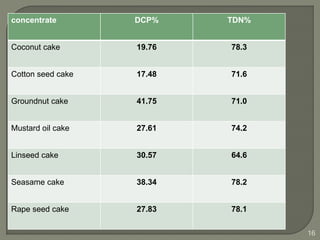
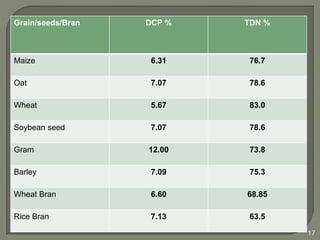
The document outlines the formulation of balanced rations for livestock, emphasizing the importance of nutrient requirements, digestibility, and variety of feeds. It provides guidelines on the composition of rations for various animals, including dry matter intake and nutrient ratios. It also discusses methods for least-cost feed formulation and includes information on the nutritional value of different feed ingredients.