DAIRY FEEDING.pptx. @ busitema University.
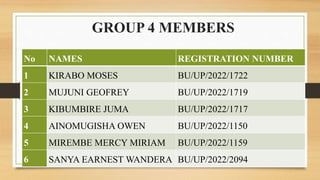
- 1. GROUP 4 MEMBERS No NAMES REGISTRATION NUMBER 1 KIRABO MOSES BU/UP/2022/1722 2 MUJUNI GEOFREY BU/UP/2022/1719 3 KIBUMBIRE JUMA BU/UP/2022/1717 4 AINOMUGISHA OWEN BU/UP/2022/1150 5 MIREMBE MERCY MIRIAM BU/UP/2022/1159 6 SANYA EARNEST WANDERA BU/UP/2022/2094
- 2. PRESENTATION OUTLINE • Feeding and feeding strategies • Steaming up • Feed supplements and concentrates
- 3. FEEDING DAIRY ANIMALS • Feeding refers to the process of providing appropriate nutrition to dairy cows to ensure their health, well-being, and optimal milk production. • This involves the selection and management of feed ingredients, formulation of balanced diets, and feeding strategies
- 4. Importance of Carbohydrates • They provide energy • Essential for the production of milk • Play a critical role in rumen fermentation. • Balanced nutritional profile.
- 5. Importance of Proteins • Are crucial for the growth and development • Essential for the synthesis of milk proteins • Are integral to the immune system of dairy animals • Serve as enzymes that facilitate various metabolic processes • For maintaining body condition
- 6. Importance of Water • Maintains proper hydration • Transport of nutrients throughout the body • Absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract • Thermoregulation • Formation and excretion of urine
- 7. Importance of Minerals • Bone and Teeth Formation • The synthesis of milk components • Act as cofactors for various enzymes • For blood clotting • For the proper functioning of the nervous system • For reproductive success • For maintaining the integrity of hooves and skin
- 8. Importance Of Vitamins • Serve as cofactors for enzymes • Contribute to the production and function of immune cells • For reproductive success • for bone development and maintenance • protecting cells from oxidative damage
- 9. Types of feeds • Roughages • Supplements. • Concentrates (grains)
- 10. ROUGHAGES • Hay, silage, and pasture plants. • These provide essential fiber for rumen function and overall digestive health. • Succulent feeds, dry roughages again classified into pastures, cultivated fodder crops, tree leaves, silage and root crops.
- 12. CALCULATING RUMINANT FEED AND INTAKE. So, considering an animal of 400kg live body weight: 3/100×400 = 12kg of the dry matter content For fresh pasture of 30% dry matter content, 12kgs of the fresh pasture will be required. Then for the whole feed of 100%, (100/ 30 ×12) = 40kgs of fresh pasture For hay of 85% dry matter content, 12kgs of hay will be required or an animal of 400kgs BW Then the whole feed of 100%, (100/ 85× 12) = 14.1kgs of hay
- 13. SUPPLEMENTS • Feed supplements are additional nutrients that are added to animal’s regular diet to enhance its nutritional value or address specific nutritional deficiencies. • Mineral supplement • Vitamin supplements • Energy supplements • Specialty supplements
- 14. Supplements Protein supplements. Urea: non vegetable protein supplement Too much urea is toxic Very bitter to the taste thus should be mixed thoroughly. Example of supplement:
- 15. Mineral supplements Minerals essential for animal life include (sodium chloride), calcium, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, magnesium, manganese, iron, copper, cobalt, iodine, zinc, molybdenum, and selenium. Excess of these can be toxic to animals if excessive amounts are eaten.
- 16. Vitamin supplements • Vitamins are organic compounds required in small quantities. • These are not produced by the body in huge amounts and, therefore, need to come from food.
- 17. Specialty supplements These ingredients are added in small quantities to feed with the aim of improving its properties or to preserve it. Examples are: Probiotics and prebiotics for gut health and organic trace minerals for optimum absorption.
- 18. Energy supplements The most common supplement feeds available to cattle are based on : High-starch grains (corn, sorghum, barley, wheat), fibrous byproducts (soybean hulls, wheat middling's and beet pulp), or fat sources (oilseeds, animal and vegetable oils).
- 19. CONCENTRATES Feed concentrates are more energy dense and nutrient rich feeds source that is derived from processing and concentrating various feedstuffs. There are two types of concentrate feeds: • Carbonaceous • Proteinaceous
- 20. Proteinaceous concentrates Examples: soybean meal, cottonseed meal, peanuts (groundnuts), flaxseed (linseed), cottonseed, coconuts, oil palm, and sunflower seeds.
- 21. Protein concentrates Cotton seed meal Soybean meal
- 22. Carbonaceous concentrates • source of energy for animals. • Are high in total digestible nutrients, but tend to be low in protein (8-11%). • include the cereal grains -corn, barley, wheat, oats, milo, and rye.
- 23. Methods of Processing Animal Feeds Processing methods aim to optimize nutrient utilization, improve feed efficiency, and enhance the overall well-being and productivity Grinding Milling Pelleting Extrusion Steam rolling and flaking Fermentation Roasting Urea treatment Addition of Additives
- 24. FEEDING STRATEGIES 1. Total Mixed Ration (TMR): TMR involves blending all feed ingredients such as grains, forages, protein supplements, minerals, and vitamins into a complete and balanced ration. 2.Pasture-Based Feeding: Involves allowing cows to graze on pasture grasses and legumes. This strategy not only provides a natural and varied diet for the cows but also reduces feed costs.
- 25. FEEDING STRATEGIES 3.Concentrate Feeding: Involves providing cows with high-energy feed concentrates such as grains and oilseeds to supplement their diet. 4.Precision Feeding: • Formulating diets based on the specific nutritional needs of individual cows. • Age, stage of lactation, body condition score, and milk production level.
- 26. FEEDING STRATEGIES 5.Supplemental Feeding 6.Feed Management 7.Balancing Rations: 8.Feed Efficiency Monitoring
- 27. FEEDING DAIRY ANIMALS AT DIFFERENT STAGES OF GROWTH. A) CALF FEEDING The aim of calf feeding should be to reduce the mortality (death) rate while maintaining a growth rate of at least 400 g/day. After the first week during which the calf is left with the dam, several methods can be used for feeding depending on ease and convenience.
- 28. Calf Feeding Methods After the first week during which the calf is left with the dam, several methods can be used for feeding depending on ease and convenience. 1. Single suckling
- 29. Cont 2. Foster mother or multiple suckling 3. Nipple suckling 4. Bottle feeding 5. Bucket feeding:
- 30. PHASES OF CALF FEEDING Colostrum phase (1–3 days) Pre-ruminant phase (4 days to 20–30 days) Transition phase (2 to 3 weeks before weaning): Post-weaning phase
- 31. Commonly usedcalf feeds: Colostrum Excess colostrum preservation: A supply of high-quality colostrum should be saved and frozen for use by calves from cows that die at birth or have mastitis or milk fever The colostrum is preserved by several methods. • Freezing is ideal but is not feasible on small-scale farms without electricity. • Natural fermentation (store at room temperature) • Use of preservatives (formaldehyde 0.05%, or formic acid 0.1%).
- 32. CONT…. Artificial colostrum • 1 egg (beaten) + 400 ml fresh warm water + 600 ml whole milk + 1 teaspoonful castor oil. • Feed this mixture 3 times a day for the first 3 days of life.
- 33. Cont • Milk • Calf starter • Roughage • Water • Milk replacers • Pre-starter • Calf starter
- 34. B) HEIFER FEEDING. • After weaning, a female calf becomes a heifer which will eventually replace the culled animals, increase the herd size or be sold to generate income. • Heifers should achieve a growth rate of 500–700 g/day Aims of heifer feeding • To come on heat at the right time • Reduce the interval between weaning and first calving • To increase the number of calving’s per lifetime • Leads to faster genetic improvement.
- 35. Feeding heifers: When heifers of different ages are fed as a group, aggressiveness varies such that when concentrate is fed to the group, some get little. • Heifers should thus be reared in groups of similar age or size: weaners, yearlings, those that are ready for breeding and in-calf heifers. • Heifers can be reared on good-quality pasture, as their nutrient requirements are low • Supplementation with protein concentrates • Protein is extremely important in the diet of growing heifers to ensure adequate frame size, wither height and growth.
- 36. STEAMING UP Steaming up is supplementation with high concentrate diet at the last month of the pregnancy to prepare the cow to have enough energy for during and post calving. IMPORTANCE • Accustom the heifer to the parlor. • Allow the rumen bacteria to get accustomed to high levels of concentrate.
- 37. Cont • It provides extra nutrients for the animal and the growing fetus. • Allow the heifer to put on extra weight (reserve energy) to promote maximum milk production from the very beginning of the lactation
- 38. Nutritional Requirements (Steaming Up) The diet should be carefully formulated to meet these heightened nutritional needs while also considering factors such as body condition score, breed, age, and environmental conditions. 1. Energy: 2. Protein: 3. Vitamins and Minerals:
- 39. Management Practices (Steaming Up) 1) Body Condition Scoring: Regular assessment ensures that cows are maintaining an optimal body condition throughout this critical phase. • Overweight cows: More susceptible to metabolic problems (ketosis) and health problems(retained placenta. Dystocia problems due to obstruction of the birth canal with excessive body fat. • Under-conditioning can lower milk production due to insufficient energy and protein reserves for mobilization in early lactation
- 40. Figures of different body condition scores
- 41. Parts used to determine the body condition.
- 42. BCS SYSTEM.
- 43. Effect of body condition score on the animal’s productivity • Dairy cows with an optimal body condition score are more likely to have improved reproductive performance • Proper body fat reserves support the energy demands associated with lactation hence improved milk production. • Cows with good body condition are better equipped to handle the physiological stresses associated with lactation and reproduction.
- 44. CONT. • Adequate body fat provides energy for the calving process and reduces the risk of dystocia • Animals with good body condition are generally more resilient and have a stronger immune system
- 45. CONT • Cows with sufficient body fat have better hormone regulation improving chances of conception. • Adequate nutrition and body condition during gestation contribute to the development of a healthy and robust calf.
- 46. c). FEEDING THE LACTATING COW. Aim of feeding the lactating cow. Maximizing milk yield by meeting the cow’s nutrient requirements. Maintain the health of the cow. To prepare the cow for next estrus . Maintenance of pregnancy.
- 48. Body condition in early lactation If cows are fat enough at calving, this is an important source of energy at a time when cows are trying to achieve peak milk production If cows are low in body condition at calving and are underfed in early lactation, their peak milk production will be depressed. They will partition less feed to milk and more towards body condition over the whole lactation.
- 49. Body condition in late lactation and the dry period Milk production falls in late lactation because: • Cows are using more of their feed intake to build body condition rather than to produce milk. • Intake ability decreases as they are being offered less feed or lower quality feed. • Cows with high genetic production potential partition nutrients to milk rather than to body condition during late lactation. • Proper feeding is carried out to put on body condition ready for their next calving.
- 50. D). DRY COW MANAGEMENT. The cow’s nutritional requirements change as she transitions from lactation to a non-lactating state. Dry period, which typically lasts around 45-60 days. The nutrition of a dry cow is crucial for maintaining health and preparing the animal for the upcoming lactation period. Components of a dry cow : energy, protein, minerals, and vitamins.
- 51. DRY COW MANAGEMENT. Energy Requirements: • support the cow’s maintenance needs and the growth of the developing calf. Protein Requirements: • Protein is essential for supporting various physiological functions like tissue repair and immune function. Mineral and Vitamin Requirements. • Minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium & vitamins such as vit A, D, and E are important for supporting immune function.
- 52. Feeding / nutritional disorders 1. Bloat Is the abnormal accumulation of gas in the rumen. Categories Frothy bloat . Free gas bloat . Bloat occurs when gases cannot escape but continue to build up causing severe distension of the abdomen, compression of the heart and lungs, and eventually death.
- 53. Acidosis Acidosis is a syndrome related to a fermentative disorder of the rumen resulting in overproduction of acid, which lowers rumen pH below pH 5.5. • The problem is related to feeding management, where the ration has high levels of digestible carbohydrates and low effective fiber. • To control, use buffers to prevent a drop in rumen pH, ensuring the presence of effective fiber in the diet
- 54. Milk fever/hypocalcaemia • Occurs within 48 to 72 hours of calving when demand for calcium for milk production exceeds the body’s ability to mobilize calcium reserves • It generally affects older, high milk producing cows. • Low blood calcium interferes with muscle function throughout the body causing general weakness, loss of appetite and eventually heart failure. • Provide a well balanced diet with calcium and other mineral supplements and in cases of occurrence, administer intravenous calcium infusion to restore calcium levels
- 55. THANK YOU FOR LISTENING