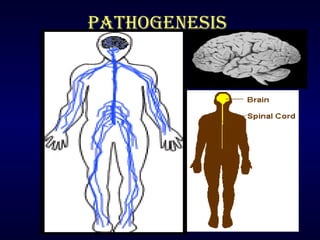
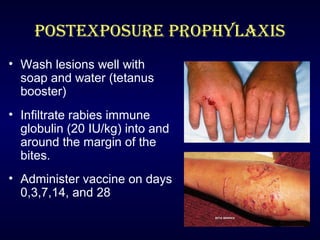
Rabies is a fatal viral disease transmitted through the saliva of infected mammals. It causes acute inflammation of the brain and is nearly 100% fatal in humans if left untreated. Dogs are the primary source of human rabies infections. Post-exposure prophylaxis, consisting of wound cleansing, rabies immune globulin injection, and a vaccine series, is highly effective in preventing the disease if administered promptly after exposure. No approved treatments exist once symptoms develop, making vaccination an important part of rabies prevention.