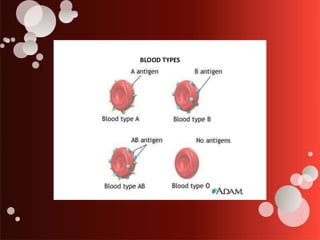
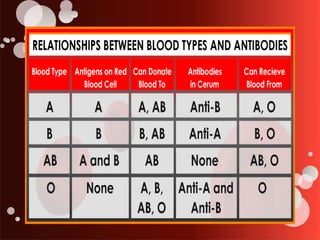
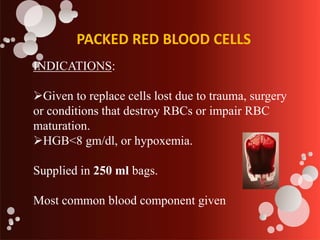
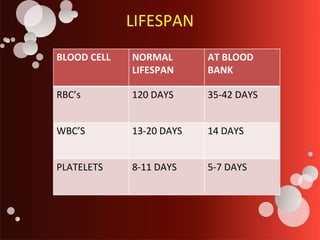
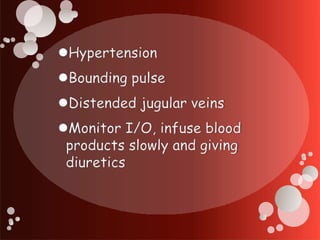
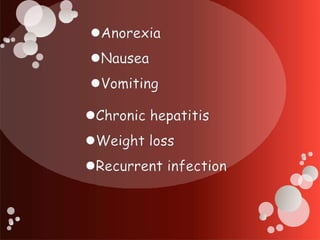
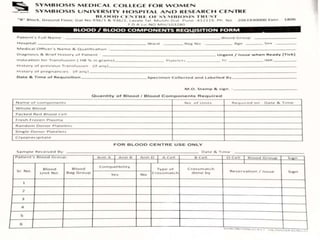
The document outlines blood transfusion therapy, including the composition of blood, its purposes, and the compatibility of blood types for transfusions. It details pre-transfusion responsibilities, the administration process, types of blood products, and potential reactions to transfusions along with nursing interventions. Emphasis is placed on thorough checks and protocols to ensure patient safety during blood transfusions.