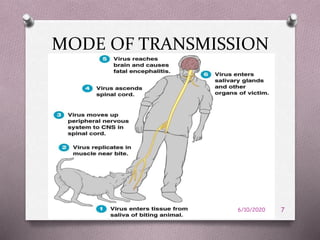
This document provides an overview of rabies disease management. It discusses that rabies is caused by a virus in the Rhabdovirus family and is typically transmitted to humans via bites or scratches from infected animals. Common symptoms include anxiety, confusion, hydrophobia, and paralysis. Diagnosis involves detecting viral antigens or nucleic acids in samples. Post-exposure prophylaxis, consisting of wound cleaning and a vaccine series with or without immunoglobulin administration, must begin immediately after exposure to prevent disease onset. Preventive measures include vaccinating pets, avoiding wild animals, and seeking medical care after a potential exposure.