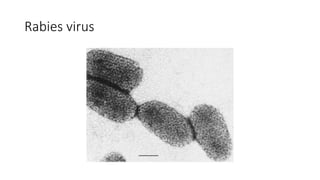
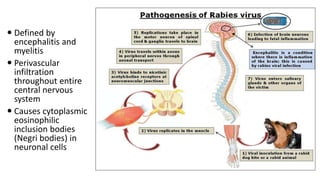
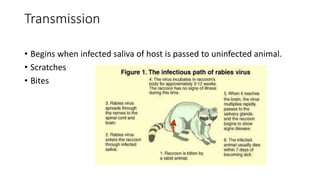
Rabies is an acute viral infection that causes inflammation of the brain. It is transmitted primarily through the bites of rabid animals. Louis Pasteur developed the first rabies vaccine in 1885 by inoculating patients with attenuated rabies virus. The rabies virus is a bullet-shaped rhabdovirus that enters the central nervous system via peripheral nerves following exposure. Symptoms progress from anxiety and insomnia to hydrophobia and eventually death. Treatment involves thorough wound cleansing and vaccination either before or after exposure for prevention and post-exposure prophylaxis. India launched a National Rabies Control Programme in 2007 to address both human and animal aspects through vaccination, surveillance and public education.