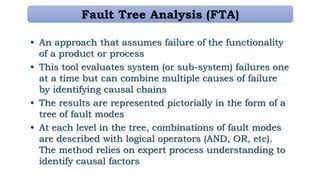
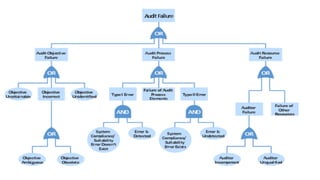
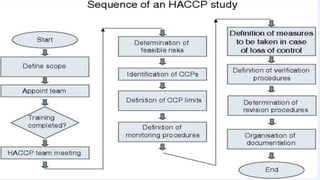
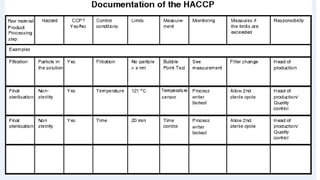
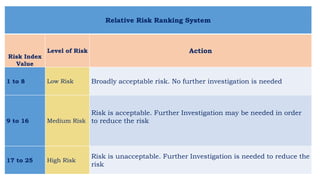
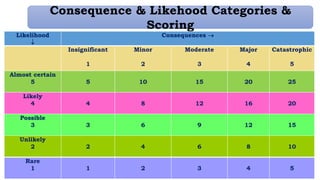
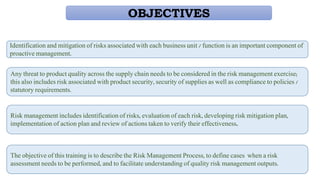
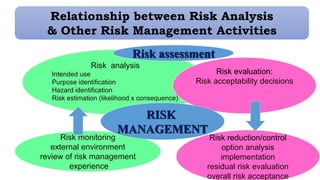
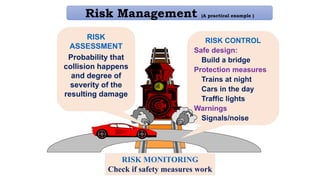
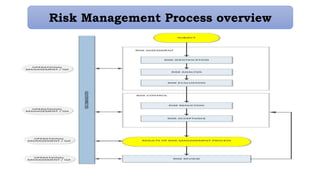
This document provides an overview of risk management in the pharmaceutical industry. It discusses the objectives, scope, definitions, and tools used in risk management. The key tools covered include Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), and Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA). The goal of risk management is to identify potential risks, evaluate their likelihood and impact, and develop control measures to mitigate risks and ensure product quality and safety.







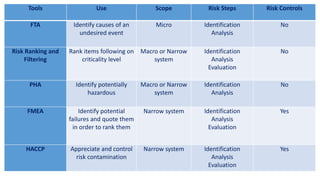

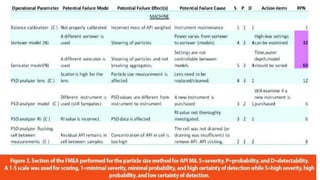
![Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
• Allows evaluation of:
potential failure modes [what might go wrong] for processes
the likely effect on outcomes and/or product performance
• Once failure modes are established, risk reduction can be used
to eliminate, contain, reduce or control the potential failures
• FMEA relies on product and process understanding
• FMEA methodically breaks down the analysis of complex
processes into manageable steps
• It is a powerful tool for summarizing the important modes of
failure, factors causing these failures and the likely effects of
these failures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/riskmanagement-170503085918/85/Risk-management-in-pharmaceutical-Industry-14-320.jpg)